Introduction
Most organizations run multiple projects in parallel using shared resource pools, often with limited visibility into workforce availability, skills, and competing priorities. When these factors are not managed systematically, projects face uneven workloads, cost overruns, and delivery delays.
Resource management techniques address this challenge by enabling managers to plan resource needs early, align capacity with demand, and optimize resource allocation. This reduces resource-related risks and improves on-time, on-budget project delivery.
This blog outlines practical resource management strategies to help organizations plan, assign, and manage resources efficiently, thereby improving project outcomes.
Let’s get started!
What are Resource Management Techniques?
Resource management techniques refer to systematic methods used to plan, allocate, and optimize business resources (people, time, finances, and equipment) across projects. They help reduce resource-related risks, control costs, boost resource utilization, and ensure successful project delivery.
In practice, these resource management methods guide how organizations forecast demand, assess capacity, and standardize resource planning and scheduling decisions. This, in turn, helps them improve operational efficiency, protect profit margins, and stay aligned with broader business objectives.
Explore this eBook to learn how 5th generation resource management is changing the way project-based businesses plan and optimize resources.
Moving on, let us explore the 11 essential techniques of resource management every organization must follow to ensure seamless project execution.
11 Resource Management Techniques for Successful Project Execution
Given below are the core project resource management techniques organizations use to plan, allocate, and optimize the talent pool across the project lifecycle.
Resource Planning
Resource planning is the process of forecasting, identifying, allocating, utilizing, and managing business resources to deliver projects successfully and meet organizational goals. It helps minimize resource-related risks, such as talent shortages, skill mismatches, cost overruns, etc., and improve project delivery, optimize the resource lifecycle, and maximize business efficiency.
For instance, a consulting firm anticipates multiple client projects starting in the next quarter, each requiring specific skill sets and experience levels. By assessing demand and capacity in advance, managers can identify capability gaps early and plan redeployment or hiring ahead of time. This prevents last-minute staffing shortages and delivery delays.
Resource Forecasting
Resource forecasting is a critical resource management strategy that involves predicting key resource metrics, such as demand, capacity, utilization, etc., to plan for upcoming work and estimate resource needs early. This foresight provides sufficient lead time to secure the right resources, reduce last-minute firefighting, and support timely project execution.
For example, a product development company forecasts resource demand across upcoming release cycles and identifies a shortage of QA engineers for pipeline needs. With this early insight, managers can choose the most viable response, such as reskilling or hiring, preventing last-minute staffing gaps and delivery delays.
Learn why accurate resource estimation is important for successful project delivery.
Use SAVIOM’s enterprise resource management software to drive better resource utilization, stronger delivery performance, and improved business results. Book a Demo Today.
Resource Capacity Planning
Resource capacity planning focuses on forecasting, analyzing, identifying, and bridging the demand vs. capacity gap proactively and future-proofing the workforce. It also helps firms determine the right mix of permanent, contingent, local, and global resources, enabling them to reduce resourcing costs significantly and drive overall business profitability.
For instance, an engineering services firm reviews its project pipeline and compares available capacity with forecasted demand across roles. After identifying a shortage of structural engineers in the coming months, managers implement the most suitable resourcing plan, such as focused hiring/upskilling to secure the right personnel on time.
Resource Allocation and Scheduling
Resource allocation and scheduling are critical resource management techniques that involve identifying and assigning available resources to current and future projects for a specified timeframe. It ensures that the best-fit resources are assigned to tasks based on critical attributes such as skill sets, availability, capacity, etc., ensuring that organizational assets are used optimally.
For instance, a marketing agency runs multiple campaigns that require the same senior designer during overlapping periods. Through resource allocation and scheduling, managers prioritize high-priority work and shift remaining tasks to later slots, preventing conflicts and ensuring on-time delivery.
Explore our blog on resource scheduling.
Resource Availability
Resource availability focuses on determining when resources are actually available for project work by accounting for leave, holidays, part-time schedules, and non-project commitments. This ensures resource plans reflect actual working capacity rather than assumed availability, enabling realistic assignments and smoother project execution.
For instance, a global consulting firm plans a client engagement during a period when several consultants have approved leave. By factoring actual availability into staffing decisions, managers avoid unrealistic project schedules and reduce last-minute reassignments that could disrupt delivery.
Resource Utilization
Resource utilization refers to how efficiently organizations use their resources to deliver projects successfully. It indicates the percentage of a resource’s available capacity spent on billable or value-adding work. By tracking utilization levels, managers can proactively mobilize resources from non-billable to billable projects, ensuring resources contribute productively to organizational goals.
