Did you know that 65% of senior finance leaders believe corporate risks have become far more complex and frequent in the last five years? – AICPA
From cybersecurity threats and economic volatility to geopolitical tensions, talent shortages, to unplanned attrition, enterprise risks are always looming. If not addressed in a timely and structured manner, these challenges can disrupt daily operations, reduce stakeholder trust, and even hinder long-term business growth.
Traditional and reactive approaches to risk management are no longer adequate in this high-stakes environment. Thus, a forward-looking, enterprise-wide framework is needed to mitigate threats and enhance decision-making. This is where Enterprise Risk Management comes in.
ERM enables businesses to integrate risk considerations into every business process, from frontline operations to boardroom strategies. Thus, it safeguards firms against potential losses and helps build agility and resilience.
In this blog, we will walk you through the types, components, benefits, and various strategies for effectively implementing an enterprise risk management framework.
But first, let’s begin with the basics!
What is Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)?
Enterprise risk management is a structured process of identifying, assessing, prioritizing, and managing the potential risks that could impact an organization’s ability to achieve its business objectives. It goes beyond traditional, siloed risk management methods and offers a comprehensive, organization-wide perspective on threats.
ERM encompasses a wide range risk categories, including operational, financial, strategic, resource-related, environmental, and third-party risk. By implementing enterprise risk management, companies can improve adaptability in uncertain environments, boost stakeholder confidence, and enhance overall performance.
Now that the definition is clear, let’s understand the various types of risks that enterprise risk management deals with.
Types of Enterprise Risk
Here are different types of risks that enterprises come across:
Compliance Risk
This risk arises when a firm fails to adhere to laws, industry regulations, or internal policies. It can lead to penalties, regulatory sanctions, business disruptions, or reputational damage. ERM helps firms stay updated on regulatory changes through internal monitoring systems and regular audits. This reduces the likelihood of non-compliance and ensures that the business operates legally at all times.
Legal Risk
Legal risk arises from the potential of facing lawsuits, contractual disputes, intellectual property issues, or failing to meet legal obligations. These issues can result in prolonged court battles, significant financial penalties, project delays, and loss of market reputation. An enterprise risk management framework enables firms to review contracts and maintain clear documentation to protect the company against potential legal threats.
Strategic Risk
Strategic risk stems from decisions that affect a company’s long-term goals. Whether entering an unstable market or launching a new product, choices made without a detailed evaluation of strategic decisions can backfire. Enterprise Risk Management integrates risk intelligence into strategic planning, helping leadership assess internal capabilities and market conditions before making key decisions.
Operational Risk
This type of risk involves disruptions in routine business activities caused by system failures, flawed internal processes, or supply chain breakdown. While operational risks are not immediately visible, the consequences can lead to financial losses, customer dissatisfaction, and reputational harm. By proactively assessing vulnerabilities, enterprise risk management enables firms to implement preventive measures and improve operational efficiency.
Security Risk
Security risk encompasses digital and physical threats such as cyberattacks, data breaches, information theft, or unauthorized access to sensitive systems. Security incidents can result in significant data loss, legal penalties, and regulatory fines. ERM helps evaluate where digital and physical security gaps exist and promotes the adoption of cybersecurity protocols and incident response strategies.
Financial Risk
This involves anything that could impact an organization’s financial health, i.e., cash flow issues, credit defaults, market fluctuations, or currency exchange volatility. This can lead to cash flow crises, credit downgrades, investment losses, and long-term insolvency. ERM facilitates early detection of these risks through forecasting, scenario analysis, and modeling to establish internal controls and stabilize financial operations.
After types, it’s time to dive deep into the various components of enterprise risk management.
Read More: Top 12 IT Project Risks: Effective Ways to Mitigate Them
Components of Enterprise Risk Management
Enterprise risk management comprises some key components. Here’s a rundown of them:
Internal Environment
The internal environment forms the foundation of the ERM framework. It refers to cultures, values, organizational structure, and risk appetite, which shape how risk is perceived and managed within the organization. A strong internal environment promotes a risk-aware culture, sets clear ethical standards, and ensures leadership support. It also defines the roles and responsibilities of teams involved in risk management.
