Whether you are running a marketing campaign, developing software, or constructing residential apartments, proper project financial management is crucial while planning. It ensures financial discipline from initiation to closure and guarantees the project’s outcome is completed within the pre-defined scope, budget, and timeline.
A well-structured project financial management plan includes fiscal details such as a clear budget, cost-control measures, benchmarks, and reporting guidelines. It allows firms to make better financial decisions, allocate resources effectively, minimize the risk of budget overrun, and improve project ROI.
On the flip side, the absence of a structured project financial framework can lead to numerous challenges, such as cash crunch, cost escalation, or fund misallocation. These bottlenecks can hamper project delivery and even lead to its failure.
In this blog, we will learn the meaning of project financial management, its challenges, and the steps to create a financial project management plan.
So, let’s get started!
What is Project Financial Management?
Project financial management is the process of estimating, budgeting, and monitoring finances throughout the project lifecycle. It also involves securing funding, handling client billing, tracking revenue, and evaluating profit margins to ensure the project stays on track and delivers quantifiable value.
Project financial management discipline governs key elements, such as cost, cash flow, revenue, and Profit. This process is usually handled by the organization’s Project Management Office (PMO) or financial stakeholders.
Let us now understand what project financials encompass.
What is Included in Project Financials?
Project financials refer to the cost required to cover all the project activities for timely and successful completion. The core of project financials lies in controlling the following elements:
Project Revenue
Revenue is the total income generated from a specific project. Project revenue or income can come from sources such as service fees or product sales, depending upon the nature of the project. For instance, revenue is typically earned through fixed-price contracts, time and material billing, or retainer models in service-based projects.
Project Cost
Project costs are the total funds needed to complete a project. It is divided into different types, such as direct, indirect, fixed, variable, recurring, one-time, sunk, and contingency costs. Understanding these types of expenses is essential to track and control expenses throughout the project lifecycle.
Read More: Project Cost Management: Types, Importance, and Steps to Calculate It
Project Profit
Profit means the project’s total returns after all expenses have been deducted from the total revenue generated. The factors influencing profitability are the cost of materials, labor, materials, equipment, and other overhead charges. The formula for calculating project profit is:
| Project Profit = (Total Revenue Generated – Total Project Cost) |
|---|
Project Cash Flow
Cash flow refers to the inflow (revenue, investments) and outflow (project costs) of money within a project lifecycle. It tracks the timeline of incoming funds, such as client payments or internal funding, and outgoing expenses, such as labor costs or vendor payments. Thus, it provides clear insights into a project’s liquidity at any given point in time.
| Projected Cash Flow = Projected Cash Inflows – Projected Cash Outflows |
|---|

Let us now shift our attention to understanding the importance of project financial management.
Read More: What is a Cost Breakdown Structure & How to Create One Effectively?
Importance of Project Financial Management
According to PMI, “27% of projects usually run over budget.”
These statistics highlight why managers should bring project financial management into practice. Effective project financial management controls unnecessary expenses, balances the investment made, aligns investments with expected returns, and ensures that the project positively contributes to the organization’s overall financial health. Here are a few more reasons that explain why project financial management matters:
- Firstly, project financial management aids in precisely estimating the cost of labor, raw materials, machinery, and equipment and developing a realistic project budget.
- It enables project managers and stakeholders to make data-driven decisions regarding resource allocation, scope adjustments, and future investments.
- Project financial management helps track and control expenses at every project lifecycle stage. As a result, the chances of overspending and budget slippage are reduced.
- Project financial management also assists in identifying potential risks, such as cash flow disruptions and funding shortfalls. Thus, managers can take proactive measures before these issues impact project execution.
- With financial management disciplines in place, managers can effectively handle finances and optimize resource usage, which improves overall project ROI.
- Lastly, it demonstrates effective project cost management and accountability, boosting the trust of stakeholders and investors.
Now that we have understood the importance of financial management in project management let us learn the challenges in managing project financials.
