Managing project budget is a continuous process where managers always look for innovative ways to complete the deliverables without any cost escalation. However, issues like last-minute hiring, improper allocation, and scope creep can blow up project costs and cause budget overruns. This can adversely affect project profitability, and as a result, managers might have to seek additional funds from the sponsors or clients to continue their work.
The good news? With effective project cost management, such setbacks can be anticipated and avoided. It provides a structured approach to monitor and control costs by reviewing project progress during each milestone. This enables managers to identify discrepancies early and take corrective actions, ensuring the project stays on track and within budget.
This blog will explain the nitty-gritty of project cost management and various strategies to reduce project expenses.
Let’s get started!
What is Project Cost Management?
Project cost management is the process of planning, estimating, allocating, and controlling project expenses. It begins at the planning phase and continues throughout the project lifecycle. The project manager continuously reviews, monitors, and adjusts costs based on actual progress and changing dynamics to ensure it remains aligned with the approved budget.
Project managers can take actions like adjusting the budget, establishing a change control process, or deploying resources from low-cost locations if there is a cost overrun. Thus, by proactively managing costs, organizations can avoid budget escalations, maintain financial control, and deliver projects profitably.
To make it easier to understand, let’s look at an example.
Example of a Project Cost Management
Imagine a software company developing a mobile app. Initially, they estimated the project cost to be $12,000, which includes developer salaries, design costs, testing, and marketing. However, clients keep asking to add new features as the project progresses. These modifications are approved and implemented without due process, and the company is compelled to hire extra resources to complete the project within the timeline. This results in an increase in cost to $18,000.
However, with a proper project cost management plan in place, the manager can do the following things to ensure that the app is developed without any cost escalation:
- Set up a cost baseline early to track actual spending against planned costs.
- Follow a change control process to review and approve the new requests. Managers can decide which new features to keep by performing a cost and impact analysis to ensure it doesn’t impact the budget.
- Adjust the original budget when hiring new resources and justify it to the project stakeholders.
- Utilize tools like earned value management (EVM) to flag instances where spending is outpacing progress.
- Check if existing resources could be retrained/upskilled before expanding the team, thereby
- Provide regular cost reports to keep stakeholders informed and manage expectations.
This approach will help keep the project budget on track, even as the scope evolves.
Now that we understand project cost management, let’s examine its different types.
Types of Project Cost
Project cost is generally divided into different types based on where and how the money is spent during a project. Understanding these types helps track and control project expenses. Let us have a look at them:
Direct Costs
In project cost management, direct expense can be linked to a specific project, task, or activity. Salaries for project-specific employees, purchased materials, transportation, and equipment used exclusively for its execution are some common examples. These costs play a crucial role in project budgeting as they directly impact the total project expenditure.
Indirect Costs
Indirect costs are not directly linked to a specific project but are essential for running the overall business or supporting a project portfolio. These costs are often referred to as overhead expenses. Examples include office rent, utility bills, administrative staff salaries, security expenses, and other general operational costs supporting the entire organizational workflow.
Fixed Costs
Fixed costs are expenses that do not change based on the project’s output or level of activity. These costs are usually time-based, remain constant, and are not affected by the project volume, making them easier to estimate and plan for in advance. Examples include costs for acquiring advanced technology, rent or lease expenses, and yearly software license fees.
Variable Costs
Variable costs change based on the length of the project or output. These costs are directly linked to the work volume and depend on project demands. Moreover, they can be more challenging to estimate compared to fixed costs. Examples of variable costs include raw material procurement, wages paid to workers, expenses of hired machinery, shipping or delivery charges, and sales commissions.
Read More: What is a Project Lifecycle? Phases, Importance, & Best Practices
Recurring Costs
The expenses that keep repeating at regular intervals throughout a project are known as recurring costs. Since these costs occur consistently, they can have a significant impact on the project’s cash flow if not properly managed. Therefore, it is important to identify and plan for them in advance. Common examples of recurring costs include employee salaries, utility bills, and software subscription fees.
One-Time Costs
One-time costs are also known as non-recurring or fixed costs. These are expenses that occur only once in a project’s lifecycle and are not part of the ongoing business activities. Accurate estimation of one-time costs is crucial for effective project budgeting and financial planning. A few examples of one-time costs are hiring a consultant for a specific task or obtaining specific software needed for a project.
Sunk Costs
Sunk cost refers to money that has already been spent and cannot be recovered. Recognizing these costs is important because it helps avoid the sunk cost fallacy. This is when businesses keep investing in a failing project just because they’ve already spent a lot, leading to poor decisions and more loss of resources and money. Examples include money spent on marketing, research, new equipment, or facilities.
