“A goal without a timeline is just a dream” ~ Robert Herjavec, Canadian Businessman and Investor
A project may be well-planned, but without a clear timeline, it lacks direction and urgency. Teams may not know which tasks to prioritize first, and stakeholders may begin to question the project’s progress. That’s why accurately estimating project duration is essential.
Project duration provides a clear picture of how long the project will take to complete. Thus, it offers a structured timeline for all project activities, enabling better planning, competent resource allocation, and proactive risk management. Moreover, it ensures the project stays on schedule, within budget, and aligned with stakeholder expectations.
However, estimating it accurately is one of the most challenging tasks because it includes unpredictable factors like scope changes, resource shortages, and unexpected delays. Therefore, project managers must use the right tools and techniques to evaluate the timelines accurately.
In this blog, we will understand what project duration is and explore seven ways to estimate it accurately.
Let’s get started!
What is Project Duration?
Project duration refers to the total amount of time required to complete a project. It comprises all five project phases, initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, and closure, and is typically measured in days, hours, weeks, or months. If the duration is not estimated accurately, managers will not have a clear idea of how long the entire project will take or when it will reach certain stages or milestones.
Let us understand it better by looking at an example.
Project Duration Example
Here is an example of estimating the duration of constructing a house, broken down by stages. This structured breakdown helps calculate the overall project duration and highlights the importance of detailed planning at every step.
| Stage | Description | Estimated Duration | Buffer Time | Total Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Project Initiation | In this stage, client requirements are gathered, stakeholders are identified, and the project scope, timeline, and budget are determined. | 1 Month | 1 Week | 1 Month |
| Project Planning | This stage includes getting an architect for the house design and obtaining necessary permits. | 1 Month | 1 Week | 1 Month |
| Site Preparation | It includes clearing of land, excavation, and foundation work. | 1 Month | 2 Weeks | 1 Month 2 Weeks |
| Structure Construction | This stage includes building the walls, constructing the roof, finishing the plastering, and working on the internal structures. | 4 Months | 2 Weeks | 4 Month 2 Weeks |
| Interior Work | It includes electrical installations, plumbing, painting and other interior finishes. | 2 Months | 2 Weeks | 2 Month 2 Weeks |
| Final Inspection | This is the last stage, which includes final fixes, addressing any remaining issues and handing over the property to the client. | 1 Month | 1 Week | 1 Month |
| Total duration of project | 10 Months | 9 Weeks | Approximately 12 Months |
So, considering buffer time for every phase, the project can be completed in a year. Next, let’s understand the different factors to consider while estimating the duration of a project.
Factors to Consider During Project Duration Estimation
Here are several key factors to consider when estimating the duration of projects.
Project Scope
Scope refers to the project’s objectives, deliverables, tasks, deadlines, and constraints. Clearly defining the scope is important as it provides a clear picture of every step in the project lifecycle. It is also important to note here that the size and complexity of the scope directly influence project duration. If the project scope is broad and complex, then the duration of the project will be longer, whereas if the scope is short and simple then the project duration will be shorter.
Work Breakdown Structure
A work breakdown structure (WBS) divides a project into smaller and manageable components called tasks. These tasks are further divided into sub-tasks and work packages. When a project is divided into work packages, it becomes easy to estimate the duration of each component more accurately. Thus, a detailed WBS helps create a precise project schedule, preventing schedule slippage.
