Introduction
A global services firm sees a sudden increase in business demand after closing several major deals in a single quarter. Multiple client engagements and strategic initiatives are scheduled to begin simultaneously, creating both growth opportunities and workforce pressure. Managers must now determine whether the organization has sufficient talent with the required roles and skills to support upcoming commitments.
This is where workforce capacity planning becomes essential. It helps organizations evaluate whether available human capacity can support growing business demand by providing visibility into resource availability, utilization, and skill requirements. With this insight, enterprises can rebalance workloads, plan upskilling initiatives, and make hiring decisions proactively instead of reacting to shortages later.
In this blog, we explore the definition of workforce capacity planning, its importance, and how it helps organizations reduce risk and improve workforce readiness.
What is Workforce Capacity Planning?
Workforce capacity planning is a structured process of evaluating and aligning available human resources with current and future business demands. It helps ensure the right people, with the right capabilities are in the right place at the right time to meet business goals without creating overload or shortages.
In practice, it involves assessing available capacity against role- and skill-based business requirements to identify gaps early. This allows managers to take timely actions such as retraining/upskilling, onboarding contingent workers, or hiring additional talent. As a result, organizations can ensure that workforce capacity decisions support sustainable operations and future business growth.
Having explored the workforce capacity planning definition, let us move on to understand why it is important for businesses.
Read our blog on workforce planning and learn how to get the most out of your human resources.
What is the Importance of Workforce Capacity Planning?
Workforce capacity planning plays a critical role in how organizations manage growth, business demand, and workforce stability over time. Here are some of its key benefits for organizations:
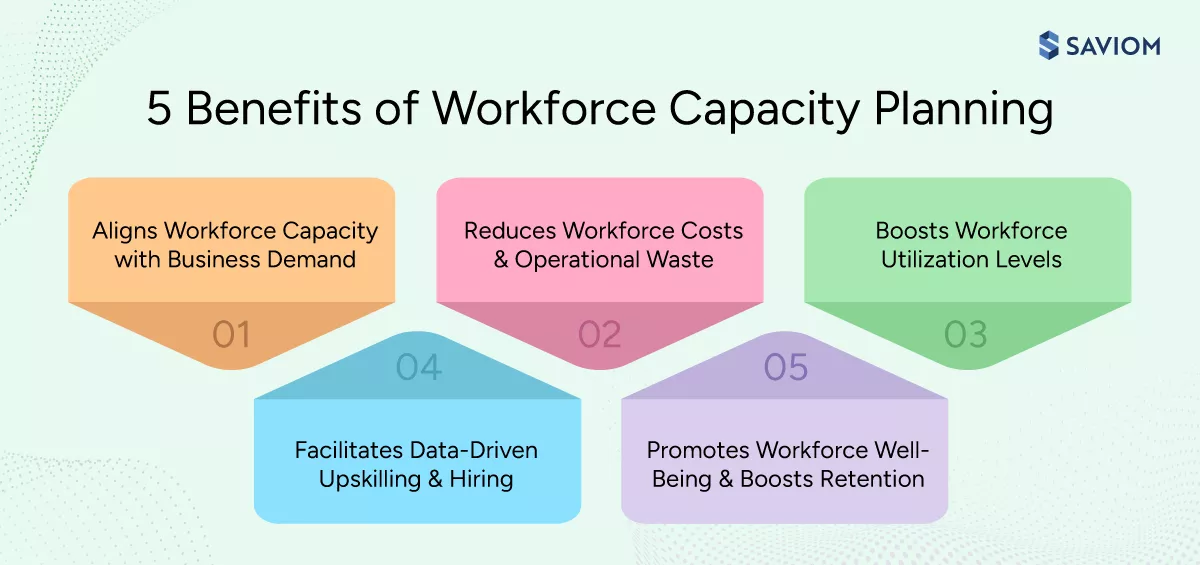
Aligns Workforce Capacity with Business Demand
Workforce or human capacity planning provides managers with early visibility into whether existing teams can support business demand across skills, roles, and time periods. This enables managers to validate delivery commitments, adjust demand expectations upfront, and prevent over-allocating the workforce.
Reduces Workforce Costs & Operational Waste
When managers have visibility into future capacity shortages or excesses, they can proactively plan redeployment, upskilling, or hiring. This helps prevent unnecessary expenses caused by hiring/firing cycles, excessive overtime, and repeated staffing corrections. At the same time, it reduces operational waste by minimizing bench time and delays caused by skill mismatches.
Learn more about resource cost reduction strategies in our blog.
Boosts Workforce Utilization Levels
Clear visibility into workforce capacity enables organizations to allocate work more evenly across teams, roles, and skill sets, preventing overloading or underutilization of resources. This helps maintain sustainable utilization levels across the workforce. As a result, organizations can improve productivity while lowering the risk of employee burnout and wasted capacity.
Facilitates Data-Driven Upskilling & Hiring
Workforce capacity planning helps managers identify whether existing workforce capabilities are insufficient to meet upcoming business needs. Accordingly, they can plan targeted upskilling and reskilling initiatives to reduce reliance on reactive recruitment. When gaps cannot be fulfilled internally, organizations can proceed with targeted hiring, minimizing last-minute workforce adjustments.
