Imagine you’re managing a growing team and need to determine how many employees you truly require to complete an upcoming project efficiently. You have part-timers, full-timers, and contractors, all working in different hours. The challenge lies in calculating your workforce capacity accurately to meet the project’s deadlines.
This is where the concept of Full Time Equivalent (FTE) becomes crucial. It offers a standardized way to measure workforce capacity, regardless of employment type, allowing for more precise planning, budgeting, and resource management.
But how exactly does Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) work?
Read this blog to explore the answers and understand the nitty-gritty of full-time equivalent (FTE) in detail.
But first, let’s define FTE.
What is FTE (Full-Time Equivalent)?
Full-time equivalent (FTE) is a unit of measurement that represents an employee’s workload in relation to a standard full-time position. It is the hours worked by a single employee on a full-time basis, regardless of whether they are permanent, part-time, or temporary staff. An FTE of 1.0 typically means a person is working typical full-time hours, while an FTE of 0.5 indicates a half-time workload. Organizations use FTE to plan and manage their workforce more optimally.
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) is mostly suitable for large-scale projects extending over months, as it eliminates the need to calculate work hours and headcount separately. For example, FTE is ideal for engineering and construction projects due to their complex and prolonged nature. These projects often involve managing diverse teams and long-term resource needs.
Full Time Equivalent (FTE) Formula
Managers can calculate Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) using the following formula:
| Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) = Total Number of Hours Worked by Employees / Number of Available Full-Time Hours |
|---|
Full-Time Equivalent Chart: 40-Hour Work Week
Here’s a chart displaying the number of weekly hours worked and the corresponding full-time equivalent (FTE) based on a standard 40-hour workweek –
| Weekly Hours Worked | FTE (Based on 40-Hour Workweek) |
|---|---|
| 40 | 1.00 |
| 35 | 0.88 |
| 30 | 0.75 |
| 25 | 0.63 |
| 20 | 0.50 |
| 15 | 0.38 |
| 10 | 0.25 |
| 5 | 0.13 |
Now that we have taken a look at the FTE explanation, let us understand the difference between full-time equivalent (FTE), headcount, and work hours.
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) vs. Headcount vs. Work Hours
The following table compares FTE, headcount, and work hours to highlight their distinct roles and approaches. Here’s a detailed comparison –
| Feature | Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) | Headcount | Work Hours |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | FTE measures the total hours employees work relative to a standard full-time work schedule. | Headcount simply counts the number of employees regardless of their work hours. | Work hours measure the exact amount of time employees spend working. |
| Use Case | Used for budgeting, resource planning, and resource allocation. | Helpful for basic staffing and payroll calculations. | Used for payroll, attendance, and time tracking. |
| Flexibility | Accounts for different employment types (full-time, part-time, temporary). | It does not differentiate between employment types; it simply counts all employees. | A part-time employee works 20 hours, while a full-time employee works 40 hours per week. |
| Example | Two part-time employees working 20 hours each = 1 FTE. | Two part-time employees = headcount 2. | Provides a detailed breakdown of individual employee work patterns. |
Now, let us go through the benefits of Full-Time Equivalent (FTE).
What are the Benefits of Full-Time Equivalent (FTE)?
Understanding Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) offers several significant advantages for organizations looking to optimize their workforce management. Some FTE benefits are listed below:
Improves Project Management
The FTE model provides a standardized approach for calculating resource demands for future projects and the number of hours required to accomplish tasks. For example, if your project needs 400 work hours, you can equate it to 9.41 FTE (400/42.5 hours) for five days. Accordingly, you can hire nine full-time and one part-time worker to fulfill the project demand. Hence, it enhances the project management process.
Read More: How to Manage Resources in Agile Project Management?
Provides an Accurate Understanding of Workforce Composition
Unlike headcount, full-time equivalent (FTE) considers both full-time and part-time workers within the organization. This comprehensive view allows businesses to decide when to hire part-time or full-time employees. By hiring the right professional, organizations can control project resource costs and ensure a smooth organizational workflow. This strategic approach helps optimize staffing levels.
