Introduction
As businesses grow, so does the number of projects, programs, and strategic initiatives competing for the same workforce. Managing these initiatives independently often leads to resource conflicts, unclear priorities, and delivery challenges. Teams may become overutilized in some areas while others remain underused, making it difficult to maintain a balanced workload and consistent delivery across the portfolio.
This is where portfolio resource management becomes essential. It provides an enterprise-wide view of resource capacity, project demand, and business priorities. With this visibility, managers can allocate resources more strategically, balance resource utilization across initiatives, and make informed prioritization decisions. As a result, strategy, capacity, and execution remain aligned, enabling more predictable delivery of high-value initiatives.
In this blog, we will delve into what portfolio resource management is, its benefits, core principles, and other related concepts.
What is Portfolio Resource Management?
Portfolio resource management is the process of planning, allocating, and optimizing resources across multiple projects and programs to support strategic business priorities. It treats resources, such as personnel, tools, equipment, and budgets, as shared organizational assets, enabling coordinated execution across departments and business units.
At its core, portfolio resource management helps organizations balance resource demand with available capacity across the entire portfolio, rather than managing resources in isolated projects. It provides enterprise-wide visibility into resource availability, skills, utilization, and project requirements. This enables managers to assign the right talent to the highest-value initiatives while avoiding overallocation and underutilization.
Now that the definition is clear, let us look at the benefits of portfolio resource management.
Learn how resource management and optimization drive efficiency in this detailed guide.
Benefits of Portfolio Resource Management
Effective portfolio resource management translates into improved utilization, reduced costs, and better delivery predictability. Let’s take a closer look at its benefits:
Aligns Resources with Strategic Priorities
Portfolio resource management ensures organizational capacity is directed toward initiatives that contribute the most to business goals and revenue growth. Instead of allocating based solely on resource availability or urgency, managers prioritize projects based on strategic value. By doing so, they prevent low-priority or non-strategic projects from consuming critical skills and budget.
Improves Portfolio Delivery Predictability
A well-defined portfolio resource management plan validates whether planned initiatives are realistically achievable within available capacity and skills. This prevents resource overutilization and unrealistic delivery timelines. Moreover, with better visibility into capacity constraints, managers can avoid last-minute staffing changes, reduce delivery delays, and minimize execution risks across the portfolio.
Optimizes Enterprise Resource Utilization
Instead of certain teams operating at 130% capacity while others remain idle, effective portfolio resource management ensures balanced workload utilization across projects and programs. This improves employee productivity, reduces burnout risk, and ensures that talent is fully leveraged across the portfolio without unnecessarily increasing headcount.
Deep dive into the concept of resource utilization.
Enables Data-Driven Portfolio Decisions
Portfolio resource management provides real-time visibility into resource availability, utilization, costs, and future demand across the enterprise. This enables managers to make informed resourcing and prioritization decisions. In addition, managers can evaluate trade-offs using actual capacity constraints. As a result, portfolio planning becomes more accurate, and strategic decisions are grounded in operational reality.
Controls Resource-Related Portfolio Costs
A robust portfolio resource management plan helps firms maintain a balanced resource mix (senior/junior, local/global, permanent/contractual). This prevents unnecessary use of high-cost senior resources for routine tasks. Additionally, proactive capacity planning reduces last-minute staffing decisions and costly hiring. As a result, organizations can keep project delivery within budget while improving cost efficiency.
Explore six resource cost reduction techniques to boost business profitability.
Now that we understand the benefits of portfolio resource management, let us explore its core principles.
Core Principles of Portfolio Resource Management
These principles form the foundation of sustainable portfolio performance and long-term strategic agility.
Portfolio-Wide Resource Visibility
Portfolio resource management begins with establishing a consolidated, enterprise-wide view of workforce capacity, skills, availability, and allocations across projects, programs, and portfolios. This single source of truth eliminates fragmented resource data stored across departments and business units, enabling informed portfolio decisions.
Strategic Resource Allocation
This is one of the critical components of project resource management, which ensures resource allocation decisions are based on strategic priorities and expected business value, not mere resource availability. This ensures that the most critical initiatives receive the required skills and capacity to succeed.