Promotes Workforce Well-Being & Boosts Retention
Workforce capacity planning supports a more stable work environment by preventing sudden workload spikes and prolonged periods of underutilization. This fosters a healthier work environment. Additionally, structured planning enables organizations to create meaningful growth opportunities through skill development and role transitions. This improves employee engagement and contributes to long-term retention.
Explore the benefits of capacity planning in professional services companies.
Once these benefits are clearly understood, the next step is deciding how organizations should respond when human capacity gaps or excesses are identified.
The 4B Framework: Buy, Build, Borrow, or Bot?
When organizations identify workforce capacity or skill gaps, they must decide how to close them efficiently and sustainably. The 4B framework provides a structured approach to workforce decision-making by evaluating four strategic options: Buy, Build, Borrow, or Bot.
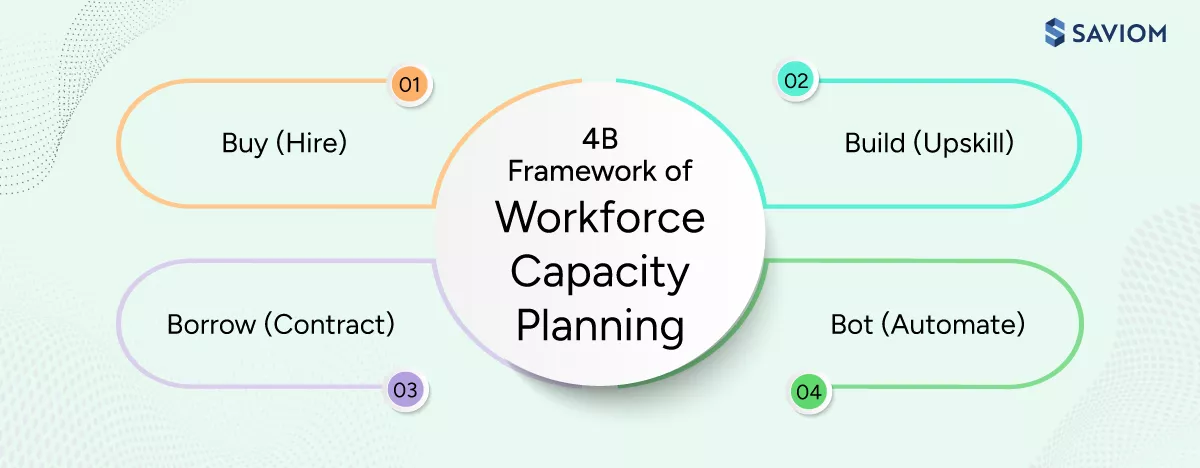
Buy (Hire)
Buy involves recruiting new employees externally to fill skill or workforce capacity gaps that cannot be met internally. Hiring helps build long-term capability and strengthens the talent pipeline when demand for specific roles is expected to remain stable.
Organizations typically buy talent when:
- Specialized expertise is required immediately
- Long-term demand for a role is predictable
- Internal reskilling is not feasible within timelines
While hiring ensures human capacity availability, it often involves higher costs, longer lead times, and onboarding effort.
Build (Upskill)
Build focuses on developing existing employees through structured training, mentoring, and learning programs to meet evolving business needs. By strengthening internal capabilities, organizations improve workforce agility, prepare employees for future roles, and ensure long-term talent readiness.
This approach is effective when:
- Skills can be developed internally within acceptable timelines
- Organizations want to retain institutional knowledge
- Employee growth and retention are strategic priorities
Building talent is often more cost-effective and sustainable, though it requires planning and investment in learning and development.
Learn how retraining/upskilling can help future-proof your business.
Borrow (Contract)
Borrowing involves using contingent workers to address short-term workforce capacity gaps or specialized skill requirements. It is instrumental when project demand fluctuates or when niche-skilled resources are required for a limited duration.
This option is useful when:
- Demand is short-term or project-based
- Specialized expertise is needed temporarily
- Hiring permanently is not justified
Borrowing provides flexibility and speed but may increase dependency on external talent pools.
Bot (Automate)
The bot option enables organizations to improve efficiency instead of increasing headcount by eliminating repetitive tasks and optimizing workflows. This allows employees to focus on higher-value work, improving productivity.
Examples include:
- Automating repetitive administrative tasks
- AI-assisted forecasting or scheduling
- Workflow automation tools
- Self-service systems
Automation helps organizations optimize workforce capacity, improve operational efficiency, and reduce reliance on manual effort.
To gain a better understanding of how organizations can respond to workforce capacity gaps, read our comprehensive eBook on resource capacity planning.
Having understood the response options organizations can use to address workforce gaps, the next step is to learn how to calculate workforce capacity accurately so that these decisions are grounded in realistic data.
How to Calculate True Workforce Capacity?
Calculating true workforce capacity requires understanding the usable human capacity available after real-world constraints are considered. Here is a practical approach to do it accurately:
Define Gross Workforce Capacity and Baseline Hours
The first step is to define gross workforce capacity, which represents the total theoretical hours the workforce can deliver within a given period. Establishing a consistent baseline across roles and teams creates a consistent starting point for capacity measurement and supports subsequent activities, including availability adjustments, demand comparison, and human capacity gap analysis.