Evaluates Role-Based Capacity
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) tracking enables you to assess the total capacity of employees based on their roles. For instance, if you have 20 content writers, each working at 0.7 FTE, their combined capacity totals 14.0 FTE. This aggregate FTE figure allows for precise role-based resource management and task allocation. This way, you can effectively match resources to various project needs
Read More: What is Resource Capacity Planning? An Ultimate Guide for Every Project Manager
Ensures Uniform Workload Distribution Among Employees
Using the FTE model, managers can ensure that tasks are distributed evenly among the team members. For example, in the network operations department, the FTE of 3 employees are 1.70 FTE, 0.34 FTE, and 0.45 FTE. By scheduling resources on tasks based on FTE, managers can ensure that each employee’s workload is proportional to their capacity. This approach helps prevent overburdening or underutilizing staff, leading to optimal utilization levels.
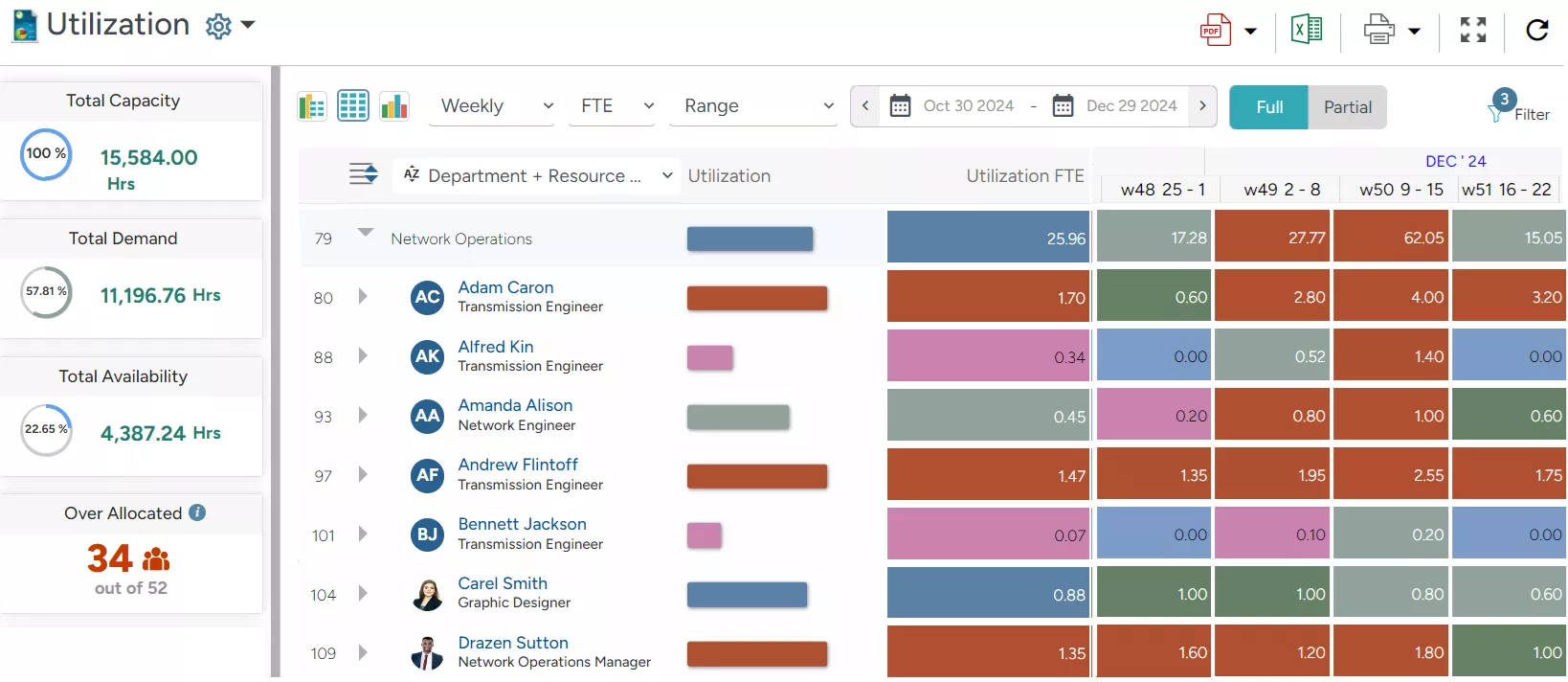
SAVIOM’s Embedded Heatmap provides managers real-time visibility into resource utilization levels across various units, including FTE, enabling them to optimize workload accordingly.
