Introduction
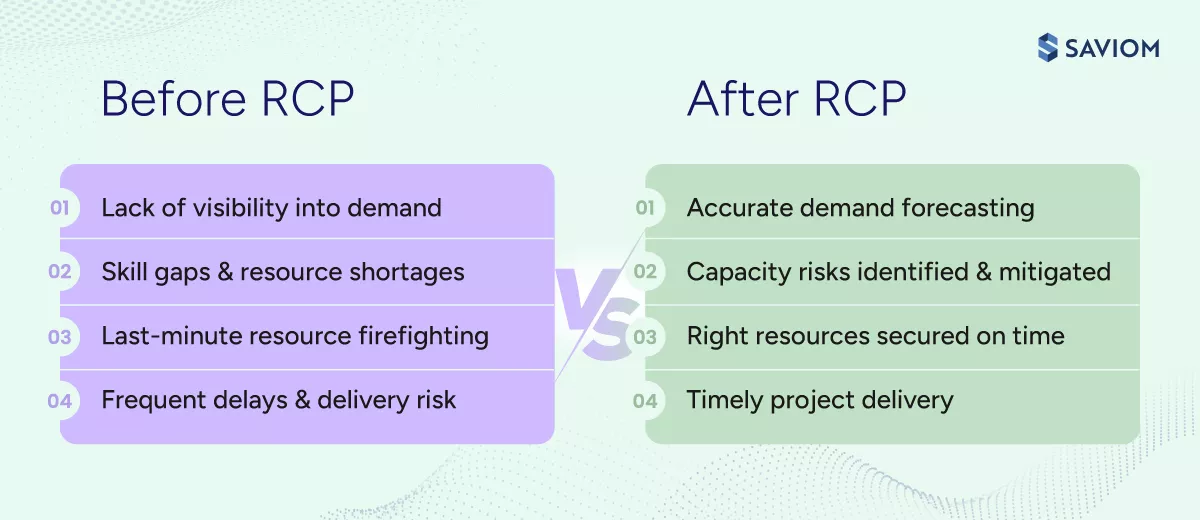
Are you juggling too many projects with too few resources? This often happens when organizations lack clear visibility into capacity or availability, resulting in resource overutilization, delayed project timelines, and subpar deliverables.
Here is where resource capacity planning makes a difference. It enables firms to assess resource capacity and demand and secure resources at the right time and cost.
In this guide, we will break down what resource capacity planning is and how it can help businesses stay competitive and future-ready.
What is Resource Capacity Planning?
Resource capacity planning is the strategic process of assessing an organization’s available capacity, such as people, equipment, finances, and tools, against forecasted project demand. It helps identify capacity gaps early, allocate resources optimally, and ensure timely project delivery.
Resource capacity planning involves a constant balancing act to prevent resource shortfalls that could delay critical project milestones. At the same time, it helps identify excess capacity, allowing managers to reassign underutilized staff to other revenue-generating initiatives. Analysing these capacity gaps enables organizations to make informed staffing decisions, such as hiring or retraining/upskilling to maintain a balanced workforce.
Read this eBook to master resource capacity planning.
Now that we understand the resource capacity planning definition, let us explore its top benefits.
Top Business Benefits of Resource Capacity Planning
Robust resource capacity planning helps businesses plan upcoming projects while futureproofing the workforce against market volatility. Here are some of the key advantages it offers:
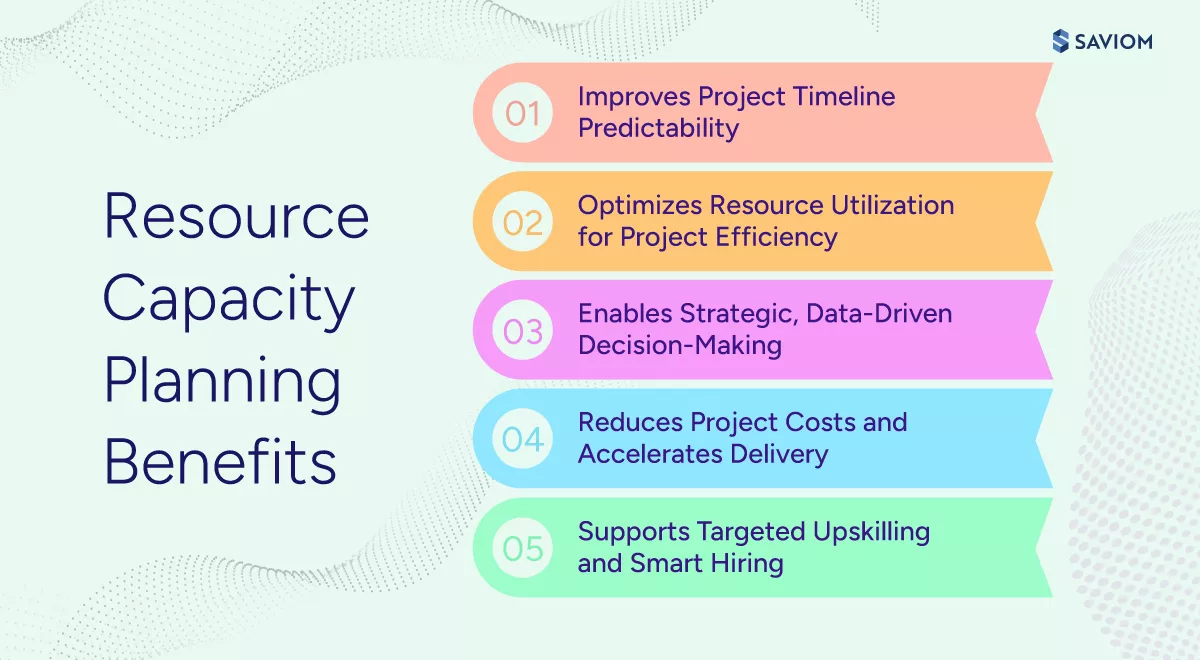
Improves Project Timeline Predictability
With a clear understanding of whether the right capacity and capabilities exist to support planned initiatives, project managers can commit to realistic timelines and reduce the chances of missed deadlines. Moreover, with fewer last-minute allocation and firefighting scenarios, project execution becomes more consistent, ensuring high-quality outcomes.