The formula to calculate gross workforce capacity is:
Where: Standard Working Hours = Workdays × Hours per Day
Calculate FTE and Standardize Headcount
The next step is converting different employment types into a common planning unit using Full-Time Equivalent (FTE). This ensures human capacity calculations remain consistent when teams include a mix of full-time employees and part-time staff. Standardizing headcount at the role level also helps organizations assess workforce capacity more accurately for specific skills and responsibilities.
The formula to calculate FTE is:
The formula to calculate FTE based on role is:
Factor Leaves and Holidays into Capacity Plans
After establishing baseline workforce capacity, adjust it for the time that is not realistically available for planned work. This includes planned leave, training time, internal meetings, and ongoing support or ad-hoc projects. Deducting these hours helps convert gross workforce capacity into a more realistic view of available working hours.
The formula to calculate Net Capacity is:
Where: Non-Available Hours = Leaves + Holidays + Training Hours + BAU / Support Time
Use Utilization Rates to Refine Net Workforce Capacity
The next step is to refine net workforce capacity by applying realistic utilization rates. Utilization reflects the portion of available time that can be spent on planned work after accounting for meetings, coordination, and operational overhead. Applying role-specific utilization benchmarks helps convert available hours into realistic workforce capacity.
The formula is:
Where:
1. Net Workforce Capacity = Available hours after deducting leave, holidays, and non-project time
2. Target Utilization Rate = Realistic percentage based on role, delivery model, and organizational maturity
Explore how businesses can measure different types of resource utilization.
Factor in Efficiency and Productivity Losses
Next, adjust workforce capacity to account for real-world efficiency and productivity losses that reduce actual deliverable output. These include ramp-up time, skill proficiency gaps, context switching, rework, and collaboration overhead. Applying an efficiency factor prevents systematic overestimation of human capacity and improves planning accuracy.
The formula to calculate this is:
Typical efficiency factor range: 0.80 – 0.95
If multiple factors apply:
Combined Efficiency Factor = Onboarding Time X Learning Curve X Focus X Rework
Adjusted Capacity = Productive Capacity X Combined Efficiency Factor
Determine True Capacity Across Roles and Skills
The final step is calculating true human capacity by combining all prior adjustments into a single, realistic figure. This calculation should be performed at the level where decisions are made, such as by role, skill, location, etc. The resulting value represents the actual human capacity available for resource planning, gap analysis, and scenario planning.
The formula to calculate true workforce capacity is:
X Efficiency
In FTE terms:
True Capacity (FTE) = True Capacity (Hours) / Standard Full-Time Hours
With true workforce capacity established, the next step is understanding how to apply this data within a structured workforce capacity planning process.
Learn how to measure resource capacity and demand effectively.
Workforce Capacity Planning Process (Step-by-Step)
A structured workforce capacity planning process helps organizations apply capacity data consistently across project lifecycles. Here is the step-by-step approach for turning human capacity insights into practical workforce decisions:
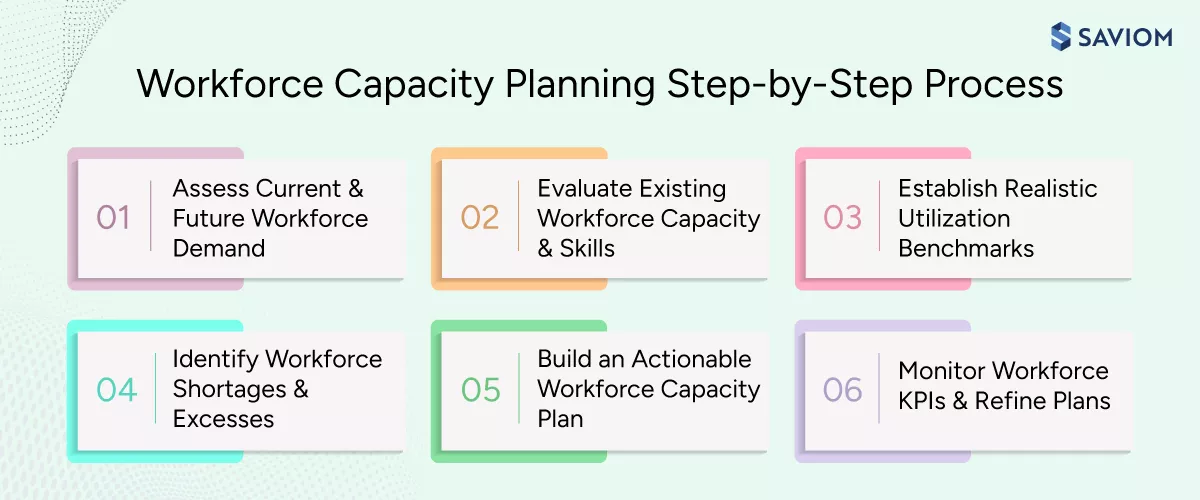
Assess Current and Future Workforce Demand
Begin by capturing current and upcoming work across operations and strategic initiatives using workforce demand forecasting. Break this down by role, skill, effort, and time period to create a time-phased demand view. This will help identify workload peaks, seasonal shifts, and upcoming delivery commitments.
Evaluate Existing Workforce Capacity and Skills
Next, evaluate available workforce capacity by accounting for working hours, leave, utilization levels, internal meetings, trainings, and non-project commitments. At the same time, use a skill matrix that captures role, skills, proficiency, and certifications to understand current capability readiness.