Helps Evaluate Employee Performance
The full-time equivalent (FTE) model aids in evaluating employee performance by providing a clear view of each individual’s workload and contribution. By comparing actual output against their FTE allocation, managers can assess productivity and identify areas for improvement. This approach enables more accurate performance reviews, helping to align employee efforts with organizational goals and fostering targeted development plans.
Read More: What is Employee Performance Management and Why is It Important
Facilitates Compliance with Labor Regulations
The FTE model supports compliance with labor regulations by offering a standardized method for tracking work hours and employment status. It helps ensure that employees are classified correctly, whether full-time or part-time, and that their work hours align with legal requirements. This systematic approach reduces non-compliance risk and safeguards the organization against potential legal issues.
As we’ve explored the benefits, let’s move on to the next section to learn how to calculate full-time equivalent (FTE) effectively.
How to Calculate FTE?
As discussed earlier, full-time equivalent provides a standardized measure of employee work hours, allowing businesses to understand and optimize their staffing levels.
Key Steps to Calculating Full-Time Equivalent (FTE)
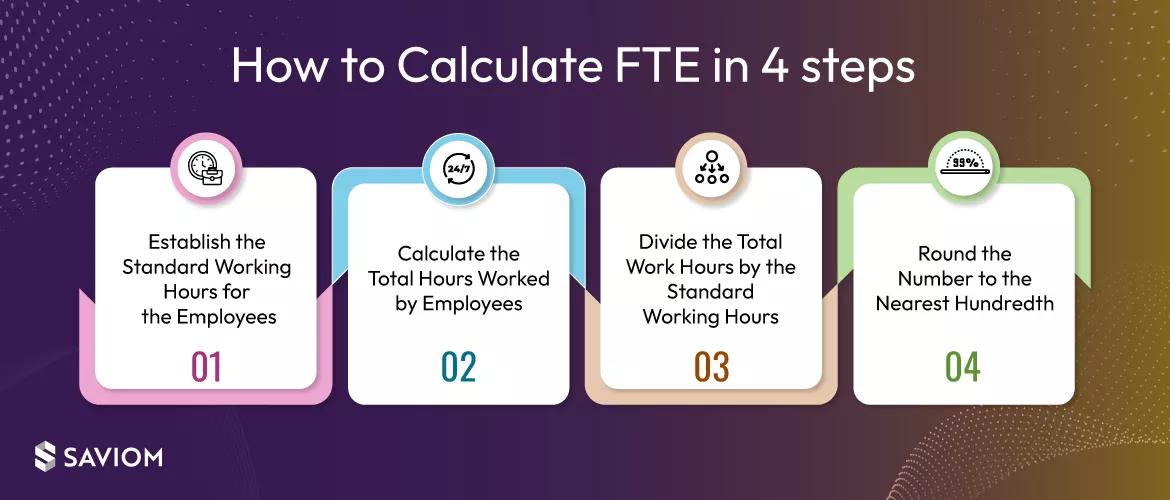
Let’s now delve into the step-by-step process of calculating FTE.
Establish the Standard Working Hours for the Employees
To calculate the full-time equivalent for a full-time employee, firms must first determine the standard working hours within a specific period, i.e., weekly, monthly, or annually. This typically represents the benchmark for calculating FTE and may vary by industry or company policies.
Calculate the Total Hours Worked by Employees
To accurately calculate FTE, it is imperative to sum up the actual hours worked by all employees within the specified period. This includes both full-time and part-time employees. Accurately tracking these hours provides a comprehensive view of the workforce’s total effort.
Divide the Total Work Hours by the Standard Working Hours
Now, one must divide the total hours worked by the standard number of hours in a full-time work week. This calculation converts the total work effort into FTE units, providing a standardized measure of workforce capacity.
Round the Number to the Nearest Hundredth
Depending on the calculation, you may obtain a decimal value. To simplify and manage the number, round it to the nearest hundredth. For example, if your FTE calculation results in 4.876, you would round it to 4.88 FTE. This ensures that the FTE value is accurate and practical for reporting and decision-making purposes.
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) Calculation Example
If an organization follows a 42.5-hour work week (equivalent to 1 FTE), employees are scheduled to work 8.5 hours a day for five days each week.