Read More: How to Develop an Effective Project Budget in 8 Simple Steps?
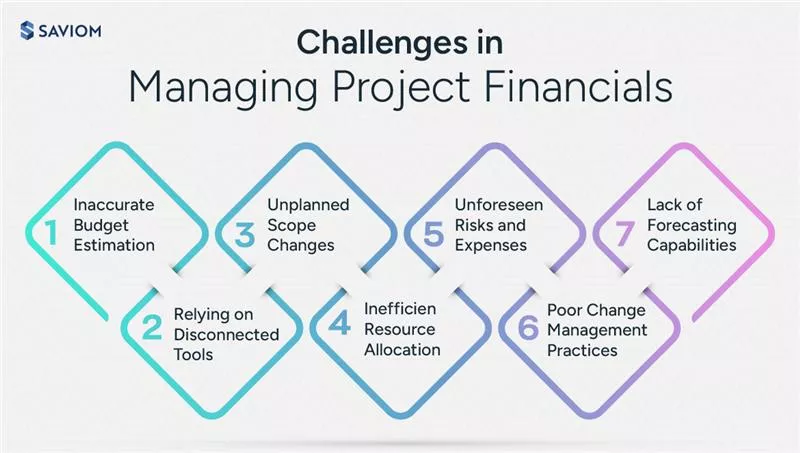
Challenges in Managing Project Financials
Here are some common setbacks that managers face while managing project financials:
Inaccurate Budget Estimation
When the actual costs of labor, machinery, or raw materials exceed the estimated costs, project finances can spiral out of control. This puts significant financial pressure on the team, making it hard to manage expenses and maintain financial stability. Moreover, budget slippage can erode stakeholder confidence and damage the ororganization’seputation.
Relying on Disconnected Tools
Using multiple standalone tools like spreadsheets, emails, and cost-tracking software leads to isolated data. This lack of integration makes it challenging to get a clear and up-to-date picture of project financials. Moreover, without an integrated platform, teams struggle to align the budget with resource planning and project execution. As a result, controlling project finances becomes difficult.
Unplanned Scope Changes
According to PMI, “37% of projects fail due to the lack of defined project objectives and milestones.”
When a project encounters various unexpected or unapproved changes, it leads to scope creep, which significantly affects the financial plan. These uncontrolled changes often require extra funding for additional labor, more materials, or delayed schedules. If the budget is not adjusted for these changes, controlling costs and achieving the expected financial returns becomes difficult.
Read More: 7 Effective Strategies to Avoid Scope Creep in Project Management
Inefficient Resource Allocation
Resource costs make up a significant part of the project budget. When resources are not assigned according to their skills, expertise, or availability, it reduces productivity and inflates project costs. For example, if under-skilled personnel are allocated to high-priority tasks, it may result in errors and rework, increasing both time and costs. Similarly, underutilized resources contribute to the wasted budget and impact the project’s profitability.
Unforeseen Risks and Expenses
Unexpected risks like machinery failure or unplanned attrition of a critical resource can emerge at any phase of the project lifecycle. Moreover, shifts in market conditions like inflation or supply chain issues can affect the prices of materials or resources, resulting in increased costs. Without financial buffers, these expenses can cause serious budget deviations and impact overall project finances.
Poor Change Management Practices
In the absence of a proper change management framework, the financial implications of changes requested by project stakeholders are often overlooked or underestimated. This can lead to misalignment between the projected budget and actual cost (which drives up due to unplanned changes). Consequently, the absence of change control methods results in financial slippage and erodes project profitability.
Read More: What is Change Management in Project Management, and Why Is It Important?
Lack of Forecasting Capabilities
Without forecasting capabilities, project managers struggle to predict resource requirements and estimate cash flow. This lack of insight makes it difficult to calculate the accurate cost of the project and plan for upcoming financial demands. Moreover, without ongoing forecasts, managers cannot spot issues such as budget shortages or resource bottlenecks early, leading to rushed decisions and cost overruns.