Read More: How to Build a Work Breakdown Structure? A Step-by-Step Guide
Task Dependencies
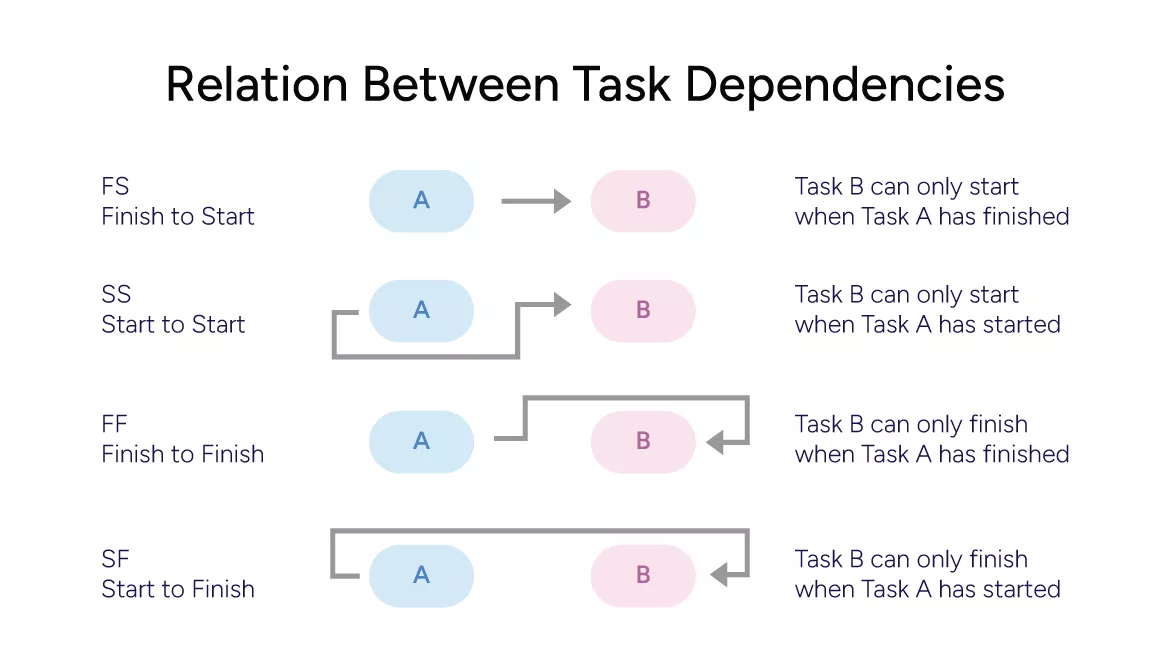
In a project, specific tasks cannot start or finish until another task starts or finishes. This relationship is known as task dependency. For example, painting cannot begin until the walls of a house are constructed. When task dependencies are overlooked, it can cause schedule clashes and unexpected delays. To manage this effectively, managers can utilize tools like Gantt charts that provide a visual timeline of task sequences.
Resource Availability & Productivity
Resource availability provides an overview of the number and type of resources available to complete the tasks. When estimating the project duration, it is essential to account for the resources’ work hours, planned leaves, and availability across the project timeline. Additionally, the productivity levels of resources play a massive role in determining the project duration. If it is high, the tasks will be completed on or before time, and vice versa.
Read More: What is Resource Availability in Project Management, and Why Does It Matter?
Experience of Team Members
The skill level and experience of your team have a significant effect on how fast tasks are completed. Experienced professionals work faster and make fewer mistakes, whereas new team members may require extra guidance and time. Estimating project duration without considering team capability can lead to overoptimistic plans. Thus, aligning task assignments and time estimates with your team’s experience is imperative.
Oversight & Approval Time
Sometimes, a few project tasks need to be reviewed or approved before moving forward, and waiting for client approvals can delay progress. Unfortunately, managers often overlook this “pause time” in their calculations. To ensure more accurate estimates, managers must include time for reviews, feedback, reports, and project meetings while calculating the duration.
Read More: What is a Project Meeting? 9 Strategies to Conduct an Effective One
Potential Risks
Every project carries some level of uncertainty or risks, like technical issues or vendor issues, that can affect the project timeline. Therefore, it is necessary to identify project risks early and add contingency time, as it helps prepare for possible setbacks. Factoring in risk buffers improves project duration accuracy and builds resilience into the project plan.
External Dependencies
Projects often rely on external factors like vendors/partners, legal permits, weather conditions, etc. These factors are not under the manager’s control and can cause delays. For example, for building a house, if a supplier delays in delivering the materials due to a storm, then the entire schedule may be compromised. Therefore, project managers must consider these possibilities while estimating the duration of the project.