Establish Realistic Utilization Benchmarks
The next step is to establish realistic utilization benchmarks for different roles and teams. Utilization benchmarks define the percentage of time employees are expected to spend on productive or billable work. Setting realistic utilization targets ensures workforce capacity is used efficiently while preventing employee burnout.
Read our blog on resource utilization and explore how it helps in boosting workforce productivity.
Identify Workforce Shortages and Excesses
According to a McKinsey & Company study, “87% of companies worldwide already have a skill gap or expect to have one within a few years.”
At this stage, organizations compare forecasted workforce demand with available workforce capacity across roles, skills, and time horizons. This analysis helps identify workforce shortages, emerging skill gaps, and excess human capacity in advance. Consequently, managers can plan corrective actions before commitments are finalized.
Build an Actionable Workforce Capacity Plan
Based on the identified shortages and excesses, define corrective actions such as workload rebalancing, upskilling programs, or onboarding additional staff. Use these actions to sequence work, adjust priorities, and prepare a capacity-feasible execution plan. This plan should clearly define who will do what and when, and how workforce capacity risks will be managed.
Monitor Workforce KPIs and Refine Plans
Finally, track resource management KPIs such as workforce utilization, productivity, schedule adherence, capacity vs. demand variance, bench time, etc., on an ongoing basis. Use these insights to assess how plans are performing in practice, take corrective actions, and improve workforce capacity planning accuracy over time.
Explore what a resource management plan is and how to build one.
With the workforce capacity planning process clearly defined, let us now see how this approach differs from resource capacity planning, which operates at a broader organizational level.
Workforce Capacity Planning vs. Resource Capacity Planning
Workforce capacity planning and resource capacity planning are closely related concepts, but they serve different planning needs and operate at different levels of decision-making. Let us understand how they differ:
| Parameter | Workforce Capacity Planning | Resource Capacity Planning |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Human resources – workforce capacity, skills, and availability | All resources – people, budget, equipment, tools, and infrastructure |
| Demand Context | Business-level workforce demand across operations, growth initiatives, and strategic priorities | Project and portfolio-level demand across approved and pipeline initiatives |
| Primary Objective | Ensure the organization has the right workforce capacity and skills to support business demand | Ensure overall resource capacity is sufficient to execute projects and portfolios successfully |
| Planning Perspective | Workforce readiness and capability planning | Delivery feasibility and execution planning |
| Core Activities | Workforce demand forecasting, upskilling, hiring, and workforce utilization optimization | Capacity vs. demand comparison across projects, resource allocation planning, and portfolio feasibility validation |
| Ownership | HR, workforce planners, delivery leaders, and PMO | PMO, portfolio leaders, project and resource managers |
| Business Outcome | Workforce readiness to support business growth and operational continuity | Confident project execution with realistic resource commitments |
Read this blog to learn more about resource capacity planning.
Having explored the differences, let us now examine how demand forecasting informs and strengthens workforce capacity planning decisions.
How Does Demand Forecasting Support Workforce Capacity Planning?
Here is how accurate demand forecasting supports human capacity planning by replacing assumptions with forward-looking visibility:
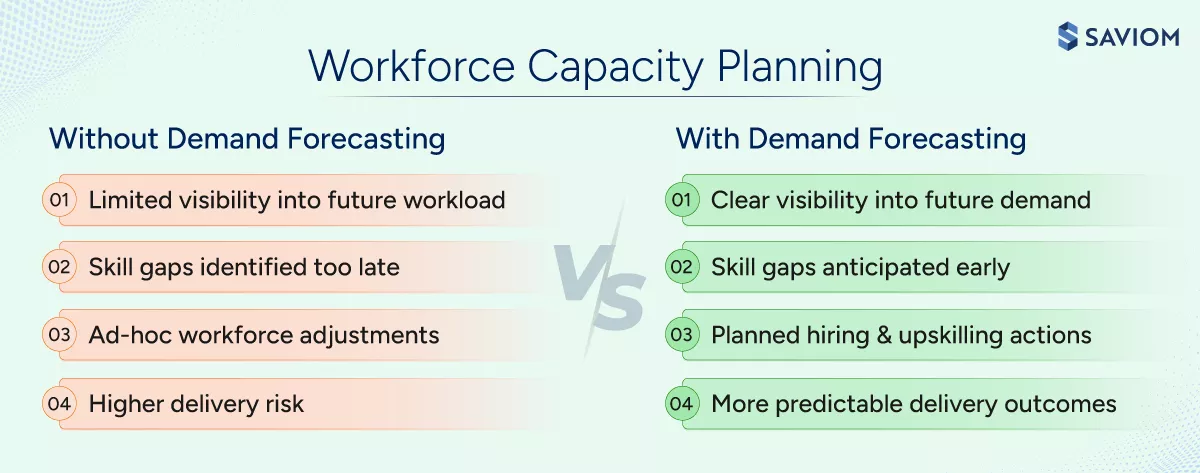
- Provides visibility into the upcoming workforce demand:
Forecasting work across projects, operations, and strategic initiatives helps organizations anticipate workforce requirements early and prepare before demand peaks. - Enables proactive workforce decisions:
Early demand insights across roles and skills enable managers to plan hiring, redeployment, or upskilling initiatives based on data rather than assumptions. - Improves workforce allocation and utilization:
Aligning forecasted demand with workforce capacity helps organizations allocate talent by skills and availability while maintaining balanced utilization across teams and roles. - Reduces workforce risks and constraints:
Analyzing future demand highlights potential workforce capacity shortages and skill gaps early. Consequently, managers can address resource risks proactively and prevent delivery disruptions.