Capacity and Skills-Aligned Planning
Capacity and skill-aligned planning ensure that portfolio plans are grounded in the organization’s actual workforce capacity across roles, skills, locations, and time horizons. Thus, instead of creating aspirational portfolio roadmaps, managers validate whether planned initiatives are achievable with available capabilities and identify gaps early.
Read our blog on resource capacity planning and explore how it drives project success.
Adaptive Resource Reallocation
Adaptive resource reallocation ensures that workload distribution can be rebalanced as business priorities, project performance, or market conditions change. This prevents the portfolio from becoming locked into static annual allocation decisions and allows organizations to respond quickly to emerging opportunities or risks.
Clear Governance & Decision Rights
This component establishes defined ownership, governance structures, and decision authority for portfolio-level prioritization and resource reallocation. A clear governance framework clarifies who can approve resource budgets, staffing decisions, and initiative sequencing, thereby reducing delays and decision-making friction.
Scenario-Driven Portfolio Planning
Scenario planning enables organizations to evaluate the impact of resource constraints, project scope changes, budget shifts, or demand spikes before making portfolio decisions. Through what-if analysis and simulation, managers can compare multiple resource plans and select the most feasible plans.
Learn more about scenario planning and its benefits.
Performance Monitoring
This component focuses on tracking portfolio-level metrics to assess strategic outcomes and value realization. By monitoring KPIs such as resource utilization, employee productivity, schedule adherence, and portfolio ROI, organizations can continuously refine resource strategies and improve long-term portfolio performance.
After principles, let us understand the difference between portfolio resource management and project resource management.
Portfolio Resource Management vs. Project Resource Management
While both approaches focus on optimizing resources, they operate at different levels of organizational scope and impact. Let’s understand the difference between the two:
| Dimension | Portfolio Resource Management | Project Resource Management |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Enterprise-wide optimization of resources across multiple projects | Efficient use of resources within a single approved project |
| Level of Planning & Decision-Making | Portfolio-level planning that prioritizes, sequences, and balances initiatives across the organization | Project-level decisions focus on delivering scoped work within approved constraints |
| Decision Authority | Executives, portfolio boards, EPMO, and senior leadership | Project managers and delivery teams |
| Scope of Visibility | Enterprise view of resources across projects, programs, and strategic initiatives | Visibility is limited to a specific project |
| Time Horizon | Medium- to long-term planning (quarters to years) | Short- to medium-term planning (weeks to months) |
| Handling Resource Constraints | Resolves conflicts by reallocating resources or reprioritizing initiatives across the portfolio | Manages constraints within the project boundaries |
| Success Measures | Strategic value realization, portfolio throughput, resource utilization, and ROI | On-time, on-budget, and scope delivery |
| Typical Tools | PPM / Enterprise Resource Management platforms | Project management, scheduling, and team collaboration tools |
Learn the difference between resource management and project management in this blog.
The next section delves deeper into portfolio capacity planning and how it helps organizations align workforce capacity with portfolio demand.
Portfolio Capacity Planning: Balancing Supply and Demand
Effective project portfolio resource management depends on effectively aligning workforce supply with pipeline portfolio demand before execution begins. Let’s see how it works:
Capture Portfolio Demand
Capturing portfolio demand includes consolidating all work across projects, programs, operational work, and strategic initiatives into a single portfolio demand view. Initiatives are then broken down into role- and skill-based effort estimates across timelines, helping managers understand the required capacity and when it is needed.
Learn in detail about resource estimation and how to do it right.
Assess Available Capacity
After demand is defined, managers evaluate the actual workforce capacity available across roles, skills, geographies, and time periods. They factor in non-project time such as leave, training, internal initiatives, meetings, and administrative overhead. This prevents inflated availability assumptions that distort resource planning accuracy.
Identify Capacity and Skills Gaps
With both demand and capacity defined, managers compare the two to identify capacity shortages or excesses, as well as skill gaps across the portfolio timeline. This analysis enables managers to upskill employees or onboard new resources to address shortages and skill gaps, and redistribute or advance work to utilize excess capacity.
