Introduction
“A goal without a plan is just a wish.” ~ Antoine de Saint-Exupéry
This quote captures the importance of structured planning when managing your resource pool. Even the most capable teams can underperform without a clear framework for planning, staffing, and executing work.
That’s why a resource management plan is no longer an option; it’s a business necessity. It brings discipline to resourcing decisions by replacing assumptions with data-driven planning.
A well-crafted resource management plan aligns resources with project and business goals. It clarifies roles, sets priorities, and ensures the right skills are available at the right time, resulting in smoother project delivery and stronger cost control.
This blog will take you through the nitty-gritties of the resource management plan, including definition, benefits, core elements, and steps.
Let’s start!
What is a Resource Management Plan?
A resource management plan is a structured document that outlines how organizations identify, allocate, monitor, and optimize resources to ensure projects are delivered within available capacity.
It provides clear visibility into skills, availability, utilization, and future demand, enabling informed resourcing decisions throughout the project lifecycle. Unlike static plans, it is continuously updated as priorities, timelines, and scope change. Consequently, this prevents resource overallocation, skill mismatches, and project delivery risks.
Read this eBook to learn why 5th gen resource management is critical for project-based businesses.
In the next section, we will understand the benefits of a resource management plan in firms.
Why is a Resource Management Plan Critical for Project Success?
Project success depends less on intent and more on execution feasibility. This section explains how resource planning turns strategic goals into achievable delivery outcomes.

Aligns Resource Capacity with Demand
An effective resource management plan ensures that available capacity is continuously aligned with both current and future project demand. It helps managers forecast workloads and business priorities to anticipate skill gaps and capacity shortages early. This enables proactive hiring, upskilling, or reallocation while preventing bench time and resource overload.
Facilitates Efficient Resource Allocation
With a structured resource management plan in place, organizations can assign resources based on skills, availability, cost, and project priority instead of last-minute urgency. It minimizes conflicts between competing projects and ensures high-impact initiatives receive the right talent. As a result, allocation accuracy improves, and delays caused by misaligned staffing are significantly reduced.
Check out our blog on resource allocation.
Improves Resource Utilization
A resource management plan provides clear visibility into workloads, enabling balanced work distribution across teams. It prevents the underutilization of valuable skills while avoiding burnout of critical resources. Thus, by optimizing work more evenly, teams can get work done without hiring new people, directly improving employee productivity.
Controls Project Costs and Margins
Poor resourcing decisions often lead to cost overruns through overtime, rework, or rushed hiring. A structured resource management plan helps in controlling labor costs by aligning staffing levels with demand and budgets. This improves cost predictability and protects profit margins at both project and portfolio levels.
Ensures Timely Project Delivery
The project resource management plan helps managers build a realistic schedule with clear visibility into resource availability and skill sets. This ensures the timely availability of resources during project execution, thereby minimizing bottlenecks and subsequent delays. As a result, tasks are completed within the defined timeline.
Explore what project resource management is and how it prevents delivery delays.
Having understood the importance, let’s explore the critical elements that support the resource management plan in project management.
Learn how organizations operationalize these benefits using an advanced resource management tool.
Core Components of an Effective Resource Management Plan
These essential components form the operational backbone of any scalable resource management plan process.
Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting provides a forward‑looking view of current and future demand by mapping upcoming work to specific roles, skills, and effort levels. It helps organizations anticipate workload peaks, seasonal demand shifts, and future hiring or upskilling needs before they disrupt delivery timelines.
Understand how to implement a demand management framework effectively.
Resource Capacity and Availability
As per a McKinsey report, “90% of leaders view capacity management as an urgent priority that requires immediate or near‑term action.”
Effective resource capacity planning evaluates available capacity against forecasted project demand. It factors in working hours, planned leave, holidays, training, internal initiatives, and non‑billable work to determine true resource availability. This creates a realistic baseline for planning, prevents overbooking, and ensures project commitments are built on achievable assumptions.
Resource Skills Inventory
A structured resource skill inventory (or skill matrix) offers a clear, up‑to‑date view of the skills, competencies, certifications, and experience levels available within an organization. It helps managers understand current strengths, identify critical skill gaps, and anticipate future capability needs, thereby supporting decisions around training, upskilling, and hiring.