Now that we have covered the challenges, let’s explore the steps to build an effective project financial management plan.
Steps to Create a Project Financial Management Plan
No matter how big or small your project is, managing its finances is essential to finishing it on time and within the allocated budget. Follow these eight steps to create a successful project financial management plan:
Define Project Scope Clearly
The first step in creating a financial management plan is clearly outlining the project scope. A well-defined scope outlines the project’soals, deliverables, tasks, timelines, and limitations. Thus, it helps managers accurately assess the cost required to complete a project, serving as a solid foundation for financial planning.
For example, a construction company takes up a project to build a small apartment complex. Before starting, the manager can create a clear scope by outlining all tasks, like site preparation, electrical work, painting, etc., along with the project duration. This detailed scope helps him to evaluate project costs accurately.
Read More: What is a Project Scope? Benefits, Best Practices, and Steps to Create an Effective One
Conduct a Feasibility Analysis
In the second step, managers can conduct a thorough feasibility analysis to assess if a project is financially and operationally viable. This process typically involves analyzing inputs from subject matter experts, market studies, and past project data to build a foolproof and realistic project plan.
Moreover, a feasibility study helps evaluate if the project aligns with organizational goals and available resources. It also enables managers to create a realistic budget, allocate the best-fit resources, and create contingency plans. In addition, it aids in determining the cost-benefit ratio and estimating project ROI.
Estimate Cost & Create Budget
To create a successful project financial management plan, it is important to accurately estimate costs and create a realistic budget. This involves identifying all the cost components associated with the project, such as equipment, material, labor, technology, and overheads.
Managers can use various estimation methods, like parametric, top-down, analogous, etc., to predict the cost. Next, they can develop a comprehensive project budget, which serves as the financial roadmap for the entire initiative and ensures better cost control. The formula for creating a solid project budget is:
| Project Budget = Total Cost Estimates + Contingency Reserves + Management Reserves |
|---|
Establish the Cost Baseline
Once managers have created a budget, the next step in the financial project management plan involves establishing the cost baseline. It serves as a benchmark to manage and control project costs throughout the project lifecycle. It also helps assess project performance using metrics such as cost performance index (CPI) and cost variance (CV).
Ideally, the estimated cost and the actual spending should be equal, or the actual price should be less than the planned budget. If the actual cost is higher than the estimated budget, it denotes overspending, which needs to be reviewed and fixed to keep the project finances under control. Here is the formula to calculate the cost baseline:
| Cost Baseline = Estimated Costs + Contingency Reserves |
|---|
Read More: Understanding Cost Baseline in Project Management: Components, Benefits & Steps
Create a Plan for Funding Sources
Developing a plan to secure and manage funding sources is an essential part of a project financial management plan. This involves identifying where the necessary capital will come from to support an initiative. Funding can come from government grants, bank loans, private investors, personal savings, or income generated from business operations.
To create an effective funding plan, managers can first identify and confirm the available funding sources. Next, they can prepare a compelling proposal that outlines the project’s objectives, the approach to achieving them, and the expected results. They can also convince stakeholders to invest in the project by showing them the expected project ROI.
Account for Risks & Contingencies
The sixth step in creating a project financial management plan includes accounting for risks that arise midway and developing financial buffer time to cover those issues. A contingency reserve act as a safety cushion to protect the project from unexpected risks like resource unavailability, technical issues, or scope changes.
For example, consider a law firm handling a large corporate case. It sets aside extra funds to hire expert advisors, if needed to support the case. This financial cushion helpscover the added cost without jeopardizing the project budget. It also ensures the case continues smoothly without interruptions due to funding gaps.
Set KPIs & Metrics to Assess Performance
In the next step, managers can set project metrics and KPIs to assess its financial performance. Key performance indicators (KPIs), like earned value (EV), Cost Performance Index (CPI), and Return on Investment (ROI), are the quantifiable measures that help track how well a project is performing financially.