Prioritize Work Based on Capacity Constraints
When project demands exceed available capacity, organizations can sequence initiatives by prioritizing high-impact projects and deferring or phasing lower-priority work. This ensures that limited workforce capacity is directed toward the initiatives that deliver the greatest business value while maintaining portfolio balance.
Read our blog on workforce capacity planning to learn how it benefits organizations.
In the next section, let us explore how to plan portfolio resources.
How to Plan Portfolio Resources Using Forecasting & Scenario Modeling?
By combining forecasting and scenario modeling, organizations can make proactive portfolio resource decisions with greater confidence. Let’s understand how:
Forecast Portfolio Resource Demand
Key focus areas include:
- Forecasting future resource needs across projects, programs, and pipeline initiatives.
- Using historical delivery trends to estimate upcoming workforce demand.
- Analyzing project timelines and strategic roadmaps to anticipate future capacity requirements.
- Predicting portfolio demand by role and skill across time horizons.
Understand the difference between project, program, and portfolio management.
Anticipate Portfolio Capacity Risks
This step involves:
- Comparing forecasted demand with available workforce capacity.
- Detecting potential resource bottlenecks and skill shortages.
- Identifying delivery risks linked to workforce constraints.
- Enabling proactive resource risk mitigation to protect strategic initiatives.
Model Alternative Resource Scenarios
This stage includes:
- Creating multiple portfolio scenarios by adjusting resource allocation, project budget, and timelines.
- Simulating how these changes impact timelines, workforce utilization, and cost performance at the portfolio level.
- Analyzing how demand and capacity variations influence portfolio feasibility and execution risk.
Select the Most Feasible Resource Plan
Critical focus areas include:
- Choosing the resource plan that balances strategic priorities and workforce constraints.
- Ensuring decisions reflect both business objectives and execution feasibility.
- Aligning workforce capacity with portfolio commitments and timelines.
Learn how to create an effective resource management plan.
The next section explains the end-to-end portfolio resource management process.
Portfolio Resource Management Process (Step-by-Step)
The following steps illustrate how portfolio resource management is implemented across the organization.

Step 1: Establish Portfolio Priorities and Governance
In the first step, managers should identify which initiatives deserve funding, staffing, and executive attention. Organizations must clearly articulate investment priorities (growth, transformation, compliance, innovation) and rank initiatives accordingly. Moreover, governance structures should clarify who approves allocations, resolves conflicts, and authorizes reprioritization, reducing delays and political friction.
For example, an enterprise IT portfolio may prioritize cybersecurity modernization over legacy UI upgrades because it directly supports regulatory compliance and enterprise risk management. This ensures that limited workforce capacity and investment are directed toward initiatives that protect critical systems and reduce organizational risk.
Step 2: Capture Portfolio Demand
Next, consolidate all approved and proposed initiatives into a unified demand pipeline to eliminate silos. Each initiative’s resource requirements should be translated into specific roles, skills, seniority levels, and timelines, creating a structured view of workforce demand. This improves planning precision, strengthens demand forecasting, and avoids vague or inaccurate staffing estimates that can disrupt portfolio execution.
Step 3: Assess Resource Capacity Across the Portfolio
In the third step, managers analyze available workforce capacity across roles, skills, locations, cost, and time horizons. They must account for current allocations, leave schedules, training commitments, meetings, and administrative work to understand the true available bandwidth. This realistic capacity visibility helps identify overcommitment risks, skill shortages, and underutilized teams before portfolio execution begins.
For instance, a construction firm reviewing multiple infrastructure projects may find certified structural engineers operating at 95% utilization for the next two quarters, creating a bottleneck that delays new bids. To mitigate this, organizations can phase delivery timelines or strategically engage pre-qualified subcontractors to maintain bid competitiveness without overextending core teams.
Step 4: Allocate Resources Across Portfolio Initiatives
In this step, managers assign resources based on strategic priority, required skills, and realistic resource availability, rather than a first-come-first-served approach. Managers evaluate trade-offs across initiatives to maximize overall portfolio value while maintaining optimized resource utilization levels. This helps distribute workloads effectively, preventing burnout and protecting workforce productivity.