Resource Allocation Strategy
This element defines the guidelines a firm uses to distribute resources across projects and non-project tasks based on business priority, financial value, and urgency. Moreover, a well-defined strategy embeds skill-based allocation, ensuring complex or high‑impact work is handled appropriately by skilled resources, reducing delivery risk and rework.
Resource Utilization Management
Clear resource utilization targets define how much work can be handled realistically without compromising employee productivity or well‑being. These thresholds act as early warning signals. Moreover, continuous monitoring of planned vs. actual utilization helps identify overload and burnout before it impacts project delivery.
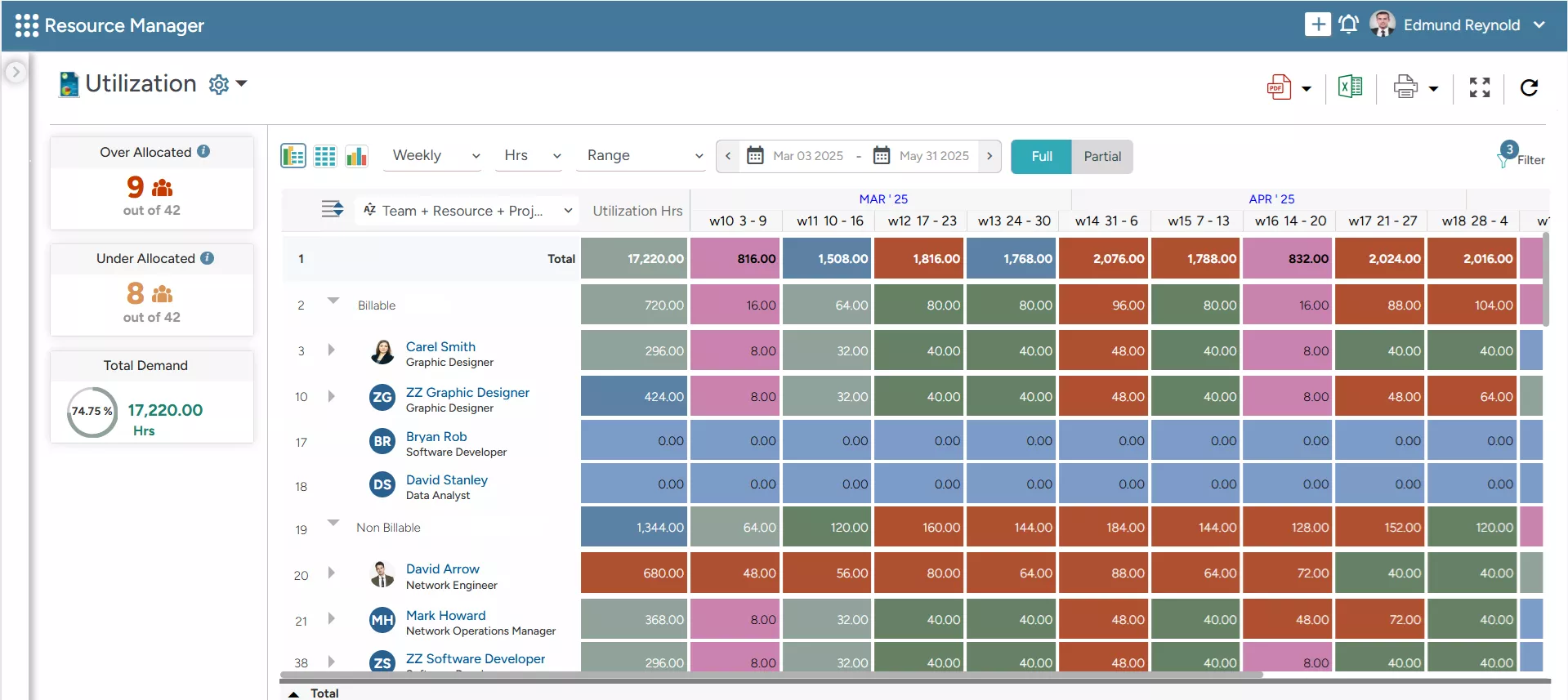 SAVIOM’s Color-Coded Heatmap helps forecast employees’ utilization levels, enabling leaders to identify imbalances and take proactive actions.