Objective Setting & Goals
Organizations set a mission and vision to ensure that everyone achieves a common goal. When these objectives are cascaded across the enterprise, employees understand their roles and responsibilities towards broader business objectives. Apart from this, it is also essential to consider both your risk appetite (the level of risk you are willing to accept to pursue your goals) and your risk tolerance (the maximum level of risk you can take to fulfill your goals) to set clear boundaries for risk.
Read More: What is PMO: Roles, Responsibilities, Types & Benefits
Risk & Opportunities Identification
During project execution, you will come across two types of events- risks and opportunities. Risks may arise due to regulatory changes, market fluctuations, technology disruption, and operational efficiencies and can disrupt the project’s progress. Likewise, emerging trends or innovation could present opportunities and can give your firm some tangible benefits. ERM framework utilizes tools like risk registers and SWOT analysis to capture these factors across all departments.
Risk Assessment & Categorization
Risks vary depending on the business areas they affect. It includes strategic risks, which pose a threat to business sustainability, operational risks, which can cause inefficiency in resource management, compliance risks, which violate the rules and regulations of a business, and so on. You can add a lot more to the list based on the nature of your business. For instance, cybersecurity risks are crucial for an IT project. The categorization of these risks will enable you to prioritize them and decide a course of action.
Risk Response & Mitigation
After carefully assessing and categorizing risks, the next step is to decide how to respond to them. The approach you will take depends on each risk’s nature, severity, and potential impact. Here are the ways in which you can respond to risks – Reduce i.e. implement measures to minimize the likelihood or impact, Accept i.e. acknowledge the impact if it’s negligent or minimal. Moreover, managers can Avoid the risk or Transfer it to assign the mitigation to a competent third party.
Checks & Balances
Checks and balances in enterprise risk management refer to mechanisms that ensure accountability, transparency, and integrity in risk-related decisions. These include segregation of duties, audit trails, approval hierarchies, and independent oversight. Moreover, the checks reduce the risk of fraud, errors, and biased decision-making while promoting compliance with internal policies and regulatory standards.
Information & Communication
In enterprise risk management, every employee must be capable of identifying potential risks and communicating them to the managers and stakeholders. This process will ensure that no risk is overlooked. To do so, firms should invest in training programs to help their employees learn all about risk assessment and identification. It ensures that everyone is aware of their roles in risk management, informed about emerging threats, and equipped with insights to make risk-aware decisions.
Read More: What is Project Communication Management? Types, Benefits & Best Practices
Monitoring & Review
Market volatility and evolving trends change the nature of the risks you are about to encounter. Organizations must, therefore, monitor and review the strategy at regular intervals. This will keep you informed on what works for you and what does not. Eventually, you will be able to introduce some improvements that will be beneficial in mitigating risks. Remember, risk management is always a Work in Progress.
After components, let’s take a look at an example to understand the concept better.
Enterprise Risk Management Example
Consider a mid-sized construction firm, UrbanCore Builders, that specializes in building high-rise residential towers across metro cities. With multiple large-scale construction projects running simultaneously, the firm is exposed to various operational, financial, legal, and environmental risks. To navigate these complexities, UrbanCore adopts a structured enterprise risk management framework. Here is how it helps them:
Risk Identification
UrbanCore’s leadership meets quarterly to assess risks and categorize them as follows:
Operational Risks:
- Crane malfunctions during vertical lifts
- Delays in concrete curing due to weather/humidity
Financial Risks:
- Price volatility of steel and cement
- Staggered client payments lead to cash flow strain
Resource Risks:
- Shortage of skilled laborers during peak construction phase
- High turnover among experienced site supervisors or crane operators
Legal & Regulatory Risks:
- Frequent changes in FSI norms and building codes
- Mandatory sustainability and green building requirements
Environmental & Safety Risks:
- Dust emission violations under local pollution norms
- Worker injury or fall from height.