Moreover, these KPIs and metrics assist managers in identifying deviations early, understanding cost trends, and taking corrective measures before the issues escalate. Lastly, incorporating these indicators into your project financial management plan improves visibility and ensures transparency and accountability.
Read More: 7 Critical Project Metrics That You Should Track
Review & Update Regularly
The final step is regularly reviewing and updating the project financial management plan. Managers must remember that a financial plan cannot be created once and then forgotten. Regular reviews are essential as they can address issues proactively, ensuring that spending remains aligned with the approved budget.
Moreover, as the project progresses, revising the financial plan may become essential due to changes in scope, timelines, and resource requirements. Revisiting the plan helps identify deviations early and take corrective actions like reforecasting the budget or adjusting funding strategies.
Now, let’s focus on the best practices for effective project financial management.
Project Financial Management Best Practices
Project managers can improve their project financial management plan by following these practices:
Monitor Project Costs Frequently
Managers can regularly track project expenses to identify any variances, avoid cost overruns, and stay within the budget. For most projects, it’s advisable to review expenses every week. However, a monthly review may be sufficient for projects with longer timelines and fewer weekly changes. The key is to review costs regularly to avoid overspending.
Read More: What is Cost Overrun in Project Management? 12 Effective Tips to Prevent It
Study Past Projects to Identify What Worked & What Didn’t
By analyzing what went well and where challenges occurred, managers can gain invaluable insights into both success and shortcomings. This also helps with more accurate cost estimation, creating realistic budgeting, better risk management, and performance benchmarking.
Implement a Change Control Process