For example, a professional services firm identifies consultants spending excessive time on non-billable internal work. By reviewing utilization reports, managers reassign them to client-facing engagements, increasing billable contribution and improving overall profitability.
Learn how to optimize resource utilization in easy steps.
Resource Leveling
Resource leveling or resource-constrained scheduling (RCS) is an optimization technique that helps align project timelines with available capacity by adjusting task start and end dates based on resource constraints. This helps prevent workload peaks, reduces burnout risk, and supports sustainable team performance.
For instance, a construction project requires the same site engineer across overlapping phases. When capacity constraints make the original schedule unworkable, the project manager shifts task start and end dates to fit the engineer’s availability. This aligns the timeline with actual capacity, preventing resource overallocation and supporting steady project progress.
Resource Smoothing
Resource smoothing or time-constrained smoothing (TCS) is another optimization technique used to balance workload without affecting the project’s critical path or delivery dates. It involves redistributing tasks within the available float to avoid resource overutilization while meeting fixed timelines. This helps managers prevent burnout and maintain productivity without compromising project quality or schedule.
For instance, a software product team experiences short-term workload peaks during the testing phases; managers shift non-critical tasks that have scheduling flexibility to less busy periods. This enables balanced workload distribution while keeping delivery timelines unchanged.
Explore more about resource optimization techniques.
Scenario Modeling
According to a GoodFirms’ 2025 survey, “34.2% of organizations leverage scenario planning for better forecasting.”
Scenario planning is a simulation technique that helps managers build and test multiple scenarios within a sandbox environment. It enables managers to evaluate each scenario’s outcomes and select the most profitable resource plan. This allows them to plan around existing resource constraints and mitigate their impact, ensuring smoother project execution.
For example, an auditing firm evaluates multiple staffing scenarios during peak compliance season to manage overlapping engagements. By modeling different team structures and schedules, managers can select the most feasible plan that minimizes resource risks before execution begins.
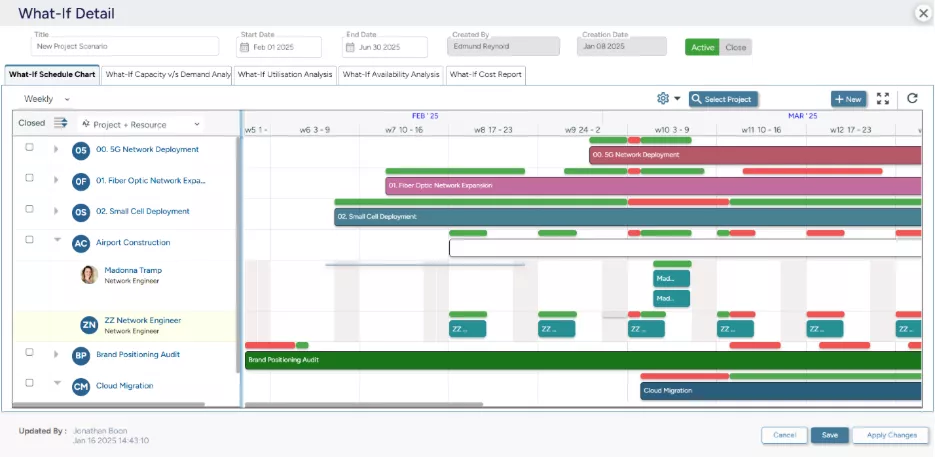 SAVIOM’s What-If Analysis empowers managers to compare various workforce scenarios and select the most favorable & profitable outcome.
SAVIOM’s What-If Analysis empowers managers to compare various workforce scenarios and select the most favorable & profitable outcome.
Skill Tracking
As per The Future of Jobs Report, 2025, “63% of employers feel skill gaps are the biggest barrier to business transformation.”
Skill tracking is a resource management strategy that involves maintaining a centralized repository of employees’ skills, competencies, certifications, and experience. This supports skill-based allocation, plans targeted retraining and upskilling decisions, and addresses capability gaps to ensure seamless project workflows and sustained business performance.
For instance, an accounting firm maintains a centralized skills inventory to track certifications and regulatory expertise. When a complex audit arises, managers quickly identify qualified professionals and plan targeted retraining and upskilling to address gaps without disrupting delivery.
Learn how businesses can use a skill matrix for success.
Time Tracking
Time tracking is the process of recording and monitoring how much time resources spend on tasks, projects, or business activities, including billable and non-billable work. This supports accurate resource planning, cost estimation, invoicing, etc. It also helps improve productivity, prevent revenue leakage, and drive profitability.