Read More: What are Project Interdependencies & How to Manage them Effectively?
Let us now look at the methods used to estimate the project duration.
Methods To Estimate Project Duration
Below are several proven methods that help project managers estimate project duration effectively.
Expertise-based Estimation
Expertise-based estimation, also known as expert judgment, relies on the knowledge and experience of professionals who have previously handled similar projects. Expert judgment is only used when the project has limited data. However, these estimations may vary depending on who is making them. Therefore, cross-checking with multiple experts is necessary to reduce bias and make a precise estimation.
Top-Down Estimation
In the top-down estimation method, the overall duration required to complete a project is estimated first, which is further divided into time slots for different phases or tasks. It is often based on historical data, expert judgement, or organizational standards. Top-down estimation is mainly used during the early planning stages when detailed task-level information is not available.
Bottom-Down Estimation
Bottom-down estimation is the opposite of top-down estimation. In this method, the project manager lists each task individually and then adds them to estimate the total project duration. Thus, this approach is closely tied to the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). Although this method takes a lot of time, it delivers greater accuracy because it considers the specific details of each task rather than broad assumptions.
Analogous Estimation
In this method, data from similar past projects is collected to estimate the duration of the current one. Experienced individuals, such as the project manager, sponsor, and senior team members, compile and assess the historical data. The evaluation includes reviewing the scope of work, applying lessons learned, and adjusting for known factors like resource availability.
Read More: 10 Common Project Management Mistakes and How to Fix Them?
Parametric Estimation
Parametric estimation uses mathematical models or formulas to calculate project duration. This method assesses each task in detail, producing the overall estimate. Managers refer to historical data to formulate estimates and decide the project budget. For example, if you are building ten identical desks, you will first estimate the time to make one, then multiply that time by nine to get the total duration.
Three-Point Estimation
Three-point estimation considers three scenarios for each task: the most optimistic case, the most pessimistic case, and the most likely case, to come up with the final project duration. Imagine you are estimating how long it will take to paint a room. In this case, the optimistic estimate will be 2 hours, the most likely estimate will be 3 hours, and the pessimistic estimate will be 5 hours.
The formula commonly used in three-point estimation is based on the Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT). The formula is:
| Estimated Duration = O + 4M + P/6 |
|---|
The PERT Method
The Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) method is used when more than one person is working on a task together. In this method, team members should have overlapping working hours to work on shared tasks. For example, if an employee works from 9.00 – 5.00 and another from 1.00 – 9.00, their overlapping hours are from 1.00 – 5.00. During this time, they can work on shared tasks.
The formula for the PERT method is:
| Optimistic + 4 X Most Likely + Pessimistic /6 |
|---|
Task-Based Estimation
Task-based estimation means estimating each resource’s time to complete a specific task and then combining them to calculate the overall project duration. This method divides large tasks into smaller tasks, and each sub-task’s effort, time, and resource are estimated. It is commonly used in Agile methodologies where iterative planning and task-level tracking are essential for adaptive execution.
Read More: What is Agile Project Management & How to Effectively Manage Resources?
The Critical Path Method
The critical path method (CPM) is a simple technique for analyzing, planning, and scheduling complex projects. It identifies the longest sequence of dependent tasks that represents the activities that cannot be delayed. This method helps review the timeline of each task, identify the most critical tasks, and accordingly allocate resources with the required skills.
The Value-Added Approach
The value-added approach prioritizes tasks that provide the most value by continuously gathering feedback to help the project deliver increasing value as it progresses. It primarily focuses on understanding and fulfilling the needs and desires of customers. The manager uses the time spent researching and developing a project to calculate the overall project duration.

Now that we have understood the methods, let us now know the difference between the duration of projects, effort, and elapsed time.