Risk Assessment
UrbanCore utilizes a standardized risk matrix to assess each risk’s Likelihood (L) and Impact (I). This helps prioritize where immediate mitigation and monitoring are required.
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Priority Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crane Malfunction | Medium | Very High | Critical |
| Steel price volatility | High | High | Critical |
| Delay in concrete curing | Medium | High | High |
| Staggered client payments | High | Medium | High |
| Skilled labor shortage | Medium | High | High |
| Changes in FSI norms | Medium | High | High |
| Worker injury | Low | Very high | High |
| High attrition of supervisors | Medium | Medium | Moderate |
| Dust emission non-compliance | Medium | Medium | Moderate |
| Sustainability mandates | Low | Medium | Low |
The company formulates risk mitigation strategies after analyzing the likelihood and impact of risks and determining their priority.
Risk Mitigation Strategy
Here are mitigation strategies UrbanCore for different types of risks:
- For Operational Delays: They conduct real-time performance monitoring for construction machinery such as cranes and incorporate chemical admixtures to speed up concrete curing times.
- For Financial Risks: They hedge steel purchases with six-month fixed-price contract and link client billing to project milestone achievement to improve cash flow.
- For Resource Risks: They forecast labor needs using resource management software for each project phase and cross-train junior engineers for supervisory backup in case of attrition.
- For Legal Risks: A compliance team continuously monitors changes in zoning laws, FSI (Floor Space Index) norms, and environmental guidelines.
- For Environmental/Safety: The company “deploy dust suppressants and install” physical barriers such as dust screens or green netting. To prevent fatal accidents, they conduct weekly safety audits.
Risk Monitoring & Reporting
The project manager maintain a risk register, which is reviewed bi-weekly, whereas site engineers flag any early signs of exposure through a mobile dashboard. Additionally, the CFO, COO, and Head of Projects receive consolidated reports monthly, highlighting red zones so that immediate actions can be taken to mitigate the risks.
Read More: 7 Project Manager Personality Types: Which One Is Yours?
So, this is how enterprise risk management helps maintain a steady project workflow. Now, let’s understand the difference between ERM and traditional risk management.
ERM vs. Traditional Risk Management
Here’s how ERM differs from traditional risk management when it comes to structure, focus, and impact:
| ASPECT | ERM | TRADITIONAL RISK MANAGEMENT |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Company-wide, across all departments and projects | Focused on specific risks within departments or projects |
| Approach | Proactive, integrated, and strategic | Reactive and siloed |
| Ownership | Shared across leadership, project heads, and functional teams | Handled by individual departments (e.g., safety, finance) |
| Risk-types Covered | Financial, operational, reputational, legal, environmental, etc. | Mostly insurable or regulatory risks (e.g., safety, liability) |
| Monitoring Frequency | Ongoing and embedded into regular reporting cycles | Periodic or incident-driven |
| Tools Used | Risk heat maps, dashboards, integrated ERM platforms | Spreadsheets, checklists, standalone reports |
| Culture | A risk-aware culture is encouraged at all levels | Risk managed by specialists or designated risk officers |
| Reporting Structure | Directly tied to C-suite and board-level oversight | Typically reports to mid-level or department managers |
| Goal | Long-term value creation, resilience, and competitive edge | Risk avoidance, cost control, and compliance |
After the difference, let’s move towards the various advantages that enterprise risk management offers.
Benefits of Enterprise Risk Management
The key benefits of incorporating enterprise risk management in an organization are mentioned below:
Improves Resilience Against Market Volatilities
Enterprise risk management enables businesses to anticipate market volatilities such as economic downturns, geopolitical events, or sudden shifts in customer demand. Organizations can adapt faster to changes, minimize disruptions, and maintain operational stability by proactively identifying potential threats and building contingency plans. This heightened resilience helps companies survive turbulent conditions.