For instance, a marketing agency tracks how team members spend time across client campaigns and internal initiatives. By comparing billable vs. non-billable time, managers refine cost estimates, improve billing accuracy, and ensure project budgets remain on track.
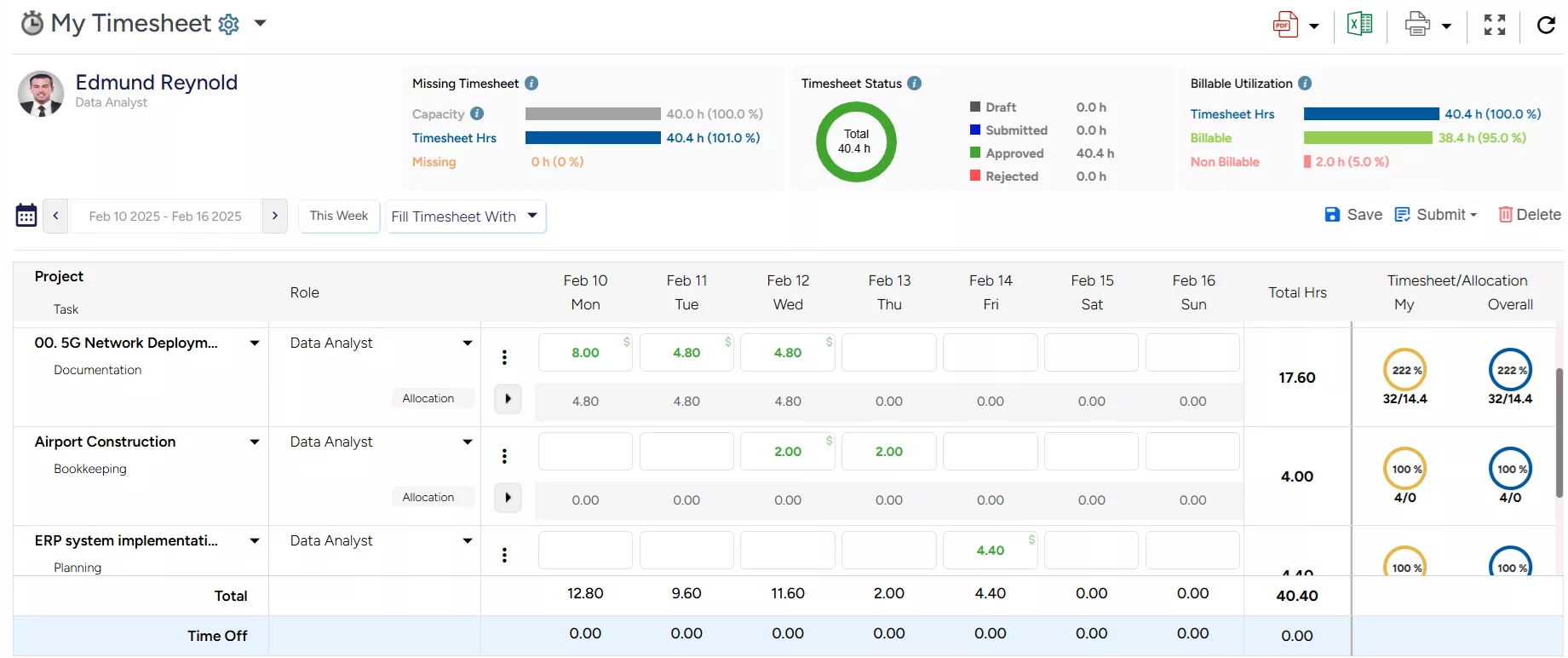 SAVIOM’s Timesheet Dashboard enables managers to accurately track the time resources spend across billable and non-billable work.
SAVIOM’s Timesheet Dashboard enables managers to accurately track the time resources spend across billable and non-billable work.
Now, let’s understand how SAVIOM’s advanced solution empowers organizations to apply these resource management strategies effectively.
How Can SAVIOM Enable These Techniques?
Implementing resource management techniques consistently requires more than spreadsheets or isolated tools. Here’s how SAVIOM’s 5th gen resource management software empowers firms to make smarter resourcing decisions:
- Multidimensional analysis enables managers to assess resources across skills, availability, and utilization to identify the right resources for each task.
- Embedded heat mapping presents utilization in a color-coded manner, enabling early identification of resource over- and underutilization.
- Intelligent match-making helps managers find best-fit resources for each task based on skills, availability, and cost.
- Resource forecasting and capacity planning highlight capacity and demand gaps to identify shortages and excesses early and take corrective measures.