For example, during peak audit season, senior auditors may be allocated first to high-revenue or regulatory-sensitive clients, while smaller engagements are rescheduled or supported by junior associates under supervision. This ensures that limited expertise is directed toward the initiatives that deliver the greatest business impact.
Learn in detail about resource allocation, its benefits, and best practices.
Step 5: Monitor Portfolio Resource Performance
Next, managers must frequently track metrics such as resource utilization rate, capacity vs. demand variance, resource allocation effectiveness, and skill gap across the portfolio. This provides early visibility into resource underutilization, overallocation, or emerging capacity constraints. As a result, managers can intervene before small inefficiencies escalate into delivery delays, cost overruns, or revenue leakage.
Step 6: Rebalance Portfolio Resources Continuously
Lastly, managers should continuously reforecast portfolio demand to respond to shifts in business priorities and market disruptions. As a result, they can dynamically reallocate resources based on evolving portfolio demand and workforce capacity realities. Continuous re-planning ensures the portfolio remains aligned with changing delivery conditions, ultimately improving portfolio outcomes over time.
For example, in a marketing firm, if a strategic initiative accelerates due to competitive pressure, resources may be temporarily redeployed from lower-impact projects. This helps maintain enterprise momentum and delivery focus without increasing overall headcount or overloading teams.
Explore our comprehensive eBook on 5th gen resource management to boost overall business productivity and portfolio.
After the steps, let us explore the critical metrics to measure the success of portfolio resource management.
Essential KPIs to Measure Portfolio Resource Management Success
The success of portfolio resource management depends on tracking metrics that link resource performance to business results. Let’s take a closer look at these KPIs:
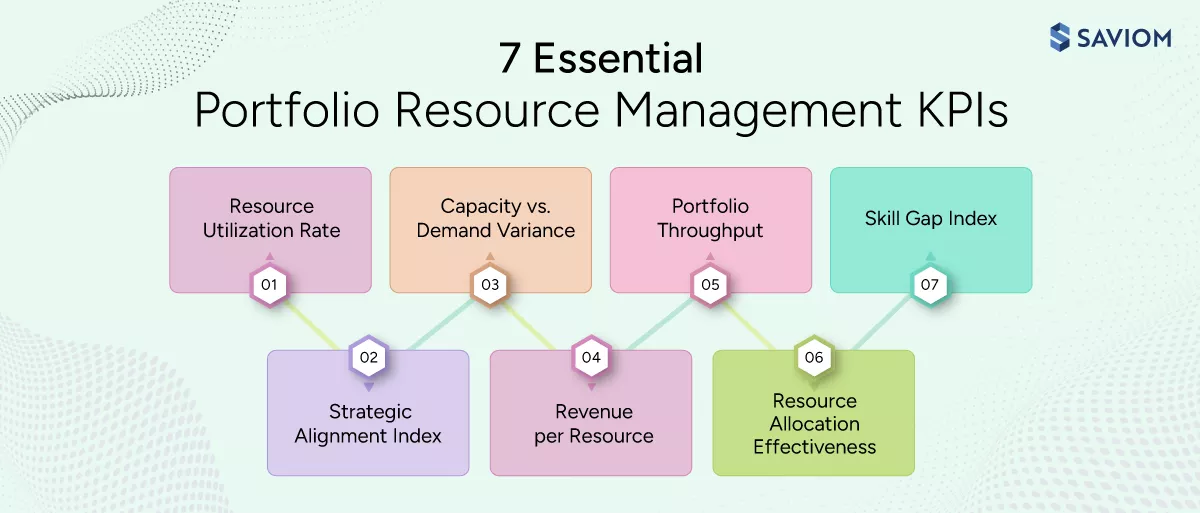
Resource Utilization Rate
The resource utilization rate measures how effectively resources (human and non-human) are utilized against their total available capacity across the portfolio. It helps firms identify instances of resource overutilization and underuse and take corrective action to prevent employee burnout and disengagement.
The formula to calculate the resource utilization rate is:
100
Learn how to track resource utilization accurately.
Strategic Alignment Index
The strategic alignment index helps businesses track the percentage of resources allocated to initiatives aligned with strategic objectives. This ensures resources remain focused on top priorities, improves funding discipline, and increases the likelihood of achieving strategic business goals.