After understanding how demand forecasting supports workforce capacity planning, the next step is to see why scenario modeling is critical for managing uncertainty.
Why is Scenario Modeling Critical to Workforce Capacity Planning?
According to a GoodFirms’ survey, “34.2% of companies rely on scenario planning for more accurate forecasting.”
Scenario modeling helps organizations understand how workforce capacity holds when demand, availability, or priorities change. Let us understand its role in workforce capacity planning:
- Assesses workforce capacity under different conditions:
By simulating changes in demand, priorities, or timelines, scenario modeling helps test how workforce availability is affected. This helps organizations validate whether workforce capacity plans remain feasible. - Flags workforce capacity and capability gaps early:
Comparing multiple scenarios surfaces potential workforce shortages, overload risks, and critical skill gaps early, allowing issues to be addressed before project initiation. - Supports cost and staffing trade-off decisions:
Evaluating different scenarios helps organizations compare alternative workforce capacity options side by side and understand their cost implications. Consequently, managers can select the most cost-effective workforce plan.
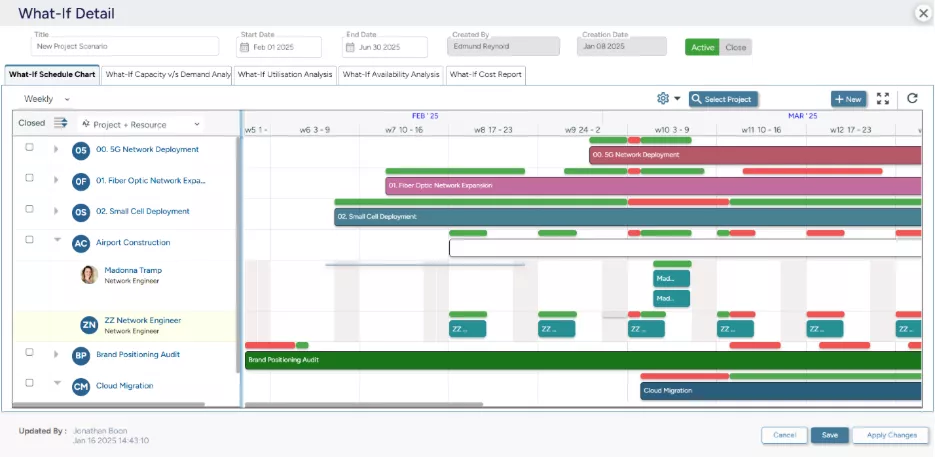 SAVIOM’s Scenario Modeling helps managers compare workforce capacity across multiple demand scenarios and choose the best course of action.
SAVIOM’s Scenario Modeling helps managers compare workforce capacity across multiple demand scenarios and choose the best course of action.
Learn more about scenario planning and its benefits.
Moving on, let us explore the common challenges organizations face when implementing workforce capacity planning.
Challenges of Workforce Capacity Planning
Despite having defined processes and tools, organizations often struggle to apply workforce capacity planning consistently in real-world conditions. Here are the common challenges organizations face in workforce capacity planning:
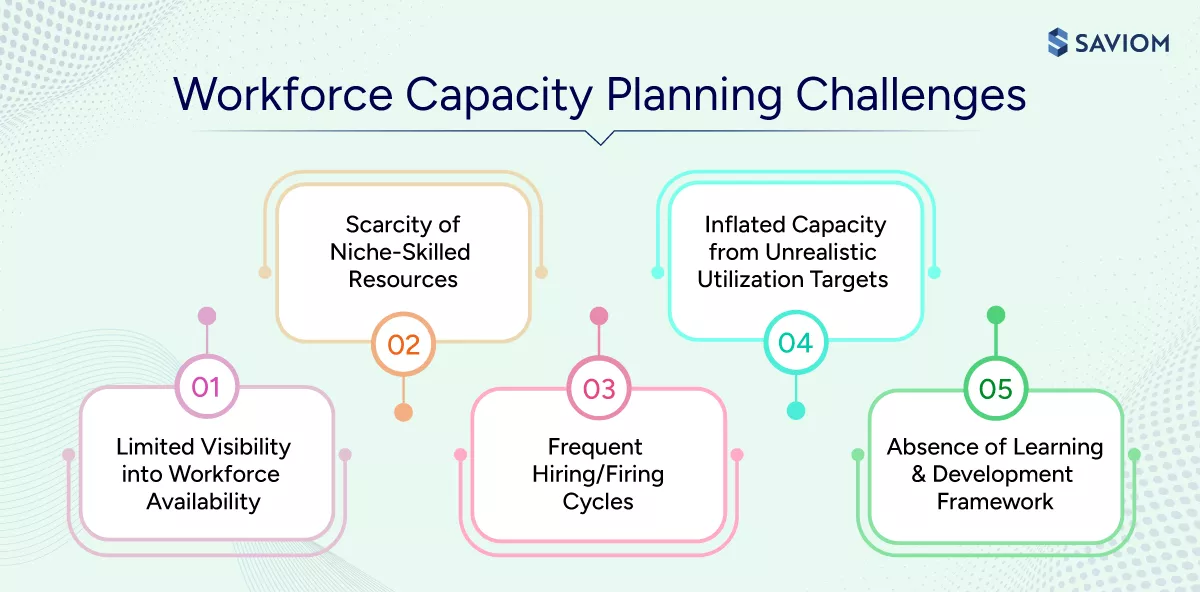
Limited Visibility into Workforce Availability
Many organizations still rely on siloed systems to store, plan, and manage workforce data. This lack of real-time visibility into workforce availability, utilization, and non-project commitments makes it difficult to assess true workforce capacity. As a result, organizations overcommit the workforce, misallocate talent, and face delivery delays.
