Whether you are spearheading a multi-dollar construction project or leading a marketing campaign for a new app, the success of your initiatives heavily relies on the project lifecycle. It is a structured approach that gives managers the clarity and control to keep projects on track and deliver the desired results.
Moreover, it guides the team through each phase from initiation to closure, enabling them to anticipate potential challenges, maximize resource utilization, and meet client expectations. As a result, it increases the likelihood of project success and boosts ROI.
This article discusses the project lifecycle in detail, its importance, types, best practices, and how implementing the five phases can lead to success.
Let’s get started.
What is the Project Lifecycle?
As per the PMI, “the project lifecycle is a basic framework that project managers and teams use to effectively structure projects and set them up for success.”
A project lifecycle is the sequence or series of phases that a project undergoes from initiation to closure. The objective of the lifecycle is to establish an easy-to-follow system for all resources to complete a project successfully. The lifecycle may vary depending on the specific needs, nature, and project scope. However, the key phases remain the same, which are:
- Initiation
- Planning
- Execution
- Monitoring and Controlling
- Closure
But who is really in charge of managing a project lifecycle? Let’s find out.
Who Manages the Project Lifecycle?
Project managers are typically in charge of managing a project throughout its lifecycle. However, they are not alone in this journey. Project sponsors often play a key role in preparing the proposal, while key stakeholders are responsible for approvals and funding. Additionally, a dedicated project team assists in executing the project and delivering the results.
The members needed to oversee the project lifecycle vary from project to project depending on its size and complexity. For smaller initiatives, a single project manager with a small team might suffice. However, in enterprises where multiple projects run simultaneously, a diverse group of professionals is required to ensure success.
In such cases, firms establish a project management office (PMO). It acts as a central hub that provides structure, governance, and oversight to ensure projects are executed efficiently. Moreover, the PMO typically comprises project managers, program managers, portfolio managers, PMO analysts, etc., who work collaboratively to drive project and business success.
Now that you know the project lifecycle and who manages it, let’s understand the phases of a project management process.
The 5 Phases of The Project Lifecycle
The project lifecycle consists of five crucial phases that play a lead role in helping the project manager and the concerned team achieve the goals set in the project.
Project Initiation
Initiation is the first phase of the project lifecycle in which the objectives and deliverables are defined. At this stage, the client requirements are collected, project stakeholders are identified, and essential project elements such as the scope, timeline, and budget are determined. Below are the key documents that are created during the initiation phase.
- Project Charter: It is a formal document that authorizes a project and defines its objectives, scope, and key stakeholders.
- Business Case: It is a document that justifies a project by demonstrating its benefits or necessity.
- Feasibility Study: This comprehensive evaluation determines a proposed project’s practicality and financial viability.
- Stakeholder Register: It identifies all the stakeholders involved in the project, their interests, influence level, communication requirements, and expectations.
- Project Kickoff Meeting Agenda: It provides insights into the project overview, roles and responsibilities of the team, key milestones, timelines, and communication protocols.
Read More: Project Initiation: Nine Effective Steps to Kick-off Projects the Right Way
Project Planning
The second phase is the planning stage, where a roadmap is created detailing how the project will be executed, monitored, and controlled. Proper planning minimizes uncertainties during execution and ensures that the project aligns with its original objectives. Below are the critical activities and documents that shape the project planning phase.
- Project Goals: Managers establish SMART (Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic, Time-bound) goals that align with the project’s outcome.
- Project Scope Document: It defines all the elements of the project scope along with its objectives, schedules, tasks, and deliverables.
- Stakeholder Management Plan: This document outlines how to engage with project stakeholders and includes a strategy for managing stakeholder conflicts and issues.
- Resource Management Plan: It defines the resource requirements of the project. Moreover, it outlines how resources will be allocated, optimized, and managed throughout the lifecycle.
- Budget Management Plan: This plan outlines the process of estimating, allocating, and monitoring the costs associated with a project.
- Change Management Document: This document summarizes the formal process for handling change requests systematically without disrupting the overall project.
- Risk Management Plan: It details how to identify, assess, categorize, and mitigate potential project risks.