Optimizes Resource Utilization for Project Efficiency
Optimizing resources means more than just keeping resources busy; it means ensuring they are working on high-value tasks aligned with their skill sets. Effective reduces bench time and prevents burnout from over-allocation, resulting in higher productivity, better employee morale, and improved project outcomes.
Read our blog on resource utilization.
Enables Strategic, Data-Driven Decision-Making
Another pertinent benefit a robust capacity plan offers is shifting decision-making from reactive to strategic. It allows leaders to gain key insights into future skill shortages or surpluses, allowing them to take suitable resourcing measures. This empowers leaders to redeploy resources, upskill existing staff, or pursue strategic talent acquisition to meet current and future demand with greater confidence.
Reduces Project Costs and Accelerates Delivery
One of the key importance of resource capacity planning is that it enables firms to identify resource shortages early and avoid last-minute, expensive hiring. By ensuring the right resources are available at the right time, firms can improve delivery predictability, reduce unnecessary project costs, and accelerate time-to-market.
Supports Targeted Upskilling and Smart Hiring
Ensuring workforce readiness is pivotal for driving long-term business success. Hence, with a practical resource capacity planning framework, organizations can gain early visibility into future skill demands in the coming months or quarters. This enables leaders to prioritize cost-effective retraining/upskilling of current staff or develop a phased, strategic hiring plan, rather than reactive emergency recruitment.
Check out our infographic on key strategies for building a capacity planning model.
Now that we have explored the importance, we shall shift our focus to the role of resource capacity planning in project and portfolio management.
Role of Resource Capacity Planning in Project and Portfolio Management
Resource capacity planning is a decisive lever in project and portfolio management. When leaders have precise visibility into capacity, it becomes easier to commit to timelines, manage risks, and ensure talent is deployed where it creates the most value.
Here are key roles and functions:
- Allocating the Right Resources to the Right Project: It ensures optimum resource allocation based on workforce capability and strategic priority, which directly improves project quality and execution speed.
- Aligning Resource Utilization with Strategic Goal: At the portfolio level, resource capacity planning ensures that critical resources are deployed primarily to projects that deliver the highest client value, strategic impact, and ROI.
- Balancing Capacity Across the Portfolio: Planning resource capacity in advance prevents resource hoarding within a single project or department. It promotes resource sharing and ensures a more equitable workload.
- Proactive Risk Management and Bottleneck Identification: Capacity plans highlight future bottlenecks, such as skill shortages or unavailability, well in advance, allowing managers to mitigate resource risks before they disrupt delivery.
- Cost Forecasting and Budget Adherence: An effective resource capacity plan improves project and portfolio budget accuracy by directly linking planned resource hours to labor rates. This offers leaders clearer cost visibility and supports more informed, smarter investment decisions.
Learn how resource capacity planning can transform project portfolio management.
Next, let’s dive into the steps of the resource capacity planning process.
How to Do Resource Capacity Planning? 7 Step Process
The resource capacity planning process is an ongoing endeavor that helps firms stay aligned with changing business demands. By following these seven practical steps, you can ensure your plan is realistic, proactive, and delivers desired results.