Let’s say you have three full-time and two part-time employees working three days a week. The total hours worked by all employees would be calculated as follows:
- Full-time employees: 3 employees × 42.5 hours = 127.5 hours
- Part-time employees: 2 employees × (3 days × 8.5 hours/day) = 51 hours
- Total weekly hours for all employees: 127.5 + 51 = 178.5 hours
Now, divide the total hours worked (178.5 hours) by the standard 42.5-hour work week:
178.5 hours ÷ 42.5 hours = 4.20 FTE
This means that within your organization of 5 employees, you have the equivalent of 4.20 full-time employees working on the projects.
Now, let’s shift our focus to how to calculate FTE for various types of employees in detail.
How Do You Calculate FTE for Various Employee Types?
Calculating FTE isn’t a one-size-fits-all process, as different employee categories, such as full-time, part-time, contingent workers, etc., require unique approaches.
Let’s delve into the intricacies of their FTE calculations.
FTE for Part-Time Employees
To calculate FTE for part-time employees, follow these steps:
Determine Standard Full-Time Hours: For this example, the standard full-time workweek is 42.5 hours.
Calculate Individual FTE: Divide each part-time employee’s weekly hours by the standard full-time hours:
- Part-time employee 1: 25 hours per week
- Part-time employee 2: 20 hours per week
- Part-time employee 3: 15 hours per week
Total hours worked by all part-time employees: 25 + 20 + 15 = 60
Compute Total FTE: Divide the total part-time hours by the standard full-time hours:
FTE = 60 hours / 42.5 hours = 1.41
Rounded to the nearest hundredth, the total FTE for part-time employees is 1.41.
FTE for Full-Time Employees
Generally, the FTE for full-time employees is equivalent to 1. However, if the FTE is greater than one among full-time employees, it likely means that the organization is paying overtime. If their FTE is less than 1, the firm is paying for additional costs that they may not have to with better resource planning.
To calculate FTE for full-time employees:
Standard FTE: Generally, the FTE for full-time employees is 1.0.
Calculate Total FTE: For five full-time employees, each working 42.5 hours per week:
- Total hours worked: 5 employees × 42.5 hours = 212.5 hours
- Divide by standard full-time hours: 212.5 hours / 42.5 hours = 5.0
Thus, the total FTE for full-time employees is 5.0.
FTE for Contingent Workers
To calculate FTE for contingent workers:
Determine Weekly Hours: Assess the hours worked by each contingent worker relative to the standard full-time hours.
Compute Individual FTE: For a contingent worker working 30 hours a week:
- FTE = 30 hours / 42.5 hours = 0.705
Rounded to the nearest hundredth, the FTE for the contingent worker is 0.71.
Sum All Contingent FTEs: Add up the FTE values of all contingent workers to get the total FTE for this category.
Read More: What is a Contingent Workforce, and Why is it Important?
By following these steps, organizations can accurately calculate FTE for various employee types, aiding in resource planning, budgeting, and compliance reporting.
Now, let’s go through some additional tips that will help you measure full-time equivalent effectively.
Additional Tips to Measure Full-Time Equivalent (FTE)
- Overtime and Extra Hours: Ensure that any overtime or additional hours are included in the total hours worked to provide an accurate representation of the workforce’s effort.
- Leave and Absences: Adjust for periods when employees are on leave or absent, as this can affect the total hours worked and the accuracy of full-time equivalent calculations.
- Part-Time Definitions: Be consistent with how you define part-time versus full-time status based on your organization’s policies to ensure uniformity in calculations.
- Shift Variations: Account for any differences in shift patterns or varying work schedules, as they can affect the total hours worked and the accuracy of your FTE calculations.
- Temporary or Contract Workers: Include the hours worked by temporary or contract workers if they are part of the resource planning. Adjust their hours based on the standard working hours to reflect their contribution accurately.
- Seasonal Fluctuations: Consider seasonal changes in workload and employee hours. Adjust full-time equivalent calculations to reflect higher or lower staffing needs during peak or trough periods.
Read More: What is Resource Planning, and Why is it Important in Project Management?
Conclusion
In today’s dynamic business landscape, the full-time equivalent (FTE) model is crucial in optimizing workforce management, enabling accurate resource forecasting, and maintaining cost control. By following the steps to calculate FTE effectively, businesses can better understand resource capacity, enhance productivity, minimize overheads, and drive profitability.
The Glossary
Read More: Glossary of Resource Workforce Planning, Scheduling and Management














Leave a Reply