Project Execution
In the execution phase, the project manager and the team implement the project plan. The most critical and fundamental part of this phase is maintaining and controlling the communication flow among the resource pool and project stakeholders. Major activities during this phase are:
- Tasks Assignment & Execution: Here, project managers allocate resources to suitable tasks based on their roles, skills, availability, and expertise. It also involves executing the tasks sequentially based on the project schedule and work breakdown structure (WBS).
- Managing Change Requests: Project managers accommodate change requests through a formal process that involves a Change Control Board.
- Mitigating Risks: The project team proactively monitors risks identified during the planning phase and implements appropriate mitigation and contingency plans to control them.
- Team Collaboration: Project managers, team members, and stakeholders must collaborate effectively to ensure deliverables and milestones are completed on time and as per expectations.
Read More: 10 Ways to Improve Cross-Departmental Collaboration
Project Monitoring & Controlling
The controlling and monitoring phase runs in parallel with the execution phase. It involves regularly monitoring KPIs such as project performance, deliverable quality, and costs. This phase allows project managers to intervene promptly, make adjustments, and maintain alignment with the project’s goals, budget, and timeline. The major steps involved in this phase are:
- Tracking Project Performance: It is done by measuring project progress against the plan using metrics like Scheduled Variance (SV), Cost Variance (CV), and Earned Value (EV).
- Assuring Quality: Managers can conduct regular reviews and implement quality control measures to ensure project work meets pre-defined standards.
- Communicating Updates: By creating project management reports managers can share project statuses, workloads, variance, etc.
- Taking Corrective Actions: Managers can implement corrective measures to address deviations from the project plan (e.g., reallocating resources or adjusting timelines).
- Conducting Regular Meetings: Project managers organize regular review meetings with clients and stakeholders to ensure deliverables align with their expectations.
Project Closure
The closing stage is crucial in the project’s lifecycle as it indicates the project’s official completion. Here, managers emphasize the final delivery and ensure that all the project deliverables are completed and approved by stakeholders. Then, resources are released from the project towards the end. Moreover, project managers also analyze the biggest wins and losses as a part of learnings that can be applied to future projects.
- Completing Project Deliverables: This ensures all the project deliverables and objectives outlined in the project scope are completed and delivered.
- Conducting Final Evaluation: It assesses the overall project performance against key criteria such as scope, time, and budget.
- Obtaining Stakeholder Acceptance: This presents the final deliverables to stakeholders and securing formal approvals.
- Documenting Lessons Learned: This document comprises feedback, lists challenges faced during execution, and highlights improvement opportunities for future projects.
- Close Contracts & Financials: This step ensures the deals with contractors/external vendors are closed and invoices are correctly settled.
- Archive Project Documentation: It involves storing all key documents such as project plans, scope documents, and reports to be used as references for future projects.
- Releasing Project Resources: This process releases the team members from their existing roles and transitions them to other projects.
Read More: Mastering Project Resource Management: A Comprehensive Guide
Now that you’ve got a comprehensive view of all project phases, let’s delve deep into the different types of project lifecycles in detail.
Types of Project Lifecycle
Depending on the organization, there are different types of project lifecycles that a company can follow to achieve the desired outcome. Primarily there are five types of project lifecycles as mentioned below:
Predictive Lifecycle
The predictive lifecycle is also called plan-focused or plan-driven. In this lifecycle, the scope, time, and costs are defined at the beginning of the project. Here activities of the project follow a sequential approach, which implies that one phase leads into the next phase and so on. Hence, predictive development tends to be the best for static/simple projects.