The formula to calculate the strategic alignment index is:
Workforce Capacity) X 100
Where:
- Strategic Initiative Allocation = Effort spent on high-priority or strategic initiatives
- Total Workforce Capacity = Total available workforce effort in a given period
Capacity vs. Demand Variance
The capacity vs. demand variance helps organizations evaluate the gap between forecasted portfolio demand and available resource capacity. Persistent variance between demand and supply signals unrealistic planning assumptions and leads to delayed project initiation.
The formula to calculate the capacity variance is:
Understand how to measure resource capacity and demand.
Revenue per Resource
Revenue per resource is a metric that measures the amount of revenue generated by each resource within a specific timeframe. It provides valuable insight into how effectively the organization leverages its workforce across the portfolio to achieve business goals and drive profitability.
Portfolio Throughput
Portfolio throughput measures the number of projects, initiatives, or deliverables successfully completed within the portfolio over a specific period. In portfolio resource management, throughput helps managers understand whether resource allocation, prioritization, and capacity planning are enabling steady portfolio execution.
The formula to calculate portfolio throughput is:
Read our blog on project portfolio management.
Resource Allocation Effectiveness
Resource allocation effectiveness measures how appropriately an organization assigns its available resources, such as people, equipment, and finances, to project portfolios to achieve optimal results with minimal waste. It reflects the organization’s ability to align resources with top priorities, ensuring that the right resources are allocated to the most suitable projects at the right time and at the optimal cost.
Hours) X 100
Skill Gap Index
The skill gap index measures the difference between the skills an organization requires and those currently possessed by its workforce. It highlights critical roles or niche expertise that are in short supply, enabling managers to initiate skill development programs or onboard new resources.
Number of Skills Required] X 100
Understand what a skill matrix is and why it is important.
Next, let us understand the various portfolio resource management challenges and how to fix them.
Common Portfolio Resource Management Challenges & How to Fix Them
Here’s a rundown of the common challenges along with their solution:

Limited Portfolio-Level Resource Visibility
When resource data sits across disconnected tools and spreadsheets, managers lack a single source of truth. This results in inaccurate resource forecasts and reactive decision-making. Moreover, without clear visibility, overutilization of resources and an increase in bench capacity often go unnoticed.
How to Fix It?
Leverage a centralized resource management tool that provides enterprise-wide visibility into skills, capacity, utilization, and allocations across the portfolio. Clear, real-time visibility improves planning accuracy and delivery confidence.
Misalignment Between Portfolio Priorities & Resource Allocation
Managers often allocate resources based on urgency, project stakeholder pressure, or historical habits rather than strategic value. Over time, this weakens focus and spreads capacity across too many low-impact initiatives. As a result, strategy becomes disconnected from execution, reducing portfolio effectiveness.
How to Fix It?
Establish governance frameworks that link staffing decisions to clearly defined strategic criteria. Conduct regular portfolio reviews to validate whether allocations still reflect business priorities. This reinforces accountability, improves resource focus, and increases overall workforce productivity.
Learn what project resource management is and why it is important.
Skills Shortages Across the Portfolio
Critical skill gaps can delay high-priority initiatives and increase dependency on a small group of specialists. In many organizations, hiring decisions are made reactively, only after delivery risks have surfaced. This reactive approach increases costs, slows execution, and weakens portfolio delivery predictability.
How to Fix It?
Leverage resource forecasting to identify portfolio-level capacity and skill demands early. This enables organizations to plan retraining/upskilling programs or conduct strategic hiring to fill the gaps proactively and maintain delivery readiness across the portfolio.
Overloaded Shared Resources Across the Portfolio
Specialists such as architects, engineers, analysts, or senior consultants are often shared across multiple projects. Without structured portfolio coordination, they get overstretched, creating bottlenecks that impact multiple projects simultaneously. Sustained overload also increases burnout risk and employee attrition.
How to Fix It?
Track resource utilization levels for the shared workforce and set utilization thresholds to prevent overallocation. In addition, managers can rebalance workloads across initiatives, adjust timelines when necessary, and maintain backup capacity for critical roles.