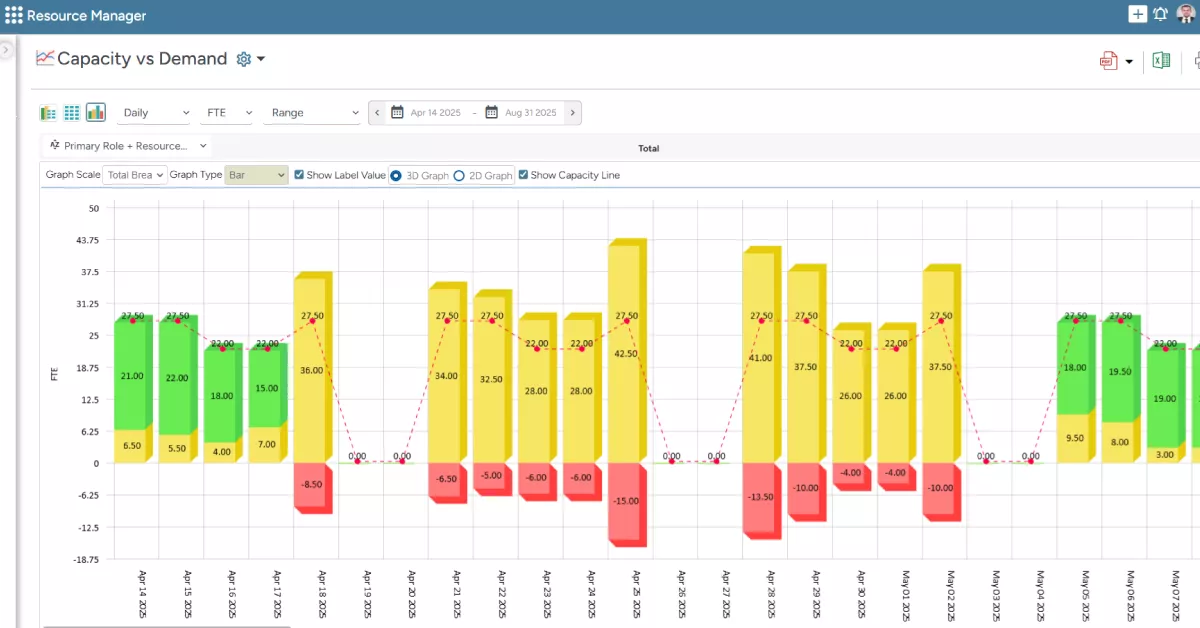 SAVIOM’s Capacity vs. Demand Graph enables managers to identify resource shortages/excesses early and take preventative measures to bridge the gap.
SAVIOM’s Capacity vs. Demand Graph enables managers to identify resource shortages/excesses early and take preventative measures to bridge the gap.
- Resource optimization ensures resources are deployed on billable or high-value work while preventing burnout.
- Competency matrix centralizes skills and certifications to support hiring, training, and upskilling decisions.
- What-if analysis enables managers to simulate and compare scenarios to select the most feasible resource plan.
Conclusion
Resource management techniques serve as the backbone of successful project delivery, ensuring that the right people are utilized at the right time and at the optimal cost. By enabling proactive workforce planning, skill-based allocation, and informed decision-making, these techniques help organizations improve operational efficiency, maximize ROI, and support sustainable business growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Resource management techniques are structured methods for planning, forecasting, allocating, and monitoring resources throughout the project lifecycle to optimize utilization and support predictable project delivery.
Resource management techniques are essential because they help organizations plan, deploy, and control resources more effectively across projects. They reduce delivery disruptions by improving enterprise-wide visibility, balancing workloads, and enabling teams to manage risks, timelines, and costs with greater consistency.
The most effective techniques of resource management include:
1. Resource Planning
2. Resource Forecasting
3. Resource Capacity Planning
4. Resource Allocation and Scheduling
5. Resource Availability
6. Resource Utilization
7. Resource Leveling
8. Resource Smoothing
9. Scenario Modeling
10. Skill Tracking
11. Time Tracking
Organizations should choose resource management techniques based on the type of work they deliver, the level of demand variability, and the decisions they need to support, such as staffing, scheduling, or capacity planning. Techniques should be implemented progressively, starting with forecasting, planning, allocation, utilization, and scenario planning as the project scale and complexity increase.
Resource management techniques support better decision-making by providing real-time visibility into capacity, availability, skills, and utilization. This enables leaders to prioritize work based on actual feasibility, adjust allocations early, and address constraints before they impact delivery.