SAVIOM’s Color-Coded Heatmap helps forecast employees’ utilization levels, enabling leaders to identify imbalances and take proactive actions.
Risk and Contingency Plans
Risk and contingency planning define backup strategies for unexpected scenarios, such as sudden unplanned attrition or demand spikes for delivery-critical roles. By outlining proactive mitigation strategies, such as cross-training, backfilling, or out-rotation, the plan ensures the project remains on track despite unforeseen internal or external disruptions.
Monitoring and Reporting Structure
A robust reporting structure establishes the reports and dashboards needed to track key KPIs, such as resource utilization trends, project progress, and capacity vs. demand. Additionally, setting regular reviews and escalation triggers ensures deviations are identified early, and corrective actions are taken on time.
Explore key resource management reports that help managers make data-driven decisions.
Now that we have explored the components, let’s shift our focus to understanding effective ways to implement a project resource management plan.
How to Create a Resource Management Plan? (Step‑by‑Step)
A repeatable step ensures that the resource management planning process remains consistent, scalable, and adaptable across projects. Given below are the steps:
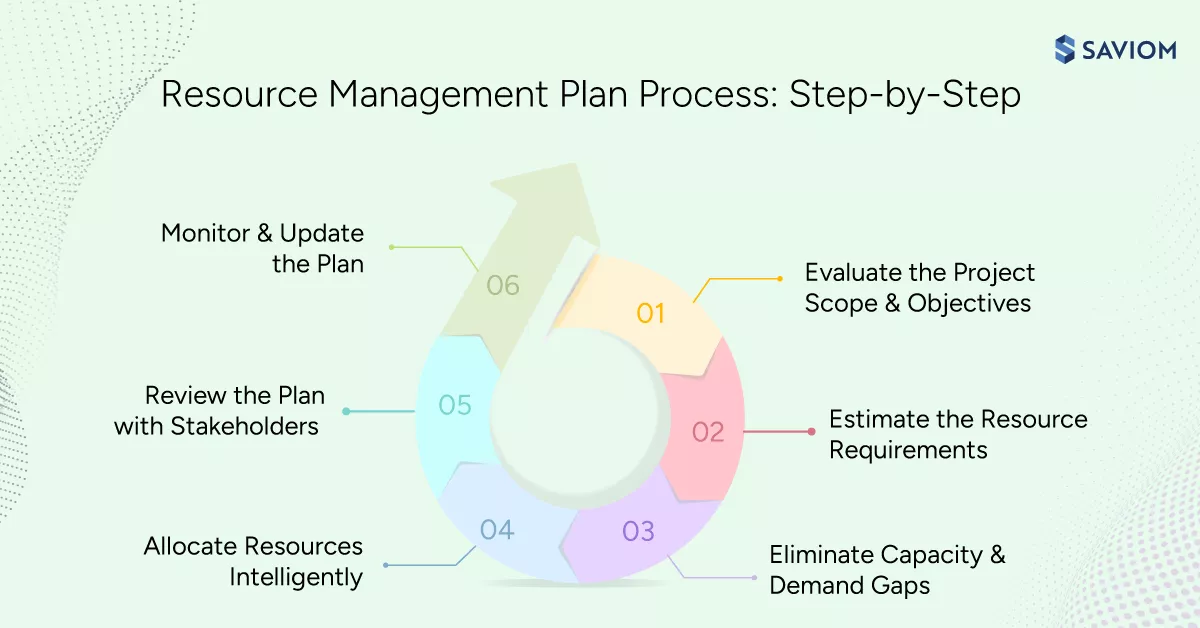
Understand the Project Scope & Objectives
The first step in creating a robust resource plan is to clearly define the project scope and objectives. This involves defining key deliverables, timelines, milestones, quality expectations, inclusions and exclusions, as well as non-project and support works. As a result, managers can forecast resource demand accurately and adjust the plan as required.
Determine the Project Resource Requirements
Here, managers must create a work breakdown structure (WBS) that breaks down the project into tasks and phases. Each of these activities is then mapped to required roles, skills, and effort level, thereby enabling accurate resource estimation. This creates a time-phased demand view rather than a one-time estimate, allowing a realistic baseline for project deliverables.