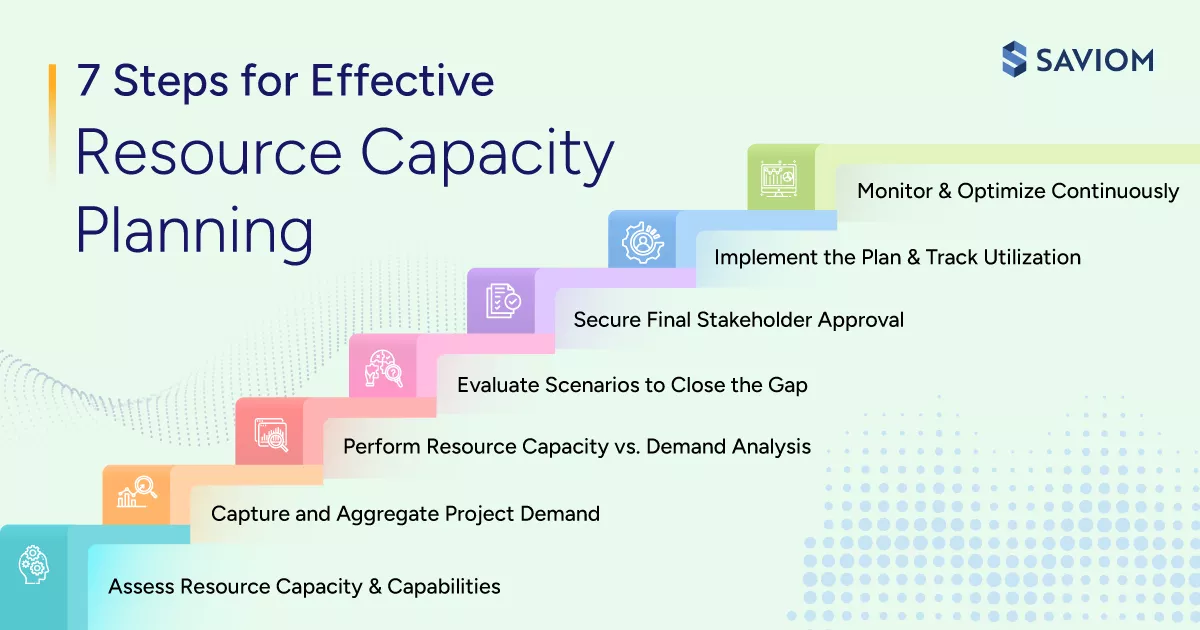
Assess Current Resource Capacity and Capabilities
It is important to calculate productive capacity and review the existing skill inventory to get an accurate picture of current workforce capabilities. Additionally, it’s pivotal to map experience levels, role criticality, and time-offs, so you know not just how many resources you have, but what they can realistically deliver.
Capture and Aggregate Project Demand
The next step is to systematically collect estimated effort (demand) for all projects and consolidate them over the planning horizon (e.g., 12 months). Ensure demand data is broken down by roles, skills, time periods, and more. This level of detail ensures demand can be compared accurately across projects before it is evaluated against available capacity.
Perform a Capacity vs. Demand Gap Analysis
Now, in this third step, you must compare your total capacity against the projected demand to identify any bottlenecks, i.e., resource excess or shortage, in advance. You can analyze gaps by skill, experience, availability, etc. This insight allows you to proactively address resource risks before they impact delivery timelines.
Analyze Scenarios to Close the Gap
Explore various scenario planning options, such as delaying projects, upskilling your team, outsourcing specialized work, or hiring staff to see what best resolves the gap. Evaluate each option by cost, risk, time-to-impact, and long-term workforce strategy to balance short-term delivery with future growth.
Secure Final Stakeholder Approval
Once you have identified the best path forward, document it and get the green light from key stakeholders. Additionally, clearly communicate assumptions, trade-offs, and expected outcomes to avoid misalignment later. Early stakeholders’ buy-in ensures smoother project execution and reinforces shared accountability across teams.
Implement the Plan and Track Utilization
As the sixth step, put the plan into action and continuously track resource utilization against the forecasted value. Track deviations in real-time and investigate root causes behind under-/overutilization. This visibility enables quick course correction before small variances turn into critical productivity risks.
Monitor and Optimize the Process
Review and optimize the process regularly (monthly or quarterly) to keep resource capacity planning aligned with business priorities. Use insights from actual execution to improve the next planning cycle. Over time, this continuous optimization strengthens planning accuracy and organizational agility.
Explore how capacity planning helps firms stay resilient and beat market volatility.
Use SAVIOM’s resource capacity planner to forecast and bridge the capacity vs. demand gap ahead of the curve to futureproof your workforce. Book a Demo Today.
Now that we’ve covered the resource capacity planning process, let us explore key KPIs that help quantify performance, identify gaps, and drive continuous improvement.
Critical Resource Capacity Planning KPIs and Metrics
Tracking the right KPIs helps organizations evaluate and improve the effectiveness of their capacity planning process. Let’s take a look at the key metrics.
Resource Capacity Utilization
It calculates the percentage of a resource’s available capacity that is actually utilized on assigned tasks or projects over a given period.