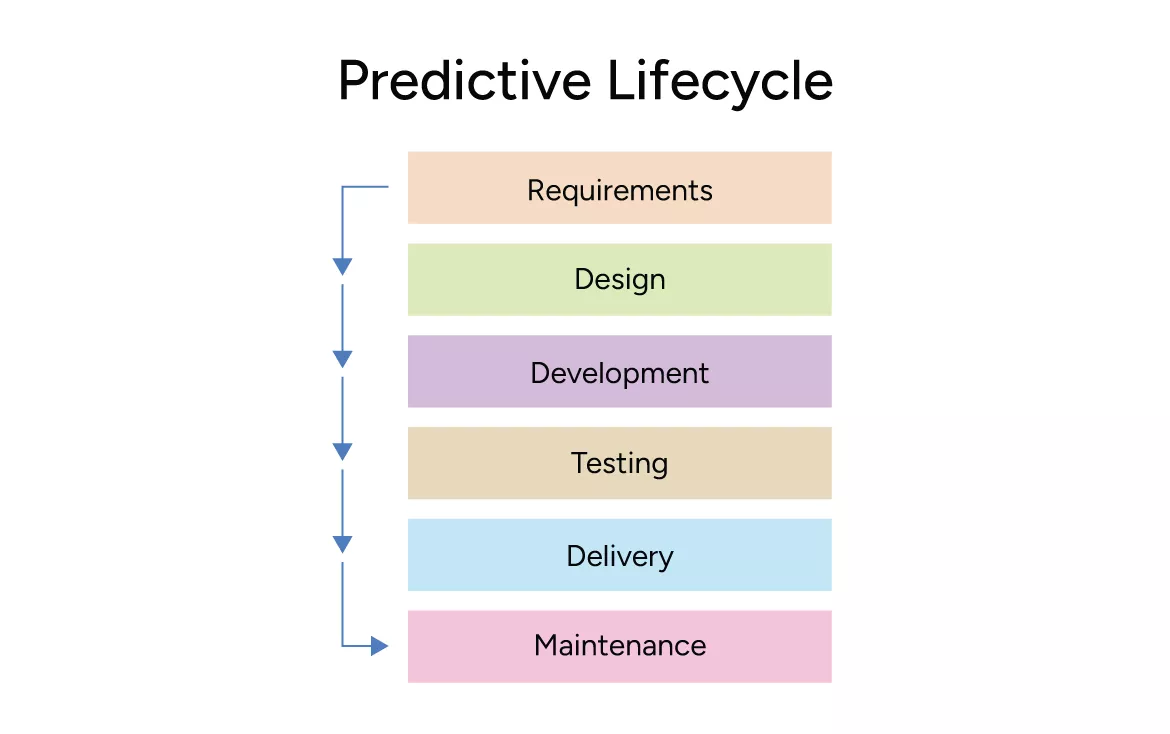
The Waterfall Model is a linear and sequential software development methodology in which progress flows in one direction, through distinct phases.
Iterative and Incremental Lifecycle
In iterative or incremental lifecycles, the events of the project are repeated in phases or iterations. It takes a project sequentially or overlappingly by a sequence of repetitive loops. In comparison, an incremental lifecycle adds a functionality feature at each iteration. This lifecycle is often used for large and complex projects, which allows input and improvements to be incorporated throughout the process.
Agile or Adaptive Lifecycle
This project lifecycle is also called a change-driven or agile lifecycle. In an adaptive lifecycle, like SCRUM or KANBAN, the project is developed over multiple iterations. Here, iterations are more rapid and take place at fixed intervals and at a cost. It is majorly used in IT projects or to build software applications that experience fast-paced changes.
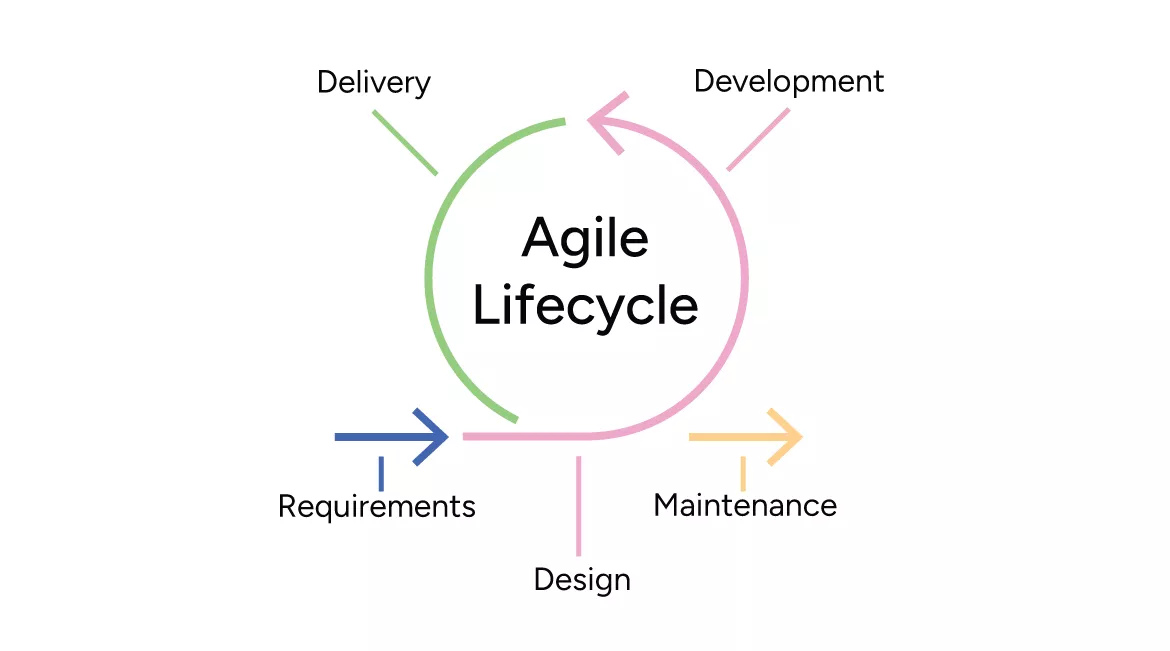
The Agile Lifecycle is an iterative and incremental approach to software development that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and continuous improvement.