Scarcity of Niche-Skilled Resources
Niche or high-demand skills are often scarce and cannot be hired, replaced, or developed quickly when demand rises. Even when overall workforce capacity appears sufficient, the absence of critical skills makes it difficult to allocate the workforce efficiently. This creates execution bottlenecks and delivery risks.
For instance, an IT services organization delivering multiple cloud transformation projects may require certified cloud architects simultaneously. Even with a sufficient overall headcount, the limited availability of these specialized roles can delay key milestones or force the organization to rely on overutilizing a few experts or hiring costly contractors.
Learn how the IT industry benefits from effective workforce planning.
Frequent Hiring/Firing Cycles
Frequent hiring during demand spikes and layoffs during slow periods indicate unstable workforce planning and weak alignment between demand and available workforce capacity. This increases recruitment and onboarding costs, disrupts team continuity, and affects knowledge retention. Moreover, frequent hiring/firing cycles reduce overall productivity, as organizations repeatedly reset teams rather than stabilizing execution.
Inflated Capacity from Unrealistic Utilization Targets
Many organisations plan workforce capacity based on unrealistic utilization targets without accounting for meetings, learning, and other real-world resource constraints. This creates an inflated view of available human capacity, leading to overcommitment once work begins. Over time, such planning practices negatively impact workforce well-being and make capacity forecasts unreliable.
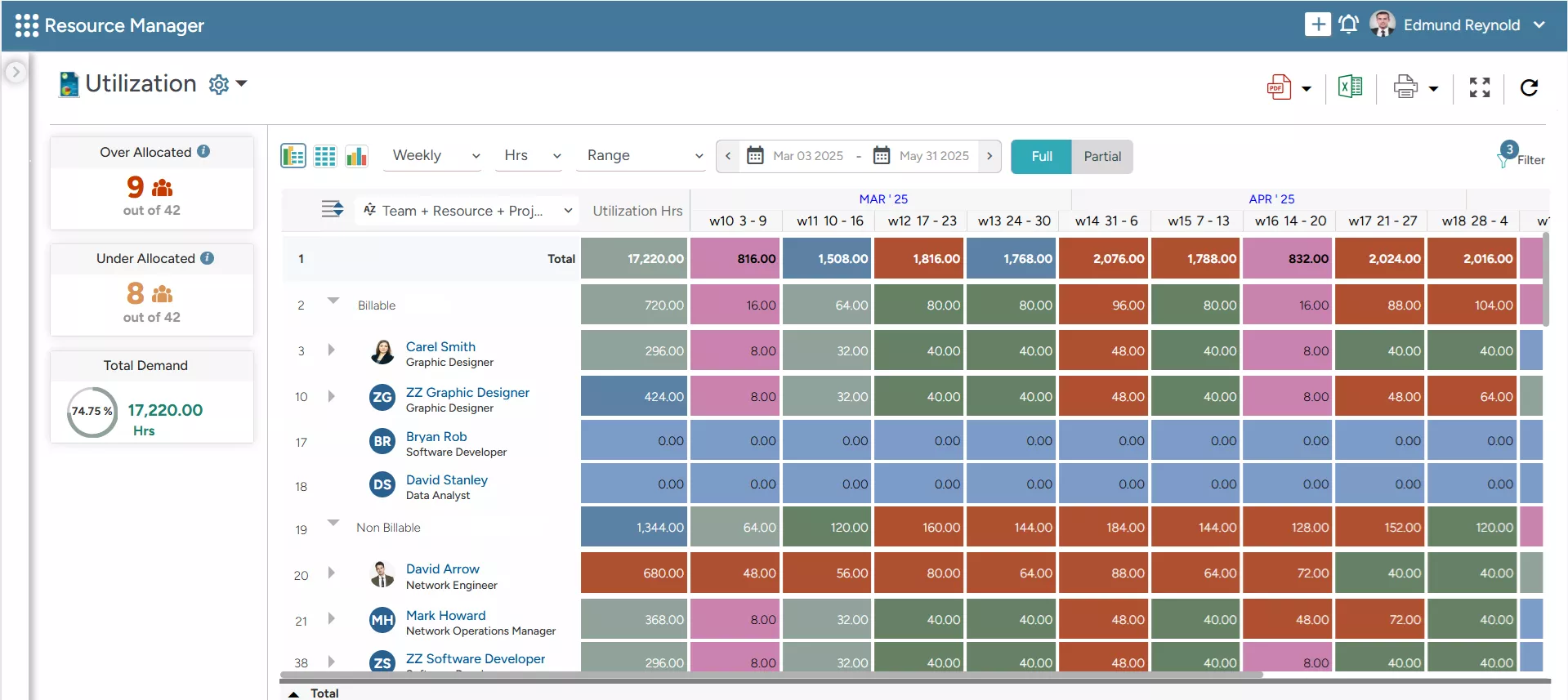 SAVIOM’s Utilization Dashboard helps managers identify over- and under-allocation caused by unrealistic utilization targets, preventing inflated capacity assumptions.