Read in detail about resource estimation and how to do it effectively.
Assess & Bridge Resource Capacity vs. Demand Gaps
Next, evaluate the existing resource capacity against demand by factoring in working hours, planned leave, ongoing assignments, and non-project commitments. This highlights potential resource shortages and excesses, enabling corrective actions, such as upskilling or planned hiring to mitigate shortages, and redeploying or selling excess capacity at discounted rates to bridge excesses.
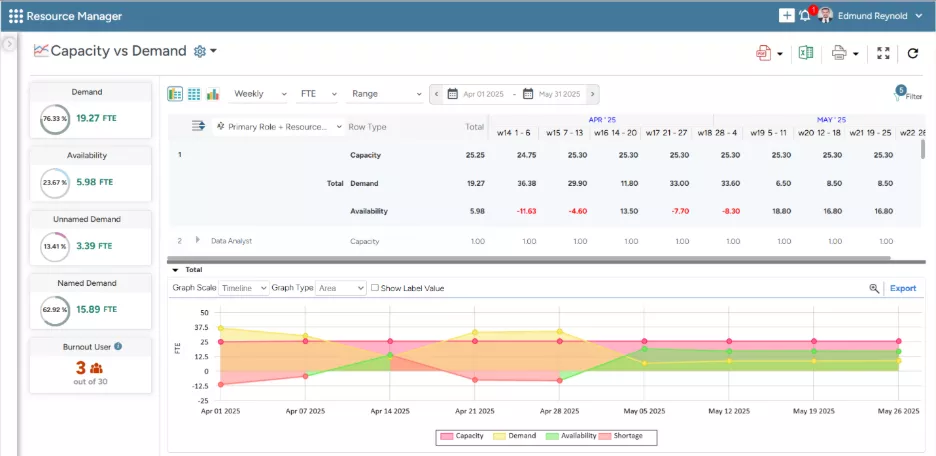 SAVIOM’s Capacity vs. Demand dashboard helps managers identify demand gaps, enabling quick, data-driven decisions.
SAVIOM’s Capacity vs. Demand dashboard helps managers identify demand gaps, enabling quick, data-driven decisions.
Allocate Resources Effectively
Now, managers must allocate resources efficiently based on factors, such as skill, role, cost, availability, and location. This ensures that the right resources are assigned to the right task at the right time, thereby avoiding under- or overallocation and skill mismatches. As a result, managers can balance the workload and maintain optimal utilization levels.
Understand ways to avoid overallocation of resources.
Review the Resource Plan with Stakeholders
This is a critical validation step to ensure feasibility, alignment, and shared accountability of the resource plan before project execution begins. The project stakeholders include sponsors, PMOs, managers, etc., who validate assumptions related to capacity, skill availability, timelines, and dependencies. With this, firms can establish clear escalation paths, reduce mid-project disruptions, and ensure the resource plan is approved and ready-for-execution.
Monitor and Update the Plan as Needed
Finally, this step involves regularly tracking key resource management metrics, such as resource utilization, capacity versus demand, allocation accuracy, and delivery progress. It also includes adjusting allocations due to changes in priorities, timelines, or scope. Ongoing monitoring enables proactive risk mitigation, prevents burnout and bench time, and keeps project delivery on track in dynamic environments.
Learn steps to optimize resource utilization levels in projects.
Let’s understand the steps better with a hypothetical resource management plan example.
Resource Management Plan Example
A mid‑size IT services firm initiates a cloud migration project for a financial services client with a six‑month delivery timeline. We can go through the steps one by one:
- The project scope covers application migration, security setup, and performance testing, excluding post-deployment support.
- The project manager builds a WBS across discovery, build, testing, and deployment, mapping tasks to roles, such as cloud architects, backend developers, QA engineers, and DevOps specialists. This creates a time-phased demand forecast showing when each skill is needed.
- Next, capacity is assessed against demand by factoring in current assignments, planned leave, and non-project work. This reveals a shortage of cloud architects during the build phase.
- To address this, the firm upskills internal resources and reallocates staff based on skills, availability, and cost to balance workloads and meet utilization targets.
- Finally, the resource plan is validated with the PMO and sponsors and reviewed weekly to track resource utilization, capacity gaps, and delivery progress, enabling timely adjustments without last-minute firefighting.