Hybrid Lifecycle
The hybrid lifecycle model blends principles and best practices from two or more project management methodologies. This style of lifecycle fits the best for firms that are looking for a flexible and adaptive approach. Moreover, it helps them to harness the robustness of various methodologies that suit the best interest of their project.
Now that we have understood the different types, let us explore the project lifecycle in depth with an example.
Project Lifecycle Example: An Overview
Let’s assume your construction company won a contract to design and build the international corporate office in the U.S. Now, what will be your approach as a project manager?
At the project’s initiation phase, managers create a Project Initiation Document (PID) that will focus on defining the scope, timeline, budget, and the right team to execute this project. During the planning phase, project managers will answer the following questions:
- What needs to be done?
- Who must do what?
- What will be the duration of each task?
- How much is the project going to cost?
- What are the potential bottlenecks, and how do we manage them?
The resource planning and scheduling resources are also carried out under WBS. At the end of the planning phase, the project draft proposal is presented to stakeholders to obtain permits and approvals.
Then comes the execution phase, where most of the resource time is spent to achieve the scope of work (SoW). From setting up brick and mortar to building an office cubicle, all construction operations are carried out.
In the closing phase, the newly constructed corporate office is handed over to the client. Project managers then report the final documents of project delivery and inform stakeholders about the project’s closure.
Many essential aspects must be taken care of to finish a project successfully. Therefore, using a multi-dimensional resource scheduling tool and following the project phase framework will help prevent risks and ensure quality delivery.
With a clear understanding of the project lifecycle from an example, let’s move on to its importance in project management.
Why is Project Lifecycle Management Important?
The project lifecycle plays an important role in project management. Imagine working on a project without a specific purpose or goal. Or assume working in a siloed work environment leads to management chaos? Odd, isn’t it?
The project lifecycle provides a systematic strategy that specifically outlines each project’s tasks and output. It also enables managers to monitor the progress of the project and review tasks that are completed in each phase.
In addition, the project phase framework also helps in defining roles and responsibilities in each phase and enhances communication among project resources. It makes project managers recognize risks and constraints and plan well in advance.
Now that we have understood the importance of project lifecycle management, let us explore the challenges project managers face while managing a project.
Challenges in Managing the Project Lifecycle
Project managers often face various challenges in managing the project lifecycle. Below are some of the key difficulties they encounter.
Scope Creep
As per PMI reports, ‘34% of projects globally were impacted by scope creep, and only 55% were completed on time.’
Scope creep is one of the most common project management lifecycle challenges. This often happens due to evolving stakeholder expectations, unclear initial project scope, or a lack of proper documentation. As a result, scope creep can lead to increased costs, resource strain, and project delays, making it difficult to maintain control over the original objectives.
Read More: 7 Effective Strategies to Avoid Scope Creep in Project Management
Unclear Task Dependencies
Poorly defined task dependencies create confusion in project execution, making it difficult for teams to determine the correct sequence of work. This often results in bottlenecks, delays, and misaligned priorities. Team members may unknowingly wait on unfinished tasks or proceed with work out of order, leading to unnecessary rework, schedule delays, and reduced productivity.