SAVIOM’s Utilization Dashboard helps managers identify over- and under-allocation caused by unrealistic utilization targets, preventing inflated capacity assumptions.
Lack of a Structured Learning & Development Framework
When organizations lack a structured workforce upskilling strategy, they struggle to address evolving skill requirements using existing talent. As a result, skill gaps persist longer than necessary, increasing reliance on expensive external hiring or outsourcing and limiting the organization’s ability to build human capacity sustainably.
For example, a manufacturing organization introducing new automation technologies may lack a structured learning and development framework to reskill its machine operators. As a result, employee productivity drops as they struggle to transition into new roles, and the organization becomes dependent on external hires or consultants to bridge skill gaps.
Explore more resource capacity planning challenges and how to overcome them.
With the key challenges of workforce capacity planning identified, the next step is to look at emerging trends shaping how organizations approach workforce capacity management today.
Emerging Trends in Workforce Capacity Planning
As workforce complexity increases, organizations are rethinking how workforce capacity planning is performed and supported at scale. The following are the key trends shaping the future of workforce capacity management:
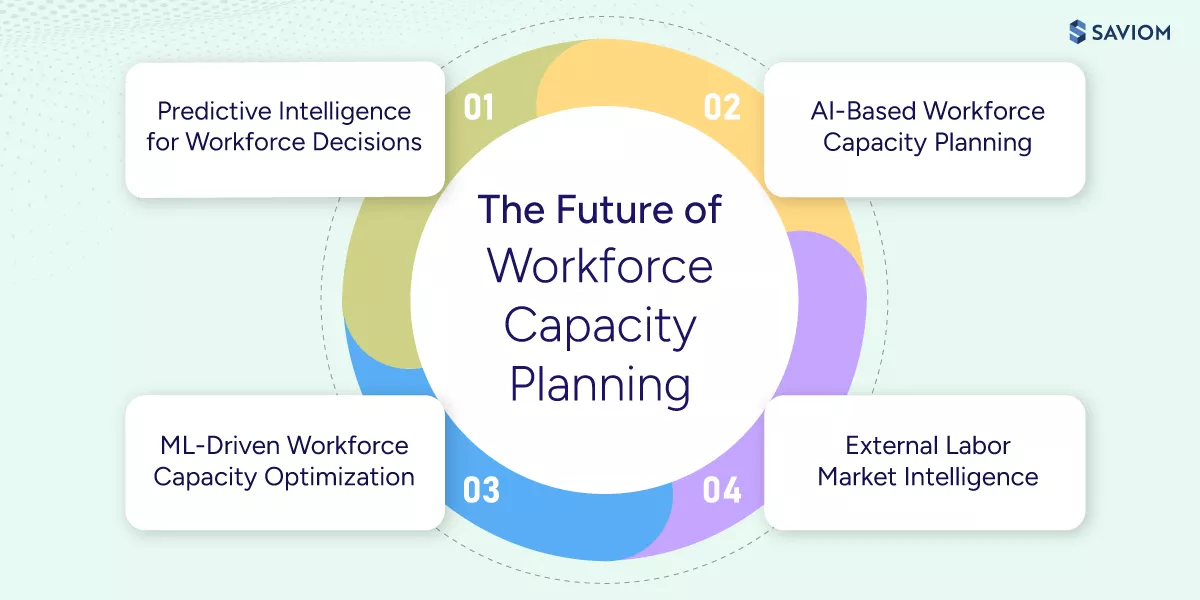
Predictive & Prescriptive Intelligence for Workforce Decisions
Predictive and prescriptive intelligence shifts workforce planning from hindsight reporting to forward-looking decision-making by leveraging workforce capacity forecasting. This helps organizations anticipate workforce capacity risks early and take corrective actions before shortages, overloads, or cost overruns occur.
Read our blog on resource forecasting and how it helps identify capacity gaps.
AI-Based & Autonomous Workforce Capacity Planning
AI-driven workforce capacity planning enables systems to continuously adjust workforce plans as demand, availability, and constraints change, rather than relying on static planning cycles. This reduces manual planning effort and improves the speed and consistency of workforce capacity decisions across the organization.
Machine Learning-Led Workforce Capacity Optimization
Machine learning models help organizations identify the optimal workforce mix by learning from historical demand, utilization patterns, and delivery outcomes. Over time, this improves the accuracy of workforce capacity requirement planning and enables continuous optimization across cost, skills, and utilization levels.
External Labor Market Intelligence and Workforce Signals
Workforce capacity planning is increasingly incorporating external labor market intelligence, including trends in skill availability, compensation benchmarks, hiring cycles, and regional talent supply constraints. These signals help anticipate talent shortages earlier, refine upskilling strategies, and build more resilient workforce capacity plans.
Learn about the top resource management trends.
Having understood the emerging trends shaping workforce capacity planning, let us now look at workforce capacity planning best practices organizations should follow.