Read More: Beat Market Volatility With Efficient Resource Capacity Planning
Ensures Regulatory Compliance
In an environment of evolving legal and regulatory standards, integrating enterprise risk management plays a critical role in maintaining compliance. A structured risk management framework ensures that the organization stays aligned with the evolving laws and regulations. With dedicated compliance tracking and documentation processes, companies can avoid fines, reputational damage, and project delays.
Facilitates Effective Resource Utilization
Enterprise risk management gives organizations greater visibility into how resources are deployed. By linking resource planning with risk signals like project delays, vendor issues, or cost overruns, ERM enables managers to make timely adjustments and reallocate resources where they are needed most. This minimizes resource wastage, prevents bottlenecks, and enhances project delivery.
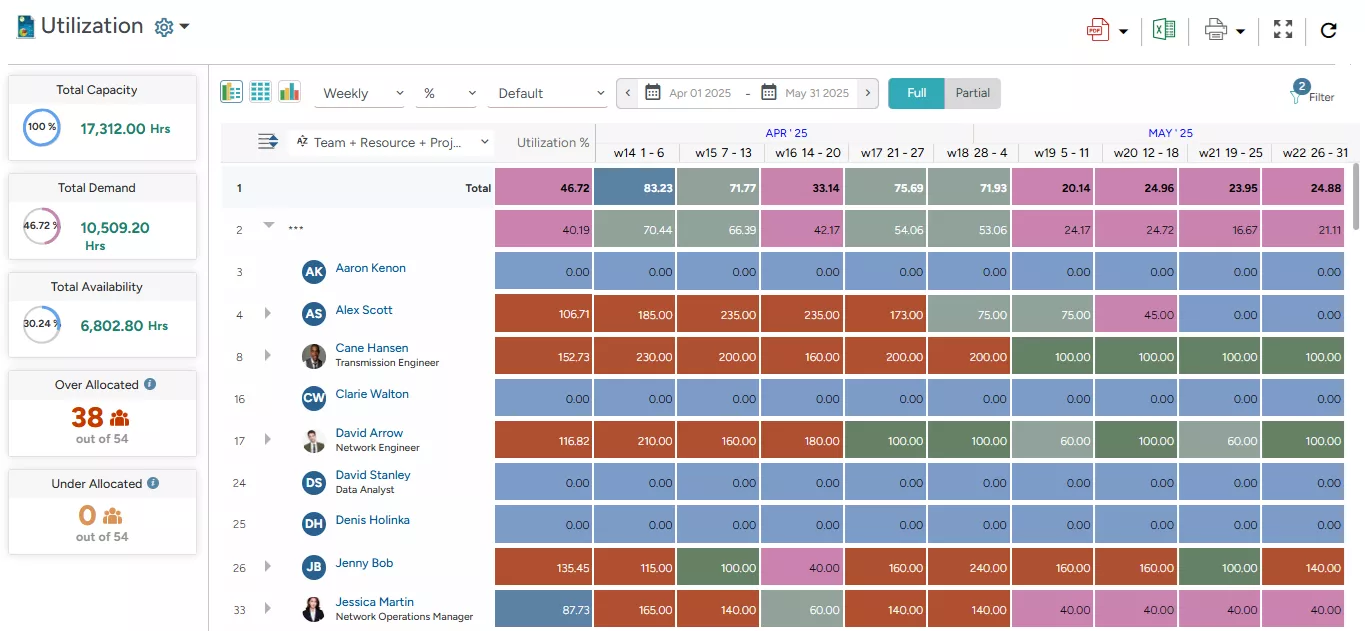 SAVIOM’s Resource Utilization Reports provide in-depth insights into the utilization level of every employee.
SAVIOM’s Resource Utilization Reports provide in-depth insights into the utilization level of every employee.
Read More: What is Resource Utilization? A Complete Guide to Improve Business Efficiency
Boosts Stakeholders Confidence
A proper ERM framework helps build project stakeholder confidence by showing them the company’s commitment to effective risk mitigation, protecting assets and reputation, and boosting market credibility. It shows that the business can handle uncertainties effectively without losing direction. Over time, this trust strengthens investor relationships and opens doors to better opportunities.