Project Duration vs. Effort vs. Elapsed Time
Here is a simple comparison table showing the differences between project duration, effort, and elapsed time.
| Aspect | Effort | Project Duration | Elapsed Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | In project management, effort means the amount of work, time, and resources needed to complete a project. | It refers to the total time needed to complete a project from initiation to closure. | The elapsed time measures the total time taken to finish a project from the moment it’s assigned to its completion, including any pauses, gaps, or delays along the way. |
| Measured in | It is measured in units of time, like hours, days, or weeks. | It is measured on an hourly, weekly, daily, or monthly basis. | It is measured in various time units, such as seconds, minutes, hours, days. |
| Used For | It is used for estimating project duration, resource allocation, and budgeting. | It is used for planning, scheduling, and resource allocation. | It is used to monitor progress and identify potential delays. |
Read More: What is Time Management? 9 Effective Strategies to Master It
Now, let us know why estimating the project duration is important.
Why is it Important to Estimate Project Duration?
Estimating project duration is crucial to ensure that projects remain on schedule, within budget, and align with project stakeholder expectations. It forms the backbone of effective planning, enabling project managers to manage dependencies, coordinate teams, and anticipate potential roadblocks. Here is why it matters:
- Estimating project duration helps define when the project will start and finish, ensuring the goals are achievable within a specified time frame.
- It allows managers to allocate human and non-human resources appropriately across the project timeline, preventing both underutilization and burnout.
- It helps communicate project timelines to clients and sponsors, reducing the chances of conflict and building trust.
- Accurate duration estimation ensures better budget forecasts and reduces the risks of project budget overruns due to extended timelines.
- Estimating project duration improves project monitoring and control as project managers can track progress against estimated durations and take corrective actions if things are falling behind.
Now that we know the importance, let’s learn the steps to calculate project duration.
Read More: How to Develop an Effective Project Budget in 8 Simple Steps?
How to Estimate Project Duration?
Here are the key steps managers can follow for effective project duration estimation. These steps ensure that timelines are realistic, achievable, and aligned with project goals:
Define Project Scope & Create WBS
The first step in estimating the project duration is to clearly define the scope. This means listing the project goals, deliverables, tasks, costs, deadlines, and constraints. Once the project scope is set, the next step is to create the work breakdown structure (WBS), which breaks the project into smaller and manageable tasks. A detailed WBS ensures that no task is overlooked, and the project duration is calculated accurately.
During this process, managers can involve their team members to ensure every part of the project is covered. They can also keep the WBS organized by phases for easier tracking. Without a proper project scope and WBS, estimation becomes guesswork and increases the risk of project delays. Thus, well-defined scope and WBS ensure that everyone has a clear idea of how much time each task will take.
Map Out Task Dependencies
Various tasks in a project are interdependent, meaning one task cannot begin or finish until another task begins or finishes. To clearly understand the sequence in which tasks must be executed, it is essential to map out these dependencies. This sequencing helps project managers identify which tasks can run in parallel and which can begin after the completion of others.
After identifying the dependencies, the next step is to categorize them based on their type (e.g., finish-to-start, start-to-start, finish-to-finish). Then, managers can find out the reasons that might affect the dependencies, such as budget limits, resource constraints, vendor issues, etc. They can also visualize the dependencies using a Gantt chart or a Kanban board, which helps calculate the project duration accurately.
Estimate Duration for Each Task
Thirdly, to estimate how long each task will take, managers should refer to historical data and request team input to calculate the overall project duration. They must also use estimation techniques like parametric, three-point, or expertise-based methods to reach an accurate estimate. Moreover, it is important to consider the complexity and resource availability for more accurate project duration estimates.
Take the development of an application as an example. First, the manager breaks the project into smaller tasks like designing the user interface, setting up the backend server, testing, and deployment. Based on team input and past projects, they estimate that design will take 1 week, backend setup 2 weeks, testing 1 week, and deployment 1 week, ensuring realistic project timelines.
Determine the Critical Path
Once the duration for each task is established, managers can identify the critical path. Critical path is the longest sequence of dependent tasks that must be completed on time for the entire project to stay on schedule. To determine critical tasks, project managers need to list all project tasks and identify dependencies, estimate the duration of each task and, sequence the tasks based on their dependencies.