A change control process helps managers understand how an unexpected requirement can affect the project’s budget before approval. Requiring formal review and documentation prevents financial slippage, maintains alignment between scope and budget, and supports accurate reforecasting.
Ensure Transparent Communication with Stakeholders
Clear and open communication with project stakeholders builds trust and improves financial decision-making. When clients are kept informed about budget status, financial risks, and funding needs, they are more likely to provide timely approvals, address concerns proactively, and support necessary cost adjustments.
Let us now understand how a 5th-generation project resource management software can help improve project financial management.
Read More: Who Are Project Stakeholders? 7 Effective Ways to Manage Them
How Can a 5th Gen Project Resource Management Software Help?
The 5th-generation resource management software plays a vital role in improving project financial management by providing better visibility, accurate planning, and efficient utilization of resources throughout the project lifecycle.
- With the software’s all-in-one resource planner, project managers can filter resources across various dimensions, like location, experience, and role. This helps them identify cost-effective employees and reduce project expenses.
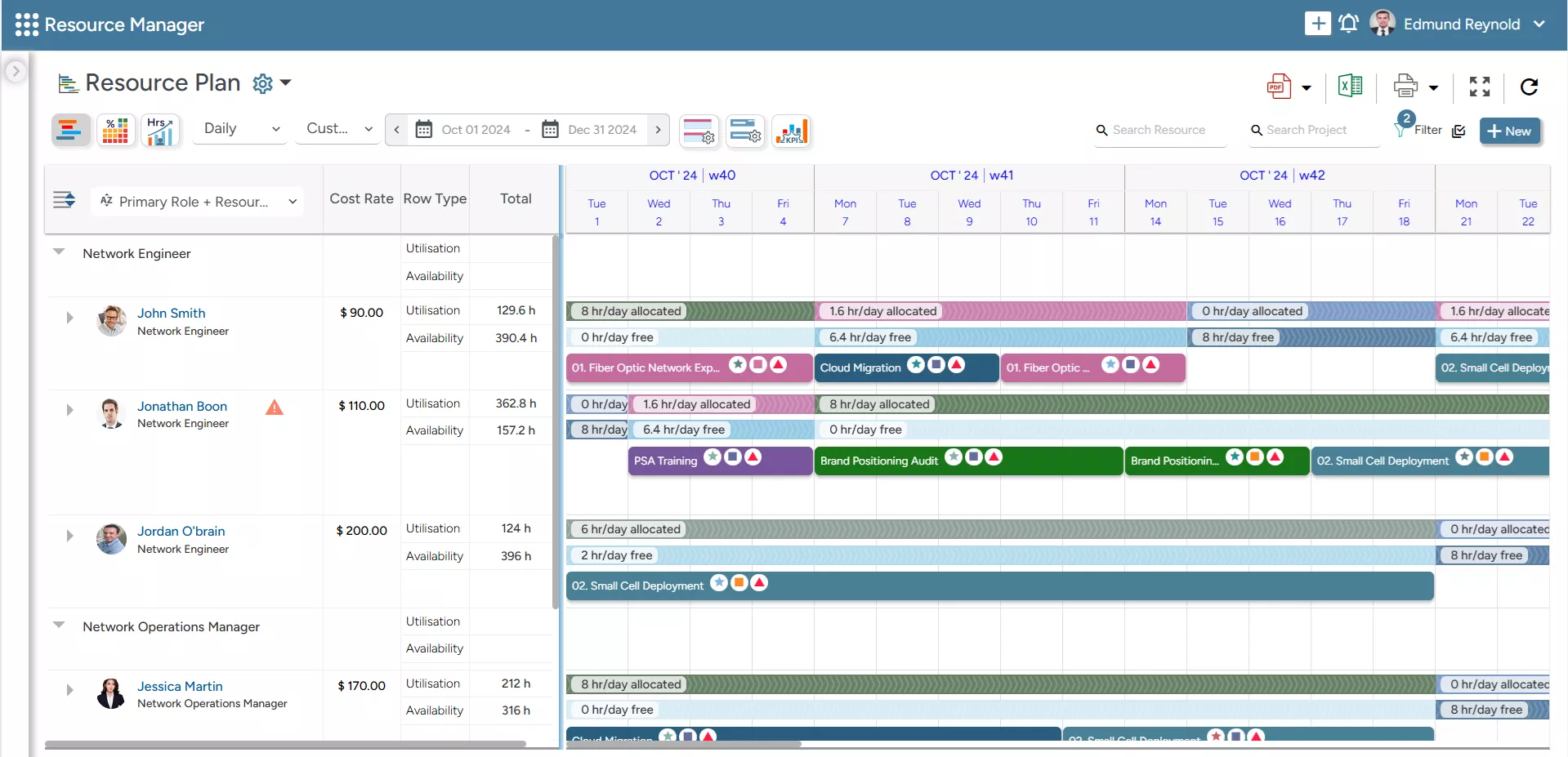
SAVIOM’s All-in-one Resource Planner helps managers customize resource plans across multiple dimensions such as role, location, cost, etc.
- The embedded capacity planner enables managers to forecast and evaluate short- and long-term resource needs. This helps in proactively bridging the gap and prevents expensive last-minute hiring, ultimately keeping the project budget on track.
- The intelligent KPI forecaster offers early alerts on key resource metrics like underutilization, overutilization, people on the bench, skill gaps, and project vacancies, enabling businesses to take steps to optimize resource use.
2. The tool’s real-time BI reports provide insights into forecasted costs versus actual expenditures, helping you track the variances and take corrective actions beforehand.