Enhances Process Efficiency
By identifying and pointing out risks early, enterprise risk management helps streamline workflows and improve process efficiency. Moreover, risk assessments reveal vulnerabilities and redundancies within the systems, prompting organizations to refine their operations. As risks are proactively addressed, the process becomes more agile, responsive, and aligned with strategic goals.
Read More: Operational Efficiency: What is it, and How to Maximize & Boost ROI?
Now that the benefits are clear let’s understand the steps for effectively implementing an enterprise risk management framework.
How to Implement Enterprise Risk Management Framework
To effectively implement an enterprise risk management framework in the organization, managers can follow the below-mentioned steps:
Clearly Define Goals
The first step is to clearly define goals for your Enterprise Risk Management initiative. Are you planning to strengthen regulatory compliance, support strategic decision-making, or improve operational resilience? Defining the objectives upfront ensures that organizations understand why ERM is being implemented.
Moreover, setting clear, measurable goals also aligns risk management activities with broader business goals. This enables project resources, leadership, and departments to stay focused on shared priorities and act decisively in navigating uncertainties such as sudden market shifts, regulatory changes, or supply chain disruptions.
Read More: 25 Business Objectives That Every Firm Must Measure for Success
Determine Risk Appetite & Tolerance
The next step is to define how much risk the organization is realistically willing to take to achieve its goals. Risk appetite isn’t about avoiding all risks; it’s about recognizing which risks are acceptable and manageable and which can jeopardize success if not properly addressed.
Once the appetite is identified, managers can translate it into specific risk tolerance levels. These are the boundaries that guide teams on when to act, when to escalate issues to leadership, or reassess strategies. Setting these thresholds provides a clear benchmark for decision-making and helps prioritize actions.
Identify Potential Risks
The next step is to conduct a thorough risk identification exercise. This means scanning all departments, business processes, and external environments to uncover potential threats that could disrupt business operations. Engage cross-functional teams such as project managers, finance heads, IT heads, and stakeholders to view risks from different perspectives and ensure nothing is overlooked.
Firms can conduct risk workshops and brainstorming sessions to bring diverse insights to the surface. They can also review historical incidents, project reports, or industry case studies to identify emerging risk patterns. Risks can originate from operational, financial, regulatory, and more sources. After analyzing bottlenecks, categorize and document them into a risk register to ensure nothing slips through the cracks.
Read More: 12 Key Project Reports for Successful Project Managers
Assess & Prioritize Risks
Once the potential risks are identified, the next step is to assess and prioritize them based on the likelihood of their occurrence and the severity of their potential impact. For this, managers can use a risk matrix to plot risks visually and categorize them into critical, high, moderate, or low levels.
This helps decision-makers distinguish between risks that require immediate action and those that can be monitored over time. Prioritizing risks helps organizations focus their attention, resources, and mitigation efforts where they have the greatest effect, ensuring critical threats are addressed first and risk management remains proactive.
Develop Risk Response Strategies
In the fifth step, managers should determine the most appropriate action for mitigating the risks. Based on the organization’s risk appetite, responses may vary. It can include avoiding the risk, reducing its likelihood or impact, transferring it to a third party, or accepting it when the potential consequences are manageable.
Additionally, it is essential to formally document these risk management strategies to ensure consistent implementation across departments. A clear and structured risk response plan enables timely action, enhances accountability, and supports the organization in maintaining operational efficiency when unexpected risks arise.
Read More: Risk Matrix in Project Management: An Ultimate Guide
Assign Responsibilities to Risk Owners
Accountability is essential to ensure that your enterprise risk management delivers the desired results. To ensure risks are consistently monitored and addressed, assigning specific categories of risks to dedicated risk owners is essential. These individuals are accountable for monitoring threats and executing relevant mitigation actions.