Next, they can identify all possible paths throughout the project schedule and calculate the total duration of each path. The sequence of activities with the longest duration is the critical path. Determining the critical path helps identify tasks that require close monitoring, enables accurate duration estimation, and helps achieve project milestones on time.
Read More: Project Milestones: How to Manage Them Effectively for Project Success?
Add Buffer Time to Manage Risks
No project goes exactly as planned, so adding buffer time is wise. Buffers account for unexpected delays like bad weather, employee absences, unplanned attrition, or technical glitches. These are also called contingency reserves. Managers must remember that adding buffer time while estimating project duration acts as a safety net, minimizes stress on the team, and allows the project to stay on track.
For example, a marketing agency is planning a promotional event, and you are the organizer. You estimate that it will take 10 days to book the venue, finalize the guest list, and coordinate with speakers. However, changes in delays in speaker availability might happen, so you add 2 extra days as buffer time. You might not need the extra days, but adding buffer time keeps your project on time even if there are minor delays.
Sum Up the Duration of All Tasks
After estimating the time that individual tasks will take, managers can add them up to get a total project duration. While doing so, it is essential to consider factors like resource availability, employee leaves, holidays, overlapping tasks, and their dependencies. This step gives the final schedule baseline, representing the outcome of all the planning and project duration estimation done so far.
For example, a law firm is preparing for a high-profile case. The tasks include legal research (4 days), drafting arguments (5 days), preparing exhibits (3 days), and mock trials (2 days). Some tasks can happen simultaneously, but some can only begin after complete research. The critical path (legal research → drafting arguments → mock trials defines the project’s minimum duration and directly impacts the delivery timeline.
Read More: What is Leave Management, and Why is it Important for Successful Project Delivery?
Validate Assumptions & Gain Approvals
Lastly, before confirming the project duration, managers must review all the assumptions made during the estimation process. These assumptions may relate to team availability, working hours, resource capacity, and internal and external dependencies such as vendor timeline and regulatory approvals. This ensures that the project duration remains realistic and achievable.
Moreover, to avoid misalignment, project managers should clearly communicate these assumptions to all stakeholders, confirm mutual understandings, and secure formal approval for the estimated schedule. Additionally, it is essential to document all assumptions and constraints so that there is a reference point to reassess and adjust the plan if changes occur.
Now, let’s focus on some best practices for estimating project duration.
Best Practices for Estimating Project Duration
Here are some of the best practices for accurately estimating project duration.
Engage Team Members in the Estimation Process
Involving team members in estimating project duration can help identify risks early, bring unique perspectives, minimize misunderstandings, and ensure everyone is on the same page. Moreover, engaging every team member in the project duration estimation process promotes transparency and allows for open communication. It is a great way to boost your team collaboration, and raise confidence and responsibility.
Read More: 7 Effective Ways to Boost Remote Team Collaboration
Use a Mix of Estimation Techniques
A single estimation technique may not work in all situations. Therefore, managers should combine various techniques like top-down, bottom-up, three-point, parametric estimation, and the PERT method. Using a mix of project duration estimation techniques can improve planning, mitigate risks, and reduce delays. Additionally, blending several strategies can help cross-check project results and ensure the best outcome.
Account for Resources’ Schedule & Availability
While estimating project duration, it is necessary to consider which employees are available and for what duration. It might take two days to complete a task, but if the employee is not available on those days, then the project duration will stretch, leading to a missed deadline. Thus, managers should look at work schedules, holidays, and leaves during the estimation process of project duration.
Use Data from Past Projects
By analyzing past projects, managers can identify what caused delays or issues before, such as scope changes or overlooked dependencies. By learning from these mistakes, the managers can avoid repeating them in current or future projects. For example, if past projects show that a particular task took longer than expected, managers can adjust their estimation accordingly.
Leverage Project Management Software
Using project management software allows managers to visualize the timeline through features like the Gantt chart. It helps identify the task dependencies and the critical path, ensuring that the activities included in a project are properly sequenced. Moreover, it allows managers to set realistic timelines, avoid unexpected delays, and estimate project duration accurately.