Contingency Costs
Contingency costs are reserve funds included in a project budget to handle unexpected expenses or resource risks that may arise during the project. They serve as a financial buffer or safety net to protect the project from unforeseen challenges like technological issues, supplier delays, etc. Moreover, contingency funds can be used to cover unexpected site conditions, changes in project scope, or unplanned repairs.
Read More: What Are Resource Risks in Project Management & How to Mitigate Them?

After learning about the types of project costs, it’s time to look at some effective project cost management methods.
Project Cost Management Methods
Organizations can use various project cost management methods to control and manage expenses effectively. Here are a few of them:
Cost Estimation
Cost estimation is one of the most important methods in project cost management. It involves predicting the total cost required to complete a project based on available information. This method helps project managers create a realistic budget by identifying all possible expenses, including materials, equipment, and other resources. Different techniques, like historical data and estimation tools, are used to calculate costs.
| Total Estimated Project Cost = Direct Costs + Indirect Costs + Contingency Costs + Reserve Costs |
|---|
Cost Budgeting
The cost budgeting method focuses on allocating the estimated costs to different parts or phases of a project. In project cost management, this method helps set a clear spending plan and ensure that required funds are available when needed. It divides the estimated cost across tasks, activities, or departments and helps create a structured budget plan.
| Project Budget = Cost Estimates + Contingency Reserves + Management Reserves |
|---|
Read More: How to Develop an Effective Project Budget in 8 Simple Steps?
Cost Control
Cost control focuses on monitoring, tracking, and managing project expenses to ensure it stays within the approved budget. It involves comparing actual costs against the planned budget, identifying deviations, and taking corrective actions to avoid overspending. This method helps project managers avoid unnecessary overspending and control project expenditures.
Earned Value Management
Earned value management (EVM) is an advanced method of managing cost that helps measure project performance and progress in terms of both schedule and project performance. It uses key metrics like Planned Value (PV), Earned Value (EV), and Actual Cost (AC) to analyze variances in the project and forecast future performance. This method helps identify budget overruns and delays beforehand.
Here are some important formulas used in the earned value management (EVM).
| Cost Variance (CV) = Earned Value (EV) – Actual Cost (AC) |
|---|
| Scheduled Variance (SV) = Earned Value (EV) – Planned Value (PV) |
|---|
| Cost Performance Index (CPI) = Earned Value (EV) ÷ Actual Cost (AC) |
|---|
| Schedule Performance Index (SPI) = Earned Value (EV) ÷ Planned Value (PV) |
|---|
Now that we are familiar with the different project cost management methods, let us move ahead and understand their importance.
Read More: What is Earned Value Management, and How to Measure it for Project Success?
Why is Project Cost Management Important?
Project cost management ensures that a project stays within its approved budget by avoiding unnecessary expenses. It helps organizations plan their finances effectively, allocate cost-effective resources, and avoid last-minute financial stress. This makes it easier for project managers to track progress and make informed decisions throughout the project lifecycle.
Moreover, effective project cost management helps increase profitability, maintain client trust, and improve project efficiency. It also prepares the project manager to handle unexpected costs through proper budgeting and contingency planning. With proper cost management strategies in place, businesses can avoid wastage of resources and achieve better control over project performance and outcomes.
Let us now shift our attention to the common challenges faced in project cost management.
Challenges of Project Cost Management
Here’s a rundown of some common project cost management that organizations face:
Inaccurate Cost Estimation
Inaccurate expense estimation is one of the most common and critical challenges in project cost management. When the initial cost estimates are unrealistic or insufficient, it can lead to budget overruns and financial stress later in the project. This typically occurs due to a lack of accurate data, incorrect assumptions, overlooking key expenses, or market volatility.
Unexpected Scope Changes
Unexpected scope changes, or scope creep, happen when new requirements, features, or tasks are added to a project after the budget and plan are finalized. These changes often lead to additional resource needs and extended project timelines, thereby increasing the cost. If not adequately managed, scope changes can completely disrupt the financial plan of a project.
Read More: What is a Project Scope? Benefits, Best Practices, and Steps to Create an Effective One
Insufficient Resource Planning
When resources like workforce, equipment, tools, or materials are not properly planned or allocated, it can lead to unexpected expenses and project delays. Poor resource planning may result in a shortage or excess of resources, affecting the project budget. Additionally, mismanagement of resources can cause inefficiencies and reduce overall project productivity.