Finally, let’s understand how a robust resource management tool enables firms to execute these steps effectively.
How SAVIOM Helps Firms Build a Resource Management Plan?
An advanced resource management software like SAVIOM offers key features that help firms create an efficient resource management plan. Here are some of them:
- All-in-one resource planner to gain real-time visibility into resource availability, capacity, and utilization across the organization.
- KPI forecaster to track and predict future resource metrics like availability, capacity, utilization, etc., enabling proactive plan adjustments.
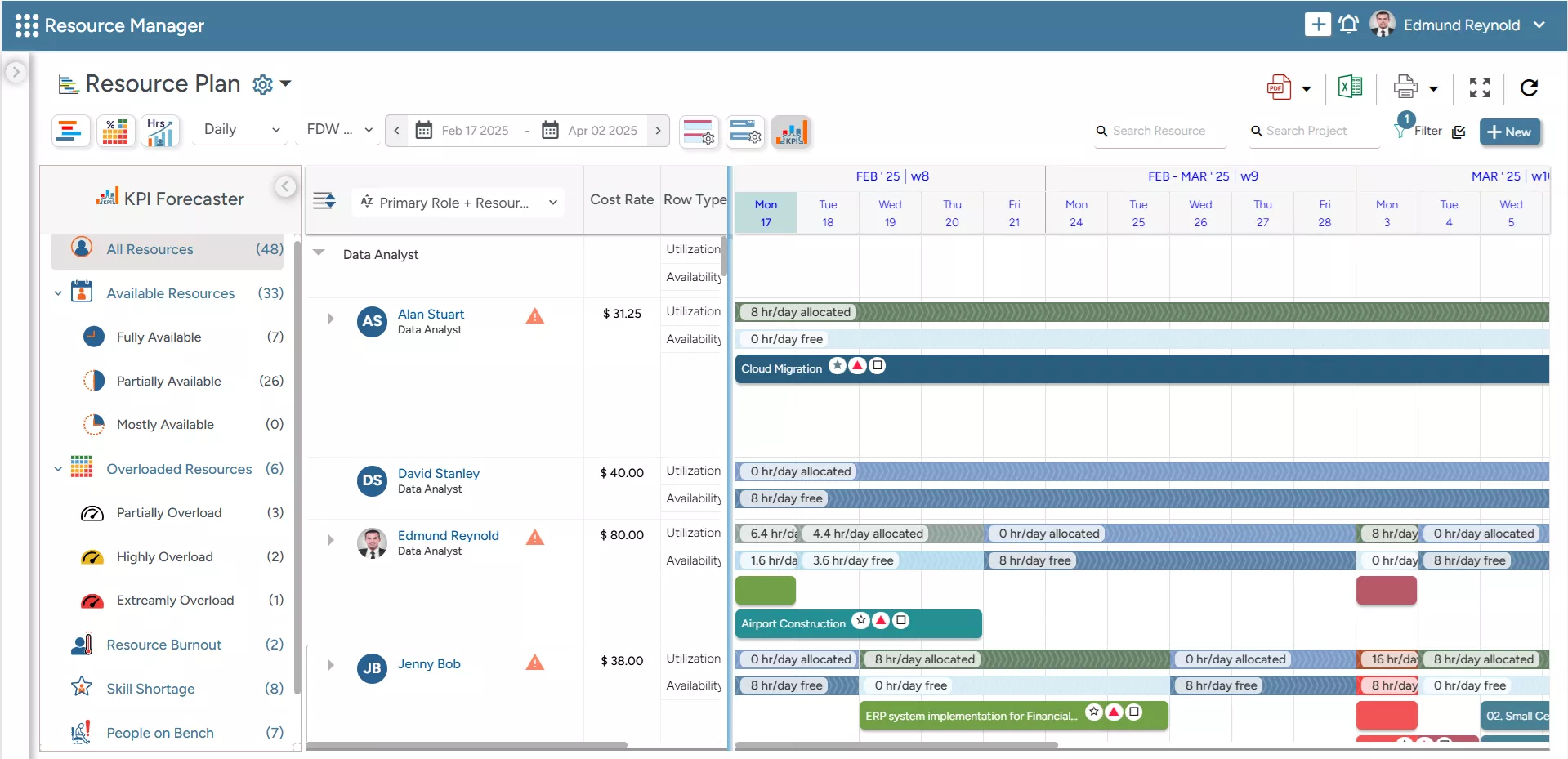 SAVIOM’s KPI Forecaster provides visibility into utilization, availability, and bench time, enabling proactive decisions and better resource planning.