Additionally, succession planning should be considered to ensure continuity in risk management, even during unplanned attrition. When responsibilities are well-defined, it becomes easier to maintain momentum, coordinate responses across teams, and embed a strong risk culture throughout the firm.
Monitor & Review Risks
To maintain the effectiveness of an ERM framework, organizations must establish robust monitoring mechanisms to track key risk indicators and early warning signs across operations. This includes reassessing risks based on changing circumstances and evaluating the effectiveness of existing mitigation measures.
Regular reviews also help detect emerging risks early and identify gaps where risk responses need to be strengthened. Moreover, as business environments evolve, continuous monitoring reinforces accountability and ensures that risk management strategies remain agile.
Read More: 7 Steps to Build a Winning Operational Strategy for Your Business
Report & Communicate Risks
Consistent and regular communication is essential for the effective execution of the ERM framework. To foster a risk-aware culture, organizations must establish a structured and reliable reporting process to ensure risk-related information is shared with all the key stakeholders across the firm.
This includes creating and sharing risk dashboards, scorecards, and executive-level reports that provide the status of key risks and demonstrate the effectiveness of emerging trends. It keeps the leadership informed and ensures risk-related discussions are integrated into strategic decision-making and not treated as an afterthought.
Utilize the Right Tools and Technologies
Lastly, to strengthen enterprise risk management, organizations can leverage tools that streamline risk identification, assessment, and monitoring. The right tools help centralize risk registers, automate tracking of mitigation plans, and generate data-driven insights. Moreover, these tools alert decision-makers when thresholds are breached, enabling quick actions.
For example, deploying compliance tracking systems helps stay ahead of regulatory requirements and avoid penalties. The right technologies improve data accuracy and monitoring speed and make it easier to integrate ERM practices across departments and teams.
Read More: How Can You Make Data-Driven Decisions with Resource Management Software?
Now that we know how to implement an enterprise risk management framework effectively let’s learn about the role of resource management software in managing such threats.
How can Resource Management Software Help in Managing Risks?
The next gen resource management software offers advanced features that can help organizations handle risks more effectively. Let’s have a look at them:
- The software provides multidimensional analysis that allows managers to slice and dice the resource plans across various dimensions like skills, team, location, role, or department and choose the most competent resources. With this granular visibility, organizations can reduce skills related to skill mismatches, project inefficiencies and delivery delays.
- Its embedded capacity planner lets business leaders anticipate and assess short and long-term resource requirements. Thus, preventing risks such as talent shortages, unbalanced workloads and excess idle capacity.
- The embedded heat mapping facility helps managers quickly identify over/underutilized professionals. This insight is critical for mitigating risks like employee burnout, disengagement and unplanned attrition.
- The tool’s intelligent match-making function ensures that managers assign the right personnel to the right project at the right time and cost. By aligning resource skills, availability and project requirements, organizations can reduce the risk of poor-quality deliverables, missed deadlines and budget overruns.
- Finally, the smart KPI forecaster is another powerful feature available only in SAVIOM. It helps managers gain foresight into resource-centric KPIs like capacity, resource utilization, availability, skill shortages, people-on-the-bench, etc., enabling data-driven decision-making.