Read More: 12 Essential Project Management Principles for Successful Execution
Finally, let’s explore how advanced resource management software can help prevent schedule overruns and enhance the timely delivery of projects.
How Can 5th Gen Project Resource Management Software Help?
A 5th-generation resource management software can help in managing timelines and adhering to project duration in different ways, such as
1. The tool’s all-in-one resource planner offers a centralized view of all the resources. It allows managers to filter them by skill, experience, role, and cost, enabling competent resource allocation. Delivery delays are minimized when the right resources are assigned to the right tasks.
2. The embedded capacity planner helps anticipate resource gaps and allows proactive hiring, upskilling, and redistribution of existing resources. This ensures project deliverables are not delayed due to resource shortages.
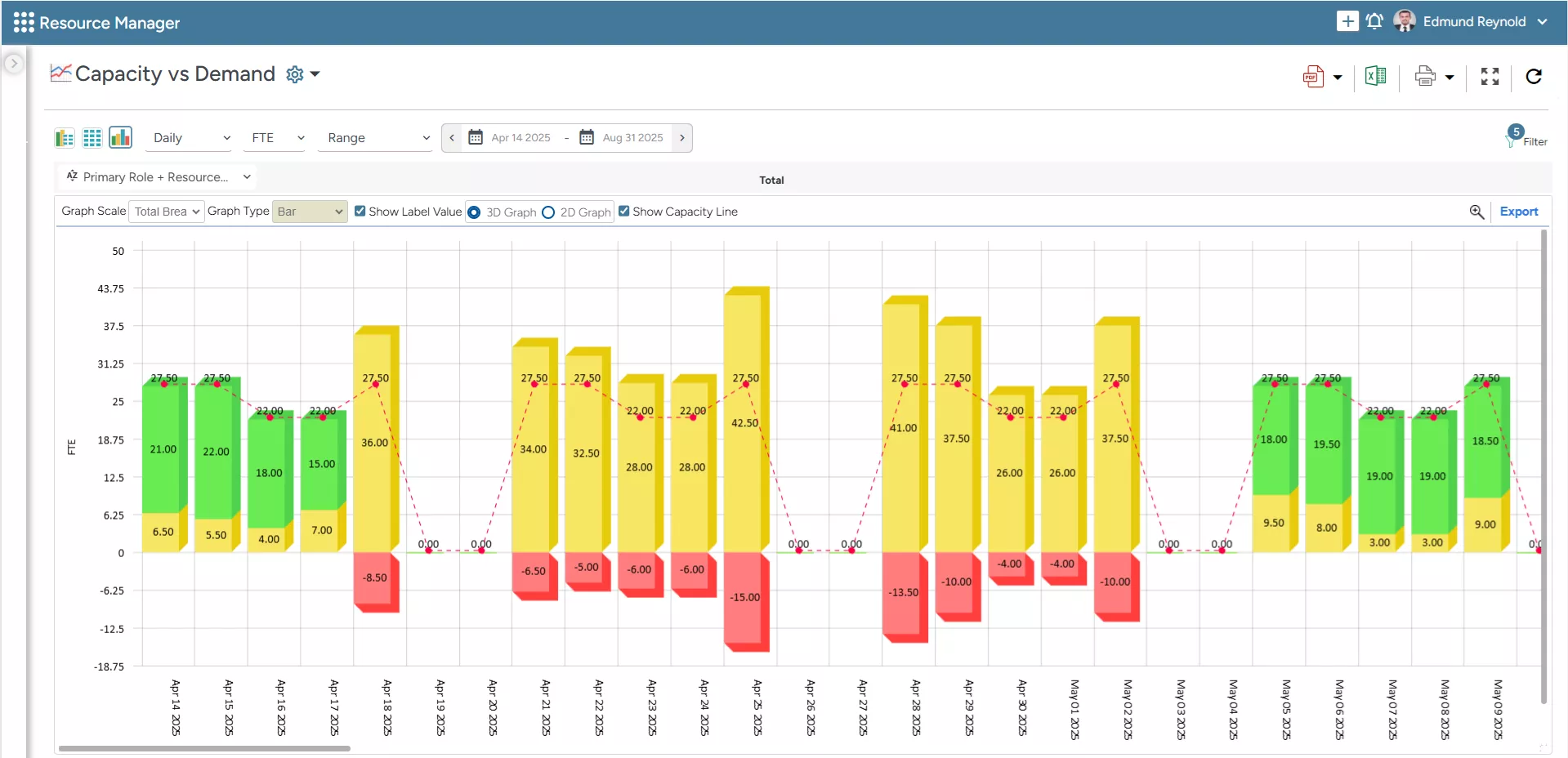
SAVIOM’s Capacity vs. Demand bar graph enables managers to quickly identify resource excesses/shortages with minimal effort.