Productive Utilization
It measures how productively resources are deployed and utilized across billable, strategic, and other high-value projects.
Resource Utilization Rate
It is a critical metric that measures how effectively resources, such as employees, equipment, and tools, are utilized against their total available capacity.
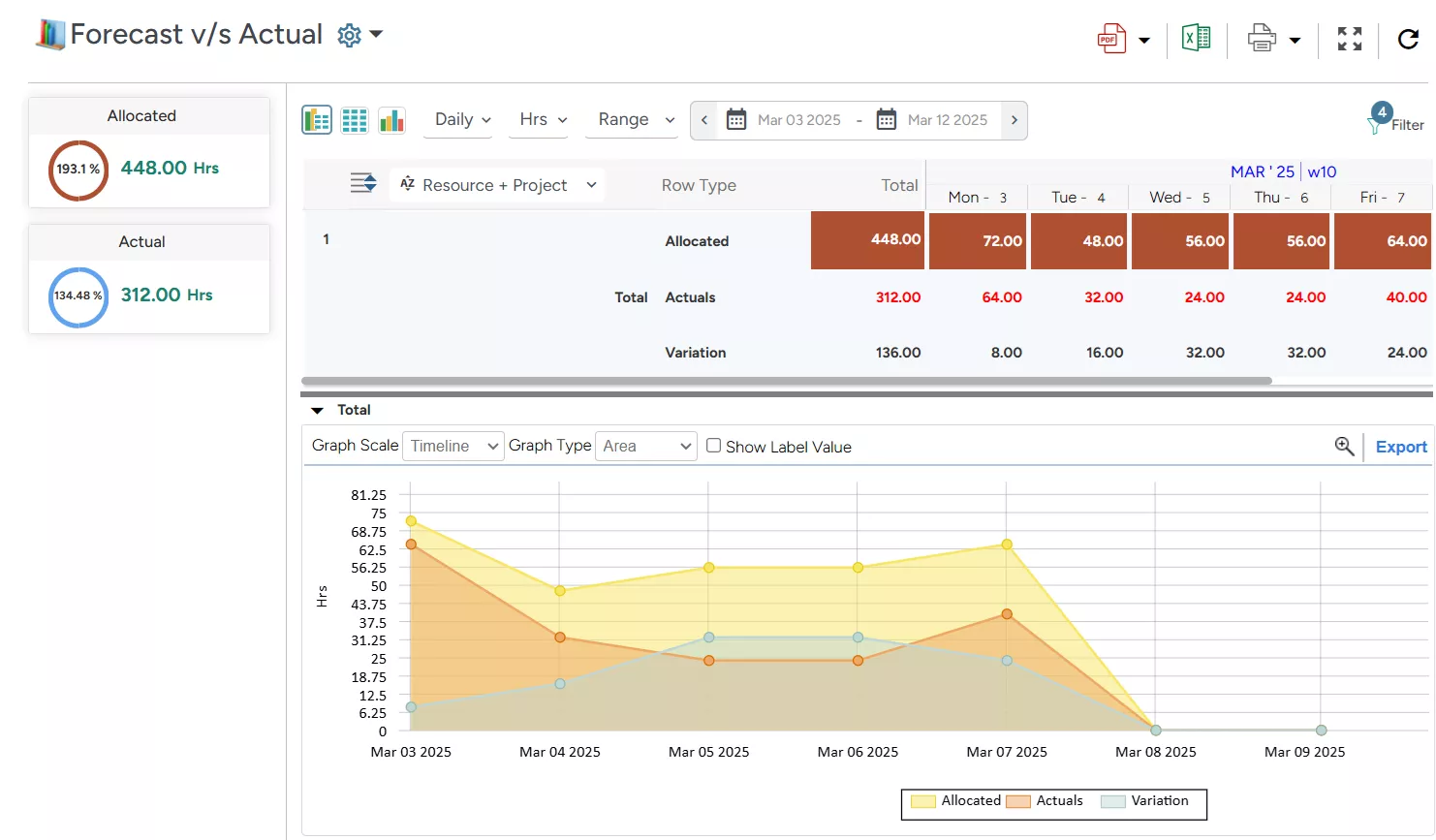
Forecast vs. Actual Utilization
It measures the variance between projected resource use and actual utilization. A significant gap indicates forecasting inaccuracy, resulting in either under- or overutilization of resources and increasing costs.
Resource Availability Rate
It is the percentage of time a resource (human or non-human) is available to perform productive work within a specific timeframe.
Resource Forecast Accuracy
It refers to the degree to which an organization’s predicted resource demand aligns with the actual resources required.
Resource Allocation Effectiveness
It measures how appropriately an organization assigns its available resources, such as people, equipment, and finances, to tasks and projects to achieve optimal results with minimal waste.
Billable vs. Non-Billable Hours
It measures the proportion of time employees spend on client-focused, revenue-generating work compared to non-project activities like BAU, general meetings, etc., that cannot be charged to clients.