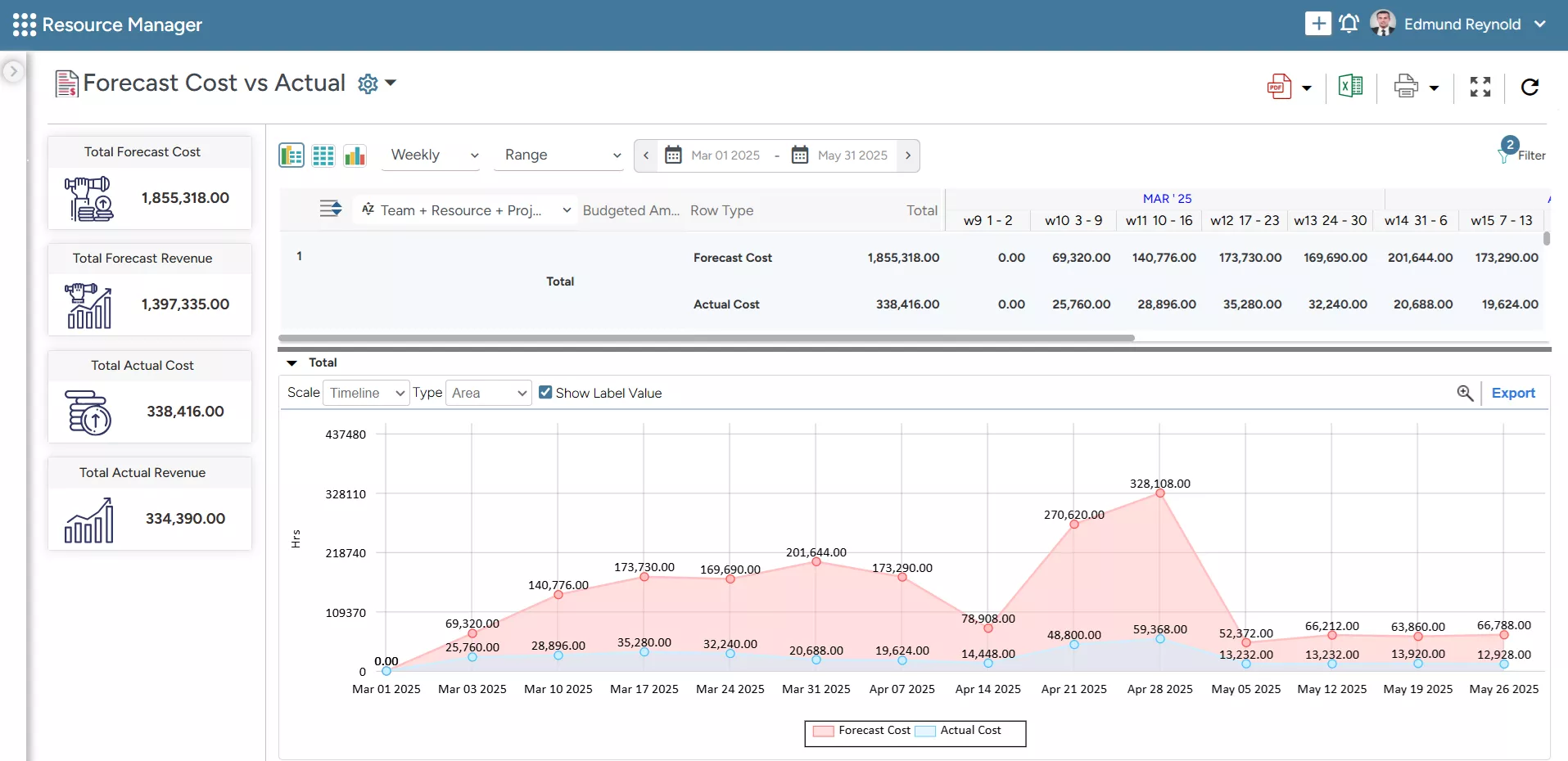
SAVIOM’s Forecasted vs. Actual Report helps in comparing the actual budget against the total spending to identify any variances.
3. The competency matrix continuously records, tracks, and updates skills, allowing managers to address skill gaps and prevent costly ad-hoc staffing proactively.
4. Finally, the what-if analysis feature allows organizations to simulate different resource planning scenarios and assess their financial impact, helping managers choose the most efficient and cost-effective plan.
Conclusion
Effective project financial management is not just a necessity. It is a strategic advantage. To gain complete control over project financials, organizations can define project scope, conduct a feasibility analysis, establish a cost baseline, boost profitability, and ensure long-term success. By leveraging the right strategies and tools, businesses can deliver projects on schedule and stay within budget.
So, what strategies do you recommend for improving project financial management?
The Glossary
Read More: Glossary of Resource Workforce Planning, Scheduling and Management