3. The tool’s advanced resource forecasting allows managers to predict upcoming resource needs and respond proactively. It also enables managers to ensure the right resources are available for timely project initiation.
4. The tool provides real-time business intelligence reports, offering insight into resource utilization and schedule deviations. This empowers managers to monitor variances and take corrective actions early.
5. The Gantt Chart provides a visual overview of all project tasks and activities and systematically shows the task interdependencies and the current schedule.
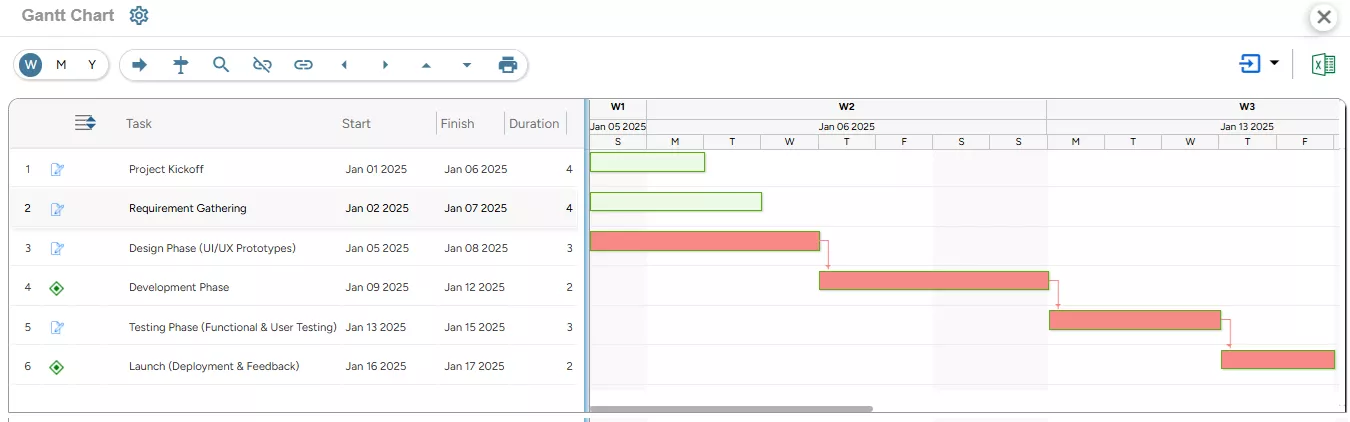 SAVIOM’s Gantt Chart allows users to view and manage tasks, timelines, deliverables, and resource allocation seamlessly on a single platform
SAVIOM’s Gantt Chart allows users to view and manage tasks, timelines, deliverables, and resource allocation seamlessly on a single platform
6. The what-if analysis feature helps you simulate various resource planning scenarios, assess their impact on project timelines, and arrive at the most efficient resource arrangement.
Conclusion
An accurate project duration helps managers plan, allocate resources, manage budgets, and build trust with stakeholders. Also, it helps to identify risks and delays and create contingency plans to maintain project momentum. Therefore, managers should estimate duration correctly because projects will only be delivered on time, and there will be progress.
The Glossary
Read More: Glossary of Resource Workforce Planning, Scheduling and Management