Skill Gap Index
It measures the difference between the skills an organization requires and those currently possessed by its workforce.
Learn about resource management KPIs you should track to boost business performance.
In the following section, let us go through the key components of resource capacity planning.
Key Components of Resource Capacity Planning
Given below are six components that are critical to building an accurate and functional. Explore what each element means and why it matters.
| Component | Definition | Strategic Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Skill Inventory | A centralized record of current organizational capabilities, such as resource skills, certifications, and proficiency levels. | It ensures resources are allocated based on the right competencies and minimizes talent-task mismatches. |
| Resource Capacity | It refers to the total amount of work a resource can complete over a specified period of time. | Sets realistic expectations for resource availability and helps prevent workload imbalances. |
| Project Demand | The total effort required to deliver all current and future projects is typically measured in hours or FTE. | Helps leadership prioritize and sequence projects based on resource availability, not assumptions. |
| Capacity vs. Demand Gap Analysis | It is a process that involves identifying and quantifying the difference between available capacity and future demand. | Enables timely interventions, such as rescheduling, upskilling, or hiring. |
| Utilization Forecasting | It refers to estimating future resource usage over a defined period to identify and prevent potential resource overutilization or underutilization. | Ensure balanced workloads and improve profitability by keeping utilization at an optimal level across the portfolio. |
| Scenario Modeling | It involves evaluating multiple “what-if” scenarios to understand their outcomes, assess their implications, and determine the most viable course of action. | Supports smarter decision-making by selecting the most feasible and cost-effective risk mitigation strategy. |
Here is the formula to calculate resource capacity and demand, as well as capacity vs. demand gap:
Resource Capacity:
Resource Demand:
Capacity vs. Demand Gap:
- A positive gap indicates excess capacity and bench time.
- Negative gaps indicate skill or capacity shortages.
Having understood the resource capacity planning formula, let’s take a look at different types of resource capacity planning strategies.
Types of Resource Capacity Planning Strategies
An organization’s resource capacity planning strategy dictates its approach to resource supply relative to demand. Here are the primary strategies to consider.
The Lead Strategy: Proactively Hiring for Future Demand
In the lead strategy, enterprises added capacity before the actual demand materialized. For instance, hiring 10 engineers because you expect a 50% growth next year.
- Risk: Higher bench time (bench costs) if the forecasted demand does not materialize.
- Best For: High-growth companies and critical, highly specialized skills.
The Lag Strategy: Reacting to Resource Overload
In this case, capacity is added only after demand exceeds current capacity and a shortage is experienced.
- Risk: High risk of project delays, employee burnout, and lost revenue opportunities.
- Best For: Conservative, cost-conscious organizations or easily outsourced, non-core tasks.
The Match Strategy: Finding the Optimal Balance Point
In the match strategy, capacity is increased in phased increments based on capacity forecasting accuracy, maintaining a steady balance between supply and demand.
- Risk: Requires precise resource forecasting to avoid oscillating between lead (overcapacity) or lag (shortage) patterns.
- Best For: Most mature organizations seeking a balance between cost control and delivery speed.
The Hybrid Approach: Combining Lead, Lag, and Match
In practice, organizations often use a hybrid approach, hiring ahead for specialized skills, and adding general support only when demand increases.
Read this blog to learn how to measure resource capacity and demand.
Let’s now explore proven best practices to strengthen organizations’ overall capacity planning maturity.
Resource Capacity Planning Best Practices
According to a McKinsey survey, “90% of leaders consider capacity building a pressing priority that needs to be addressed now or soon.”
This urgency highlights the need to move beyond manual spreadsheets and adopt structured resource capacity planning best practices. Here’s what high-performing organizations do differently:

- Leverage a Dedicated Centralized Resource Management Platform: Move beyond spreadsheets and use a centralized system that stores complex resource data and serves as a single source of truth for accurate decision-making.
- Prioritize Resource Request Based on Strategic Value and ROI: One must avoid allocating resources on a first-come, first-served basis. Every resource request should be prioritized based on the project’s estimated strategic value, compliance necessity, and calculated ROI.
- Differentiate Hard, Soft, and Tentative Resource Allocations: Clearly define commitment levels, hard allocation (committed), soft booking (planned), and tentative allocation (prospective), to enhance planning accuracy and transparency.
- Forecast and Optimize Resource Utilization Early On: Gain foresight into future resource utilization to identify instances of over- and underutilization. In case of discrepancies, take suitable corrective measures to improve productive utilization.
- Implement Targeted Upskilling and Data-Driven Hiring: Identify forecasted skill gaps and upskill internal staff through cross-training before initiating external, often more expensive, data-driven hiring.
Read our blog to master resource management best practices.
Having understood resource capacity planning tips, let’s explore some critical bottlenecks faced by organizations and ways to overcome them.