Explore strategies to improve cross-departmental collaboration.
Inability to Adjust Portfolio Plans Dynamically
Many organizations rely on static annual plans that quickly become outdated. Moreover, market volatility, regulatory changes, or new opportunities require rapid reprioritization, but rigid processes slow response. This, in turn, reduces portfolio agility and limits the organization’s ability to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
How to Fix It?
Adopt well-defined scenario modeling practices. Additionally, conduct periodic portfolio reviews to reassess priorities and reallocate resources as needed. Continuous planning enables organizations to adapt quickly while maintaining strategic direction.
After challenges, let us learn the best practices for effective portfolio resource management.
Portfolio Resource Management Best Practices
By adopting best practices, organizations elevate portfolio resource management from reactive firefighting to a disciplined, enterprise-wide capability. Below are the essential practices that enable this transformation:
Align Portfolio Prioritization with Strategic Objectives
Managers should rank initiatives based on measurable business impact, risk exposure, regulatory importance, and growth potential. Capacity feasibility must also be considered to avoid approving work that cannot realistically be delivered. This helps direct capital and talent to initiatives that create the highest enterprise value and strategic impact.
Balance Portfolio Demand with Resource Capacity
Organizations should consistently compare approved portfolio demand against actual workforce capacity across skills and time horizons. This prevents systemic overcommitment and reduces last-minute firefighting. Moreover, when gaps appear, firms can make early trade-offs by delaying, phasing, or descaling initiatives before execution risks escalate.
Read our blog on resource capacity requirement planning.
Monitor and Optimize Portfolio Resource Utilization
Managers should continuously track resource utilization across the portfolio to ensure workforce capacity is used effectively without causing overutilization or prolonged bench time. By regularly reviewing utilization trends, managers can redistribute workloads, adjust timelines, or reassign resources across initiatives to maintain portfolio balance. This improves workforce productivity and prevents burnout.
Adopt Skills-Based Portfolio Planning
Resources should be planned based on competencies and proficiency levels, rather than solely on job titles. This ensures that the right expertise is matched to the right initiative at the right cost. Moreover, skills-based planning improves forecast accuracy, highlights capability-building gaps early, and supports targeted hiring or upskilling strategies.
Understand how skill development helps in creating a future-ready workforce.
Balance Global and Local Resources Across the Portfolio
Organizations should distribute work strategically across global and local teams to optimize cost efficiency, availability, and time-zone coverage. This approach prevents overreliance on expensive local resources while avoiding communication gaps that may arise from fully distributed execution models. A balanced global–local resourcing model helps prevent cost overruns while ensuring consistent delivery outcomes.
Manage portfolio resources with SAVIOM’s advanced software to ensure timely availability, enhance delivery predictability, and gain a competitive edge. Book a Demo Today.
Now, let us understand the role of AI in portfolio resource management.
What is the Role of AI in Portfolio Resource Management?
AI enhances analytical depth, speed, and responsiveness within portfolio resource management. Let’s understand how:
AI-Driven Portfolio Demand Forecasting
AI analyzes historical project data, seasonal patterns, pipeline trends, and strategic roadmaps to generate more accurate portfolio demand forecasts. It detects patterns that manual planning may overlook, such as recurring skill spikes or cyclical workload fluctuations. This improves the precision of strategic workforce planning and helps organizations anticipate capacity gaps well before execution begins.
Intelligent Resource Allocation Recommendations
AI-powered algorithms evaluate skills, availability, utilization levels, cost rates, and initiative priorities to recommend optimal resource assignments. This reduces the complexity of manual coordination and accelerates portfolio-level decision-making. Managers can also quickly simulate multiple allocation scenarios, helping them balance resource utilization, cost efficiency, and strategic priorities more effectively.
Early Detection of Capacity Risks
Predictive analytics continuously monitors utilization trends, project velocity, and workload distribution across the portfolio. It can flag potential bottlenecks, overcommitment risks, skill shortages, or underutilized capacity before they impact delivery timelines. These early insights enable managers to intervene proactively rather than reacting to execution issues later.