Inaccurate Resource Estimation
Inaccurate resource estimation can stem from a lack of historical data, unrealistic assumptions, or inadequate involvement from subject matter experts. Overestimating resources leads to unnecessary costs, while underestimating them results in workload imbalances, burnout, and missed deadlines. Ultimately, wrong resource estimation can disrupt the project workflow or escalate the budget, increasing the likelihood of failure.
Read More: Effective Strategies for Resource Estimation in Project Management
Poor Budgeting
A poorly planned budget can put a project at risk of financial strain, leading to cost overruns or funding shortages. Factors such as unforeseen expenses, fluctuating costs, and inadequate financial forecasting often contribute to such budgeting issues. Misallocation or insufficient funds may force project managers to reduce the scope or compromise quality. This can lead to demand for improvement from the stakeholder’s end, which can impact the lifecycle and can even derail the entire project.
Insufficient Risk Analysis
Inadequate risk assessment occurs when project managers overlook potential threats and neglect to follow a proper risk management process. This results in unexpected disruptions that can surface at any phase of the project’s lifecycle. As a consequence, the team turns to reactive crisis management, leading to hasty decision-making, delayed deadlines, increased costs, and strained resources.
Read More: Enterprise Risk Management Framework: 8 Core Components
Compromised Project Quality and Delivery Delays
Project quality and delivery delays mainly arise from resource shortages, inadequate testing, and rushed work. When deliverables fail to meet defined quality standards, it often results in rework affecting resource plans, incurring additional costs and unnecessarily extending the project lifecycle.
Inadequate Stakeholder Communication
Major information gaps arise when project managers fail to provide regular updates and ignore stakeholder concerns. This often gives rise to issues such as delayed approvals, conflicting priorities, defects, and rework. Consequently, it can cause reduced support and dissatisfaction with the final deliverables. Ineffective communication can even escalate to project failure and damage to the company’s reputation.
Read More: Who are Project Stakeholders and How to Manage Them Efficiently?
Now that we have understood the challenges faced while managing a project, let’s move on to the best practices to consider while managing one.
Best Practices to Effectively Manage the Project Lifecycle
Following best practices in project lifecycle management ensures efficiency, minimizes risks, and enhances project success. Here are some key practices to effectively manage each project lifecycle phase.
Define Project Goals & Scope at the Outset
The first step to ensuring an undisrupted lifecycle is to define the project’s goals and objectives. A well-defined scope helps prevent scope creep, ensuring that project resources, timelines, and deliverables remain manageable. On the other hand, by setting measurable objectives and aligning them with business goals, teams can create a strong foundation for successful execution.
For this, project managers should engage key stakeholders in initial discussions to define requirements, expectations, and success criteria. A formal project charter or scope document can serve as a reference point throughout the project, ensuring that all team members remain aligned and accountable.
Read More: What is a Project Scope? Benefits, Best Practices, and Steps to Create an Effective One
Establish Clear Milestones, Tasks, and Dependencies
Setting clear milestones is quintessential for effectively managing the project lifecycle. Project milestones are a checkpoint for tracking the project’s ongoing status at every phase. It helps the team track project progress and ensure all tasks are completed within the set timeline.
Another essential thing to be taken care of for a seamless lifecycle is the creation of tasks and sub-tasks. Defining tasks and sub-tasks and establishing their dependencies, help project managers convert complex projects into smaller workable components. As a result, it becomes easier to accomplish the deliverables.
Utilize Past Project Data for Accurate Resource Estimations
Project managers can always leverage past project data for resource estimation. By carefully observing the number of human and non-human resources required in similar past projects, they can come across several valuable benchmarks. This data can help managers enhance the accuracy of resource forecasts for current projects.
Moreover, they must use advanced forecasting techniques to understand recurring trends and patterns, allowing them to identify setbacks such as skill shortages, unplanned absenteeism, and resource overutilization before escalating.
Read More: How Can You Make Data-Driven Decisions with Resource Management Software?