Resource Capacity Planning Challenges and How to Solve Them
Even though capacity planning is critical to business success, many organizations struggle to execute it effectively. The table below highlights common challenges and practical ways to address them.
| Challenge | Description | Practical Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Inaccurate Resource Estimation | Resource estimation is often based on assumptions rather than historical data. Frequent scope changes without proper control also distort capacity forecasts. | Mandate standardized estimation techniques (e.g., T-shirt sizing) and require formal governance (change requests) before allowing changes that affect committed resource requirements. |
| Outdated Skills Inventory | Businesses often lack an up-to-date record of employee skills, certifications, and proficiency levels, leading to ineffective capability assessment. | Implement a centralized platform that integrates with HR systems and requires managerial validation of skill proficiency during regular review cycles. |
| Poor Utilization Forecasting | Organizations often fail to anticipate future utilization levels. This lack of foresight results in uneven workloads and reduced productivity. | Institutionalize a rolling, forward-looking utilization forecast review (e.g., monthly). This forces decision-makers to focus on future gaps rather than historical data. |
| Uneven Workload Distribution | Often, high-performing employees are overloaded with critical assignments. At the same time, certain departments tend to hoard skilled resources, even when demand elsewhere is higher. | Establish an executive-level resource governance committee that has the authority to approve and enforce cross-functional resource sharing. |
| Resource Conflicts in Matrix Organizations | In matrix organizations, employees report to multiple managers, causing unclear ownership and competing priorities. Conflicts arise when multiple managers vie for the same skilled resources. | Use a centralized resource management platform that provides a clear, single view of a resource’s total allocation and requires sign-off from both the functional manager and the project manager. |
Learn about critical capacity planning bottlenecks and ways to overcome them.
Now let’s explore how resource capacity planning principles apply in Agile and Scrum environments.
Resource Capacity Planning in Agile and Scrum Environments
Capacity planning is not just for traditional Waterfall projects; it is essential for scaling Agile and Scrum teams effectively. It helps them align delivery capacity with business priorities and maintain a sustainable pace of work.
- Aligning Agile Capacity Planning with Strategic Goal: Agile capacity planning aligns long-term portfolio strategy (quarterly or yearly) with the tactical work of the development team (sprint-based). It ensures that teams stay focused on the highest-priority features that deliver maximum business value.
- Sprint-Based Capacity Planning: In Scrum, capacity is calculated on a sprint-by-sprint basis by factoring in holidays, time off, and the team’s historical velocity (how many story points they typically complete).
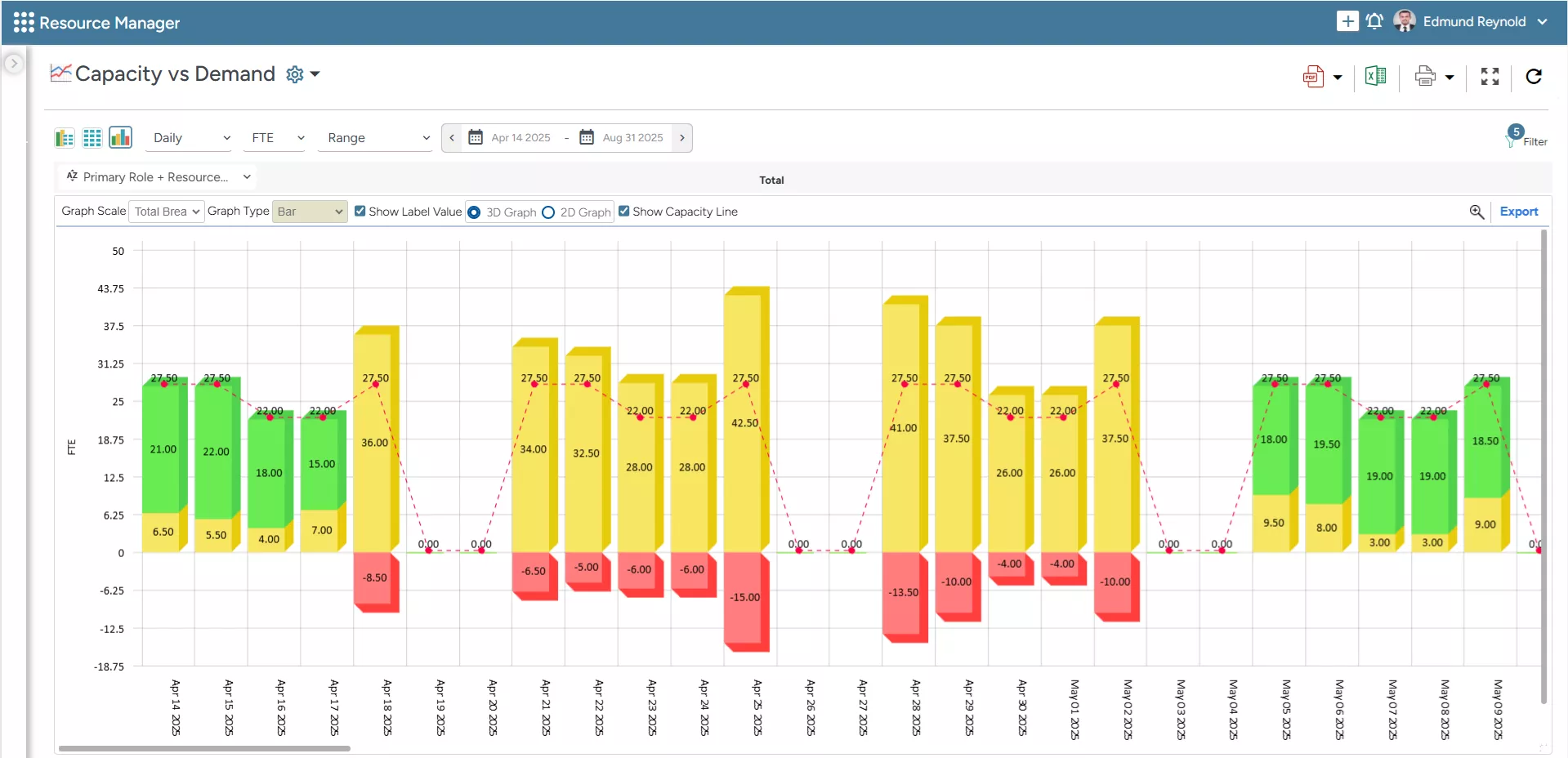
SAVIOM’s Capacity vs. Demand Graph enables managers to quickly spot resource shortages or excesses, and take timely action to balance supply and demand.
- Balancing Velocity and Resource Availability: A good capacity plan ensures that the workload (story points pulled into the sprint) never exceeds the team’s velocity, promoting a sustainable and consistent pace.
- Accounting for Interruptions and Shared Service Resources: Agile capacity planning must factor in buffer capacity, time set aside to handle inevitable interruptions, bug fixes, and demands from shared services, protecting the team’s focus time.