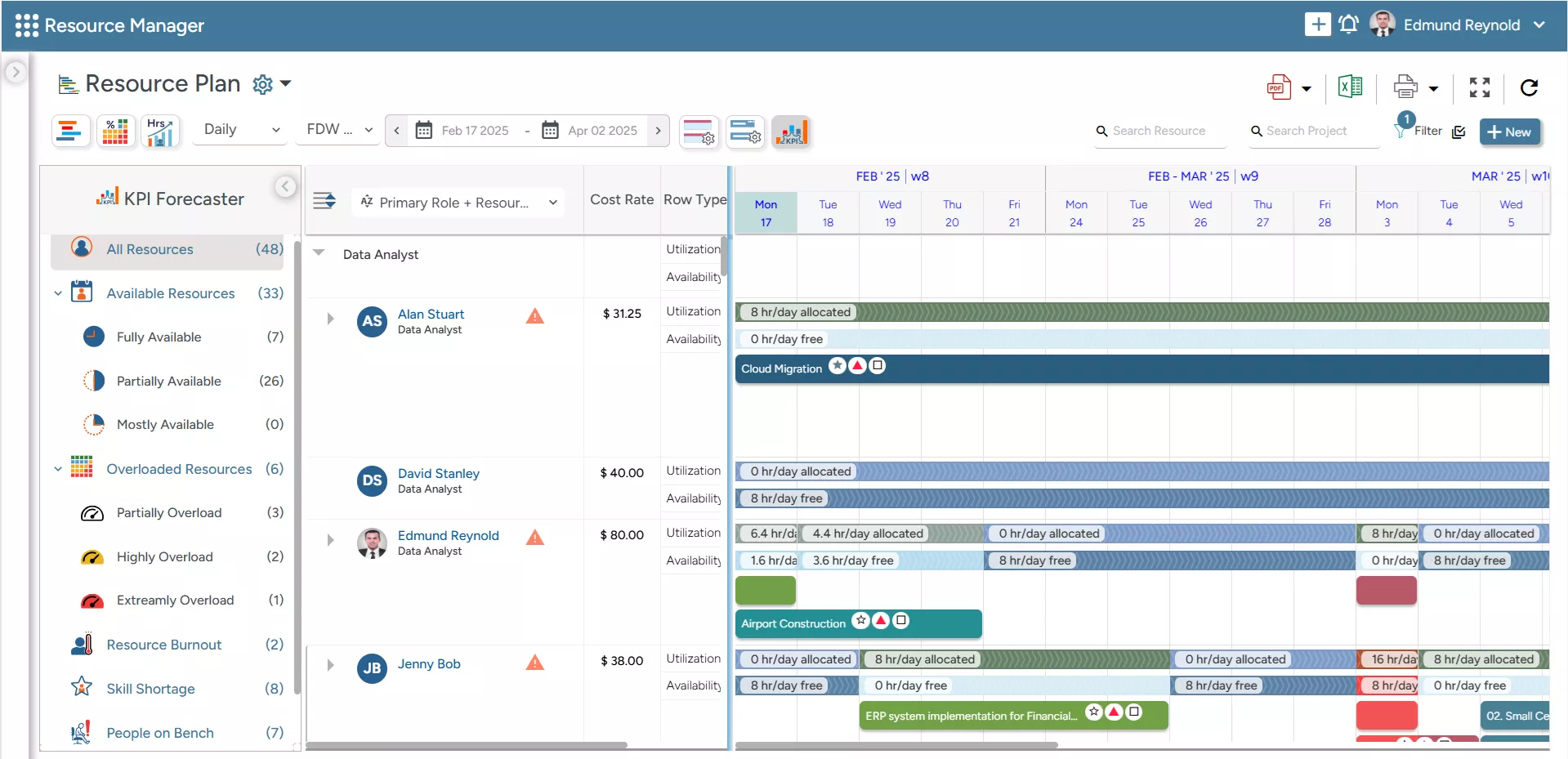
SAVIOM’s KPI Forecaster provides insights into key resource-centric KPIs like availability, capacity, skills, etc. to enable data-driven decision-making.
- The what-if analysis features allows managers to create and compare various resource allocation scenarios under different business conditions. Thus, allows firms to simulate potential risks such as talent shortages or unplanned leaves and design the most resilient and profitable resource plan.
Conclusion
Enterprise risk management isn’t about eliminating every risk; rather, it’s about knowing what the potential threats are, how they could affect the organizational goals, and how to handle them. By integrating enterprise risk management across the organization and building a culture of transparency, businesses can stay competitive, agile, and well-prepared for handling unexpected risks.
So, are you ready to build a robust enterprise risk management framework in your organization?
The Glossary
Read More: Glossary of Resource Workforce Planning, Scheduling and Management