Continuous Portfolio Optimization
AI systems track real-time performance data and recommend dynamic rebalancing actions as conditions change. This supports continuous demand forecasting, agile reprioritization, and more adaptive portfolio planning. Additionally, continuous resource optimization ensures workforce capacity remains aligned with changing business priorities, improving delivery predictability and overall portfolio performance.
Conclusion
Portfolio resource management is not an operational scheduling function; it is a strategic capability that determines whether the enterprise strategy can be realistically executed. When organizations align capacity with priorities, delivery predictability improves, utilization stabilizes, and investment returns increase. The future of execution excellence lies in integrated portfolio visibility, continuous forecasting, and adaptive resource governance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Portfolio resource management is the process of planning, allocating, and optimizing resources across multiple projects and programs to support strategic business priorities. It treats resources, such as personnel, tools, equipment, and budgets, as shared organizational assets, enabling coordinated execution across departments and business units.
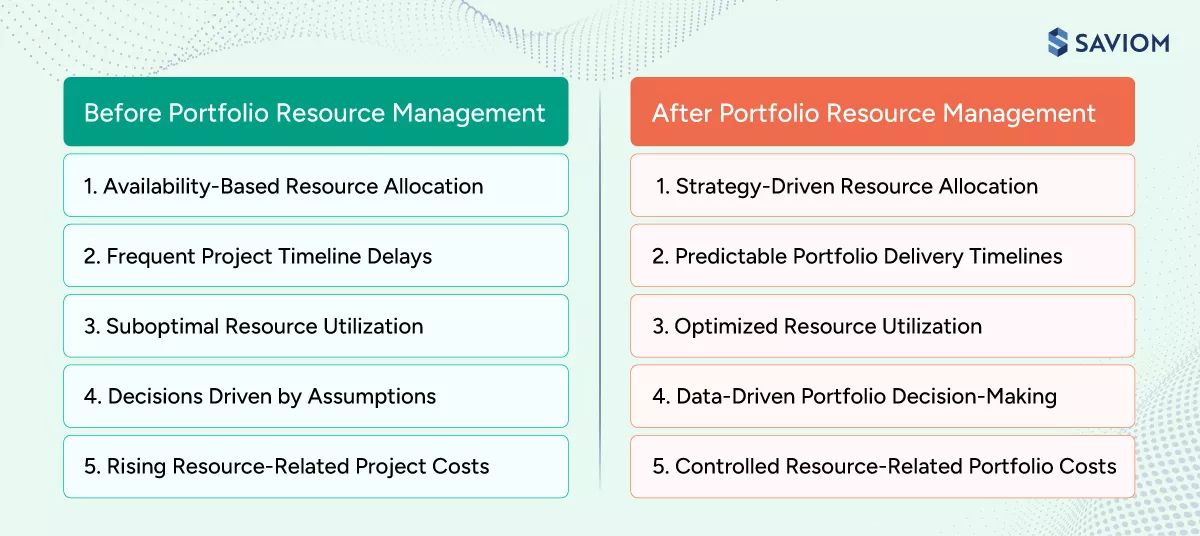