Explore our article on the fundamentals of agile capacity planning.
Now, let’s examine some capacity planning examples across key industries.
Resource Capacity Planning Examples Across Industries
Resource capacity planning (RCP) doesn’t look the same for every industry because each one faces unique demands and constraints. Below are real-world scenarios showing how RCP helps teams operate with confidence.
Professional Services & Consulting
A global consulting firm started using resource capacity planning to forecast project demand 8–12 weeks ahead by role and skill set. This gave leaders early visibility into where certain consulting roles would be overloaded, and where gaps would appear for upcoming engagements.
Impact: They could plan rotations, bring in contractors in advance where needed, and avoid last-minute staffing conflicts on critical projects.
Explore how resource capacity planning benefits professional services.
IT & Software Services
An IT services organization implemented resource capacity planning to forecast demand across delivery teams based on upcoming client projects, technology stacks, and skill requirements. They compared projected demand against available developers, testers, and solution architects across locations.
Impact: This enabled proactive redeployment of internal talent, early upskilling for emerging technologies, and selective hiring well before project kick-offs, reducing delivery risks, improving utilization, and minimizing last-minute staffing escalations.
Architecture, Engineering & Construction
An engineering firm mapped capacity for architects, structural engineers, and site supervisors against project phases instead of staffing reactively. With robust resource capacity planning, they saw that certain engineering roles would be underutilized early and heavily stretched in later phases.
Impact: They staggered project start dates and adjusted hiring and subcontracting decisions so that the right roles were available when phases ramped up, reducing phase slippage and minimizing bench time.
Understand how you can implement resource capacity planning in AEC firms.
Audit & Accounting
An audit firm used capacity planning to model workload for tax and audit seasons across offices. They projected the hours required by engagement type and compared them against available staff capacity months before peak periods.
Impact: This enabled balanced workload distribution across teams and offices, early temporary staffing decisions, and deferment of low-priority work, easing overtime pressure and turnaround risk.
Read our blog to effectively navigate capacity planning challenges in audit and accounting firms.
Healthcare & Pharma
A hospital group rolled out capacity planning to understand future demand for key specialties (like radiology and oncology) based on historical patient volumes and planned programs. They compared that demand against specialist rosters and machine availability.
Impact: With that view, they could adjust rosters, schedule elective procedures more realistically, and avoid chronic overbooking of a few specialists while others remained underused.
Now, let us understand how resource capacity planning software helps firms anticipate future needs and maximize billable utilization in a dynamic business environment.
Stay Future-Ready with the Resource Capacity Planning Tool
Effective resource capacity planning is essential for improving project and business performance. That’s why organizations must choose robust resource capacity planning software to move beyond the limitations of traditional solutions. It offers advanced functionalities like:
- All-in-one resource planner with 360-degree visibility into project pipelines and resource schedules.