Track Financial Indicators Periodically
Financial indicators are quantitative measurements that help businesses understand the project’s financial health. These metrics allow managers to assess the project expenses and gauge whether they are within the pre-defined criteria. Therefore, managers must calculate and regularly track parameters such as Planned Value (PV), Actual Costs (AC), and Earned Value (EV).
By periodically tracking these financial indicators, managers can detect deviations early on and take the necessary actions accordingly. As a result, it helps keep the project budget under control, enhance stakeholder confidence, and support overall delivery success.
Develop a Structured Risk Management Plan
Managers must develop a comprehensive risk management plan to identify, analyze, and mitigate potential risks that could derail the project’s progress. The plan should include key components such as risk identification methods, qualitative and quantitative risk analysis, response strategies, and contingency planning.
Project managers can use tools such as risk registers, probability-impact risk matrices, and mitigation strategies to categorize, prioritize, and manage constraints effectively. Additionally, they must assign specific team members as risk owners and clearly define their roles and responsibilities for mitigating each identified risk. Lastly, they must conduct regular risk reviews and updates to ensure that the plan remains relevant throughout the project lifecycle.
Read More: Risk Matrix in Project Management: An Ultimate Guide
Monitor and Optimize Team Utilization
Tracking project team utilization levels periodically is critical to ensure optimal productivity and timely task execution throughout the project lifecycle. It involves tracking how much time team members spend on various project tasks and monitoring their overall workloads. This allows managers to take corrective actions to optimize team performance and prevent instances of underutilization or employee burnout.
Besides, project managers can leverage resource management tools to gain real-time insights into employee utilization levels. These advanced software solutions have embedded timesheets that enable managers to gauge individual productivity. Furthermore, it allows them to compare planned vs. actual work hours, identify variances, and implement measures to rectify it.
Create a Comprehensive Communication Strategy
A well-structured communication strategy serves as a structured approach to ensuring that all stakeholders receive timely, relevant, and clear information throughout the project’s lifecycle. It outlines the key communication objectives, target audiences, preferred communication channels, frequency of updates, and responsibilities of team members in disseminating information.
Moreover, the communication plan should account for varying stakeholder needs, ensuring that information is tailored to different audience groups, such as executives, teams, clients, and external partners. It must incorporate a mix of synchronous (meetings, video conferences) and asynchronous (emails, reports, dashboards) communication modalities to facilitate seamless information flow.
Let us now look into how a robust resource management tool can assist during a project lifecycle.
Read More: Why Project Communication Skills are Important and How to Master Them?
How Does Modern Resource Management Software Improve the Project Lifecycle?
SAVIOM’s next-gen resource management software can help project managers streamline resource planning, optimize utilization, and gain better control over the project lifecycle. Here’s how:
- 360-degree Resource Visibility: Provides details into the current and future schedules, allowing managers to plan efficiently for upcoming phases.
- Resource Forecasting & Capacity Planning: Allows managers to foresee future project demands, identify capacity vs demand gaps, and take proactive measures.
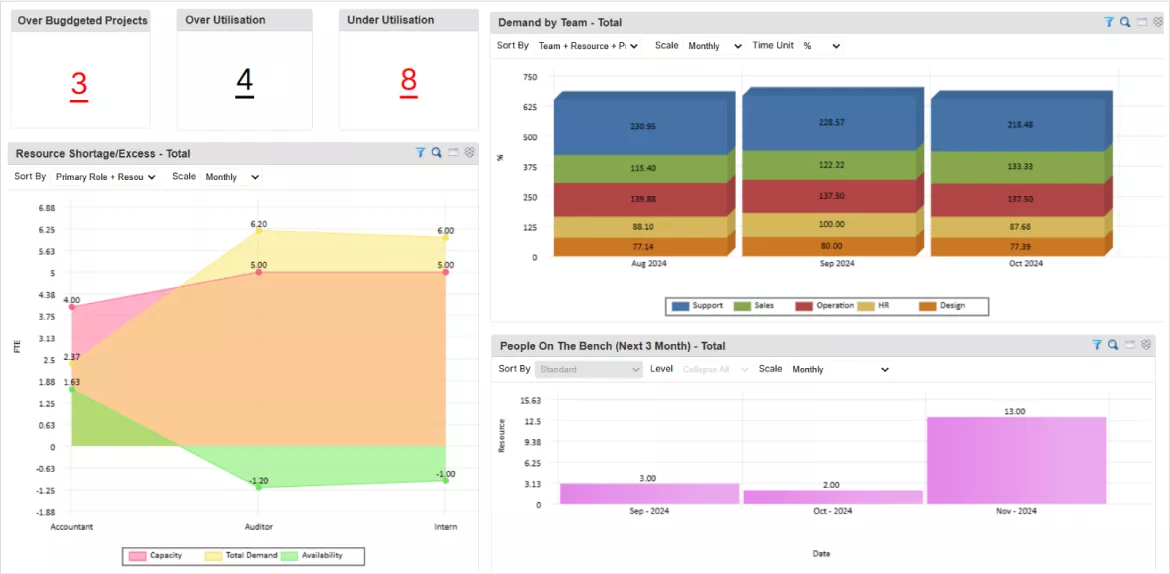
SAVIOM’s Real-time BI dashboard provides critical insights that help streamline resource planning and ensure on-time project delivery.