The benefits of effective project portfolio resource management are:
1. Strategy-driven resource allocation
2. Predictable portfolio delivery timelines
3. Optimized resource utilization
4. Data-driven portfolio decision-making
5. Controlled resource-related portfolio costs
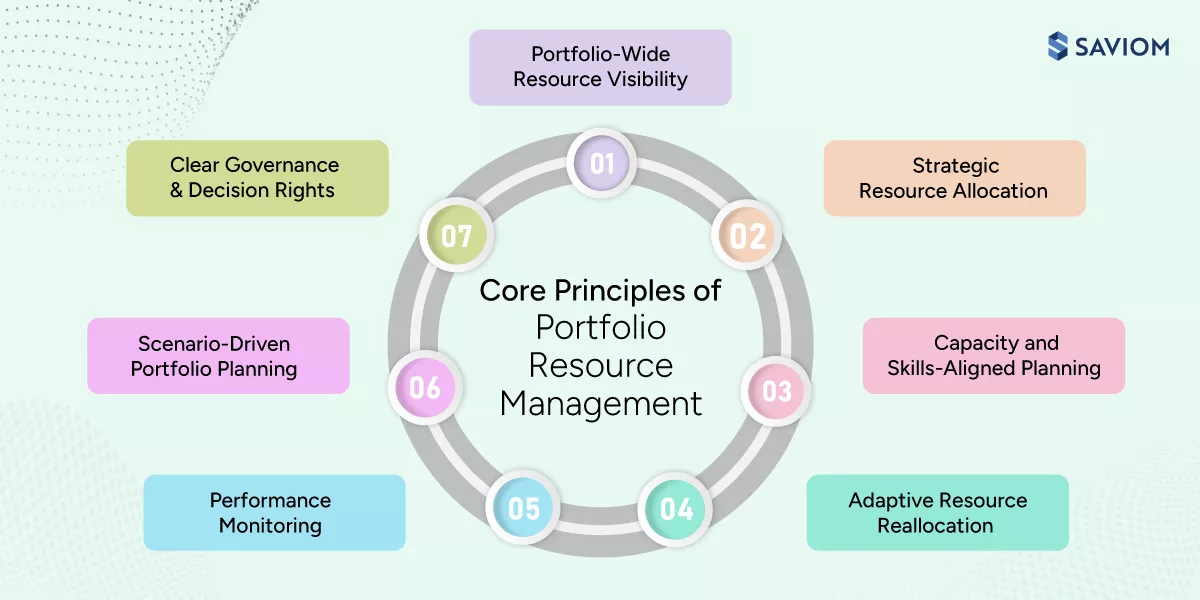
The core principles of project portfolio resource management are:
1. Portfolio-wide resource visibility
2. Strategic resource allocation
3. Capacity and skills-aligned planning
4. Adaptive resource reallocation
5. Clear governance and decision rights
6. Scenario-driven portfolio planning
7. Performance monitoring
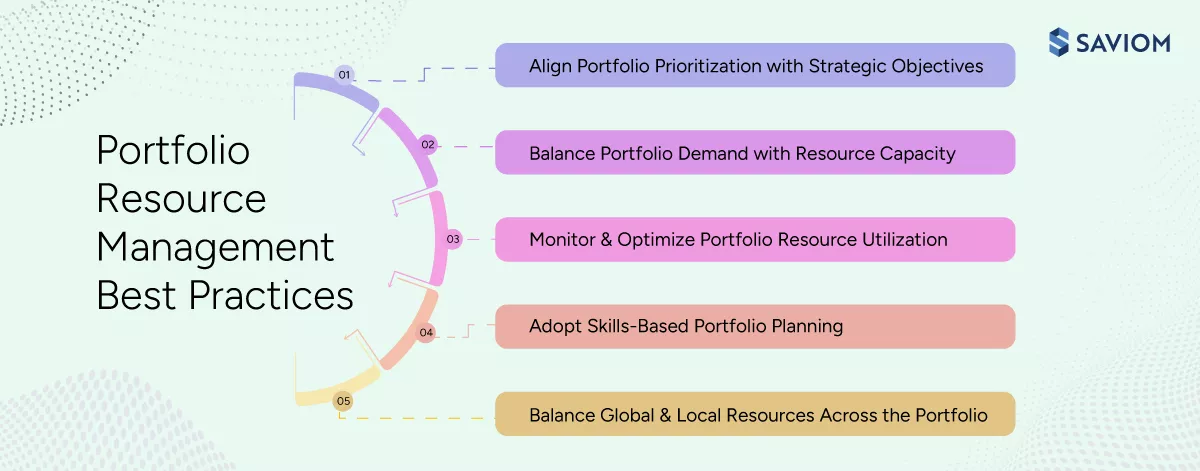
The following are the best practices for effective portfolio resource management:
1. Align portfolio prioritization with strategic objectives
2. Balance portfolio demand with resource capacity
3. Monitor and optimize portfolio resource utilization
4. Adopt skills-based portfolio planning
5. Balance global and local resources across the portfolio
The common portfolio resource management challenges are:
1. Limited portfolio-level resource visibility
2. Misaligned portfolio priorities and resource allocation
3. Skills shortages across the portfolio
4. Overloaded shared resources across the portfolio
5. Inability to adjust portfolio plans dynamically