- Embedded capacity planner to forecast demand and address skill gaps.
- KPI forecaster for insights into availability, utilization, burnout, and skill gaps.
- What-if analysis to simulate scenarios and optimize resource management plans.
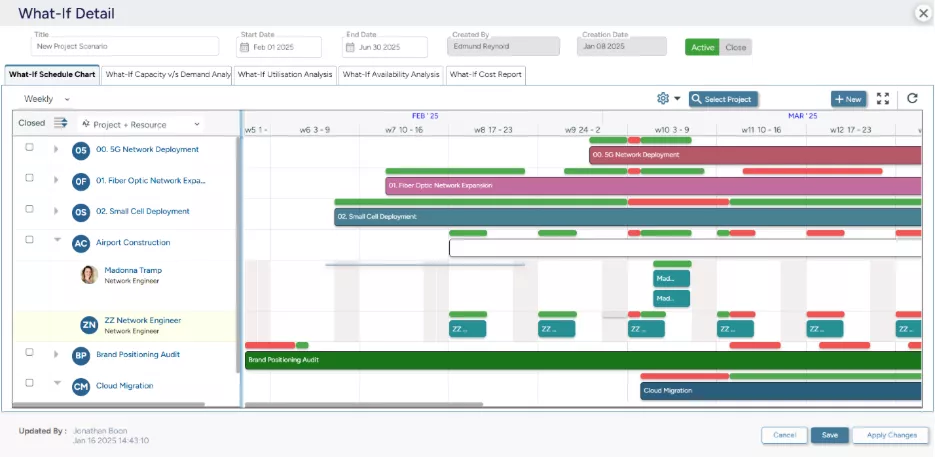
SAVIOM’s scenario modeling feature allows managers to create and test multiple workforce scenarios in a sandbox environment.
- Competency matrix to track and update resource skills to quickly identify and address gaps.
- Real-time BI reports like forecast vs. actual, project vacancy, and people-on-the-bench for granular insights and timely corrective actions.
- Intelligent matchmaker with filters to align resources to tasks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Resource capacity planning is a process of determining whether your current resource capacity (people, equipment, capital, etc.) can meet future project demand. It involves proactively identifying and closing short- and long-term excess or shortages of resources within an organization to improve workforce productivity, drive operational efficiency, and enhance profitability.
Resource capacity planning gives business leaders early visibility into future skill requirements, ensures projects are staffed realistically, and improves delivery predictability. It also helps organizations avoid costly last-minute firefighting and future-proof the workforce against market volatility.
The key components of resource capacity planning that support an accurate and future-ready capacity plan include:
1. Skill Inventory
2. Resource Capacity
3. Project Demand
4. Capacity vs. Demand Gap Analysis
5. Utilization Forecasting
6. Scenario Modeling
Organizations use different types of resource capacity planning strategies to ensure that the resource capacity aligns with project demand. The primary approaches include:
1. Lead Strategy: Increase capacity before demand rises, so the organization is prepared early.
2. Lag Strategy: Increase capacity after demand rises to avoid unnecessary costs upfront.
3. Match Strategy: Increase capacity in small steps as demand grows to stay closely aligned.
4. Hybrid Strategy: Combine all three approaches to find the most practical and flexible way to meet demand.
While both capacity planning and resource planning are essential for effective resource management, they serve different purposes.
Resource planning is a comprehensive process that involves forecasting and allocating suitable resources to projects at the right time and cost. It also ensures that the organization effectively utilizes human and non-human resources, such as people, equipment, materials, and more, to meet its current and future business goals.
Capacity planning, as a subset of resource planning, focuses specifically on determining whether an organization has enough resources to meet anticipated demands. It involves analyzing demand forecasts, assessing resource capacity, and making strategic decisions like hiring or upskilling to prevent shortages or excess.
The resource capacity planning process is a data-driven approach that helps organizations align resource capacity with evolving business demand. These seven steps keep the capacity plan realistic, proactive, and effective.
1. Evaluate Current Resource Capacity and Workforce Capabilities
2. Gather and Consolidate Project Demand
3. Compare Resource Capacity Against Project Demand
4. Model Scenarios to Address Identified Shortages or Surpluses
5. Implement the Right Resourcing Strategies and Get Approval
6. Execute the Plan and Monitor Resource Utilization
7. Review Performance Regularly and Optimize the Process
The following best practices help organizations move beyond manual spreadsheets and build a more accurate, scalable, and future-ready resource capacity planning framework.
1. Use a Centralized Resource Management System
2. Evaluate Resource Request Based on Strategic Importance
3. Distinguish Between Hard, Soft, and Tentative Allocations
4. Anticipate and Improve Resource Utilization Proactively
5. Address Skill Gaps Through Targeted Upskilling and Hiring












Leave a Reply