Workforce Capacity Planning Best Practices
To achieve consistent outcomes, organizations must apply workforce capacity planning with clear governance, disciplined execution, and ongoing review. Let us take a look at the best practices organizations should follow:
Align Workforce Capacity Planning with Business Strategy
Workforce capacity planning should align with business strategy so that the right skills are available at the right time to support growth initiatives, transformation programs, and operational priorities. This involves translating strategic objectives into forward-looking workforce and skill requirements, helping managers prepare talent pipelines that support future demand.
Base Workforce Capacity Planning on Real-Time Data
Workforce capacity decisions should be grounded in real-time data on availability, skills, and planned work rather than static or outdated assumptions. Using current information improves workforce capacity analysis, reduces planning errors, and enables faster adjustments as demand and priorities change.
Read our blog to learn about the resource capacity model and how it helps businesses.
Shift from Headcount-Based to Skill-Based Planning
Relying only on headcount makes it challenging to assess whether the organization actually has the skills required to meet demand. Thus, organizations should plan workforce capacity taking into account roles, skills, and proficiency levels. This reduces misalignment between available talent and work requirements, preventing execution bottlenecks.
Plan Workforce Capacity Continuously, Not Annually
Workforce demand and priorities change frequently, making static annual human capacity plans less effective. Thus, organizations should adopt continuous workforce capacity planning, which involves reviewing and updating plans regularly as demand evolves. This approach enables timely adjustments in human capacity, helping organizations address shortages or surpluses proactively.
Read in detail about resource capacity building and how it helps drive business growth.
Balance Utilization with Workforce Well-Being
According to a 2025 study by Infinite Potential, “82% of employees are at risk of burnout.”
Pursuing consistently high utilization levels may improve short-term output but often leads to fatigue and declining productivity over time. Setting realistic utilization targets helps protect workforce well-being, reduce attrition, and sustain delivery performance without placing prolonged strain on employees.
Gain clear visibility into workforce demand, capacity, and skill gaps with SAVIOM’s resource management software. Book a demo today to see it in action.
Having explored workforce capacity planning best practices, let us now examine how this approach drives workforce cost optimization, delivery reliability, and retention outcomes.
Workforce Capacity Planning for Cost Control, Delivery & Retention
Workforce capacity planning directly influences how effectively organizations control costs, meet delivery commitments, and retain critical talent over time. Let us see how:
How Workforce Capacity Planning Helps Control Costs?
Workforce capacity planning helps control resource costs by ensuring workforce demand is aligned with available human capacity before work begins. This prevents reactive hiring, excessive overtime, and prolonged bench time.
Moreover, by identifying workforce shortages and excesses early, managers can make cost-effective decisions such as redeploying existing talent, upskilling employees, or planning targeted hiring. Consequently, they maintain better control over workforce-related costs while ensuring consistent delivery performance.
Discover what is a capacity report and how to build one.
How Workforce Capacity Planning Improves Delivery Predictability?
Workforce capacity planning helps firms improve delivery predictability by aligning business commitments with realistic workforce availability across skills, roles, and time periods.
This enables organizations to validate whether delivery plans are achievable before execution begins. As a result, enterprises can prevent last-minute schedule changes, avoid mid-project human capacity shortfalls, enabling teams to execute work more consistently and on time.
How Workforce Capacity Planning Enhances Employee Retention?
According to a Gallup study, “12% of US employees left their jobs due to a lack of career development opportunities.”
When organizations plan workforce capacity based on availability, skills, and realistic utilization limits, they reduce the likelihood of prolonged overload and role misalignment. This helps maintain both productivity and workforce well-being.
In addition, workforce capacity planning also supports career development by helping organizations identify future skill requirements and create structured upskilling and role-transition opportunities. As people gain opportunities to grow and learn new skills, job satisfaction increases, and employee retention increases.
Conclusion
Effective workforce capacity planning ultimately determines whether organizations operate with control or constant disruption. When demand, skills, and availability are evaluated together, managers can make timely resourcing decisions and maintain execution stability as priorities evolve. In increasingly complex environments, this discipline separates reactive organizations from those that scale with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Workforce capacity planning is the practice of aligning workforce supply with forecasted demand over specific time periods. It helps organizations identify capacity shortages and excesses early and take proactive actions such as hiring, upskilling, or workload rebalancing before execution risks arise.
Here is why workforce capacity planning is important for organizations:
1. Aligns workforce capacity with business demand
2. Reduces workforce costs and operational waste
3. Boosts workforce utilization levels
4. Facilitates data-driven upskilling and hiring
5. Promotes workforce well-being and boosts retention
Workforce capacity planning best practices are:
1. Align workforce capacity planning with business strategy
2. Base workforce capacity planning on real-time data
3. Shift from headcount-based to skill-based planning
4. Plan workforce capacity continuously, not annually
5. Balance utilization with workforce well-being
Here is the process to calculate true workforce capacity:
1. Define gross workforce capacity and baseline hours
2. Calculate FTE and standardize headcount
3. Factor leaves and holidays into capacity plans
4. Use utilization rates to refine net workforce capacity
5. Factor in efficiency and productivity losses
6. Determine true capacity across roles and skills
Workforce capacity planning reduces attrition risk by maintaining realistic workload levels and preventing overutilization. It provides early visibility into emerging workforce capacity gaps, enabling upskilling or targeted hiring. This creates a more balanced work environment, improving employee engagement and long-term retention.