SAVIOM’s KPI Forecaster provides visibility into utilization, availability, and bench time, enabling proactive decisions and better resource planning.
- An embedded capacity planner to highlight resource shortages and excesses in advance and take corrective measures.
- Intelligent matchmaking to assign the best-fit resources to projects based on skills, role, cost, etc.
- Embedded resource heatmap to visualize instances of resource over-/underutilization, thereby preventing employee burnout and disengagements.
- Competency matrix to centralize data on resource skills, certification, experiences, etc., thereby supporting training and hiring decisions.
- Real-time BI reports and analytics to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and make data-driven decisions.
- Scenario modelling or What-if analysis to create, compare, and select the most profitable resource plan.
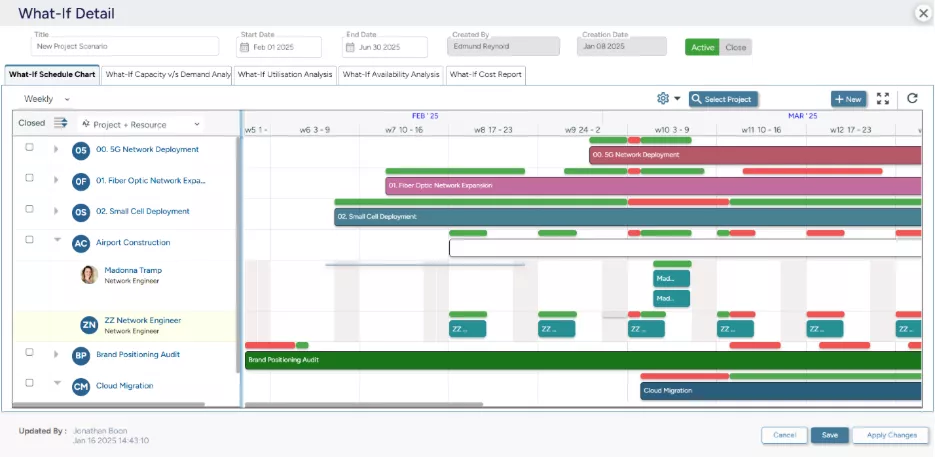 SAVIOM’s Scenario Modelling functionality allows managers to simulate different workforce scenarios in a sandbox environment and select the most profitable plan.
SAVIOM’s Scenario Modelling functionality allows managers to simulate different workforce scenarios in a sandbox environment and select the most profitable plan.
Conclusion
Resource management planning is no longer a static exercise performed at project kickoff. It is a continuous process that determines whether organizations can deliver reliably while protecting profit margins and workforce well-being. As a result, teams that treat the resource plan as an ongoing control mechanism gain sustainable utilization, predictable delivery, and long-term operational resilience.
FAQs
A resource management plan defines how resources are identified, planned, allocated, and monitored across projects to ensure balanced capacity, realistic workloads, and predictable project delivery outcomes.
The key importance of implementing a resource management plan includes:
The key importance of implementing a resource management plan includes:
1. Aligns Resource Capacity with Demand
2. Facilitates Efficient Resource Allocation
3. Improves Resource Utilization
4. Controls Project Costs and Margins
5. Ensures Timely Project Delivery
The critical elements that support an effective resource management plan are:
1. Demand Forecasting
2. Resource Capacity and Availability
3. Resource Skills Inventory
4. Resource Allocation Strategy
5. Resource Utilization Management
6. Risk and Contingency Plans
7. Monitoring and Reporting Structure
Managers can build a robust resource management plan by following the steps below in order:
1. Understand the Project Scope and Objectives
2. Determine the Project Resource Requirements
3. Assess and Bridge Resource Capacity vs. Demand Gaps
4. Allocate Resources Effectively
5. Review the Resource Plan with Stakeholders
6. Monitor and Update the Plan as Needed