- Multi-Dimensional Scheduler: Helps managers allocate the best-fit resources from low-cost locations to keep project costs in check.
- Real-time BI Reports: Offers insights into resource utilization and availability to prevent underutilization or overallocation and keep the project on schedule.
- Competency Matrix – Maps employee skills and proficiency to assign the most suitable team members to tasks and prevent resource-related challenges in the project lifecycle.
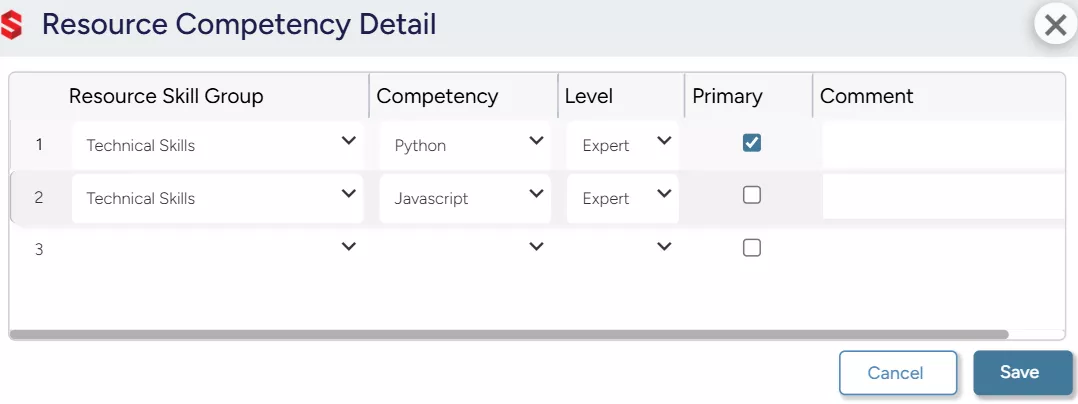
SAVIOM’s Competency Matrix allows firms to store, update, and track resource skills, qualifications, and competencies on a centralized platform.
- Timesheets – Tracks the time spent on tasks, helping to monitor the efficiency of the resources and overcome productivity bottlenecks.
- What-if Scenarios – Helps simulate and compare scenarios to create the best-fit resource capacity plans, maximizing the potential of existing resources.
Read More: How Outdated Resource Management Tools are Hurting Businesses?
Now, let’s quickly look into some takeaway tips to manage the project lifecycle effectively,
Key Takeaway: Additional Tips
In a nutshell, a well-structured lifecycle ensures projects stay on track, within budget, and aligned with business goals. By effectively implementing the best practices mentioned above, teams can work productively, overcome risks, and improve project execution.
Here are some add-on tips that managers can follow to further optimize the project lifecycle and ensure successful delivery:
- Summarize the objectives and deliverables of a project in a project charter.
- Outline project risks, dependencies, constraints, and priorities in a project plan well in advance.
- To get real-time status reports of all the project activities, use a project resource management tool.
- To see the whole project at a glance, use Gantt Charts to list all tasks over a project schedule.
- After the closure of a project, managers document the information they have gathered and knowledge gained to use it for similar future projects.
How do you handle the project lifecycle in your organization?
The Glossary
Read More: Glossary of Resource Workforce Planning, Scheduling and Management