Absence of Risk Mitigation Plan
Every project carries certain risks, such as market fluctuations, lack of timely resource availability, technical failures, or unforeseen delays. Without a proper risk mitigation plan, these unexpected situations can lead to sudden expenses, pushing the project over budget. Moreover, the absence of early risk identification can hinder timely responses, compounding issues and escalating overall project costs.
Read More: Risk Matrix in Project Management: An Ultimate Guide
Neglecting Cost Tracking & Monitoring
If project expenses are not tracked regularly, small cost overruns can go unnoticed and eventually become major financial problems. This lack of visibility often results in mismanaged funds, resource wastage, and delayed project completion. Inconsistent expense tracking can also make it difficult to forecast future costs accurately, leading to poor financial decisions and reduced project stakeholder confidence.
Poor Stakeholder Communication
A lack of clear and timely communication between project managers, team members, and key stakeholders can lead to misunderstandings, confusion, and wrong assumptions about project costs. This can result in delayed approvals and conflicts over resource allocation, which can result in overspending. Furthermore, there can be last-minute firefighting and financial strain without transparent project communication.
After exploring the challenges, let us now learn how to calculate project costs.
Read More: What is Project Communication Management? Types, Benefits & Best Practices
How to Calculate Project Cost?
Let us now understand how calculating project cost plays a key role in setting a realistic budget and managing expenses efficiently.
Define Project Scope & Create WBS
The first step in calculating project cost is clearly defining the scope. This means identifying what work needs to be done, what goals must be achieved, and what deliverables are expected. Once the scope is clear, creating a work breakdown structure (WBS) is the next important step. A WBS breaks the entire project into smaller manageable tasks, helping the team complete them sequentially and efficiently.
Identify Resource Requirements
Once the project scope and tasks are defined, the next step in project cost management is identifying the resources needed to complete each task. Resources can include employees, materials, equipment, software, and tools required for the project. Proper identification of resources helps estimate how much they will cost and ensures that the project has everything it needs to run smoothly without delays.
Read More: What are Project Resources? How to Manage Them Effectively?
Assess All Cost Categories
Assessing all cost categories means dividing the total expense into different types, such as direct, indirect, fixed, variable, recurring, and contingency. Each category covers various expenses, like salaries, materials, rent, utilities, or risk-related costs. Breaking down the expenses into these categories makes it easier to get a clear and complete view of the total project cost.
Calculate Total Project Cost
Calculating the total project expense gives a precise estimate of how much the project will cost from start to finish. It is done by adding up the cost of all tasks, project resources, and expenses listed in the previous steps. A well-calculated total project cost helps set a realistic budget and manage funds effectively throughout the project. It also prepares the firm to handle any financial risks that may arise during project execution.
Read More: What is Billability and How to Calculate It?
Review and Validate
The final step is thoroughly reviewing and validating the estimated budget. This means carefully checking all the calculations, resource costs, and assumptions made during the estimation process. Additionally, involving project stakeholders and team members in this review can provide valuable feedback and help identify discrepancies. This reduces the chances of surprises and helps keep the budget under check.
Now that we know how to calculate project cost, let’s explore some effective ways to reduce it.
Read More: 10 Common Project Management Mistakes and How to Fix Them?
7 Effective Ways to Reduce Project Cost
Reducing project costs without compromising on quality is a key goal for every project manager. Here are 7 effective ways to reduce expenses and ensure better project cost management.
Plan the Resources Effectively during the Project Initiation Phase
Managers can deliver projects within time and budget by carefully analyzing the requirements and assigning the right resources during the initiation phase. It helps prevent the misallocation of under-skilled or over-skilled personnel to project tasks. Using under-skilled resources can result in compromised quality, whereas engaging over-skilled resources may inflate costs and lead to budget overruns.
Moreover, project managers must allocate the best-fit available resources instead of the first visible first-fit ones. Distributing high-skilled resources across all projects instead of assigning them to a high-priority one further helps reduce costs. Getting this balance right from the start enables smoother project execution and ensures that all tasks are handled by appropriately skilled team members.
Read More: Project Initiation: Nine Effective Steps to Kick-off Projects the Right Way
Leverage Cost-effective Global Resources to Keep the Budget in Check
Matrix organizations offer the advantage of sharing highly skilled resources across multiple projects and functional teams. Visibility across matrix boundaries enables managers to identify and allocate cost-effective local and global resources by skills. If local resources for a particular skill set are not available, a multi-location policy helps leverage global resources from low-cost locations to do the job.
By leveraging this approach, businesses not only ensure optimal utilization of their global workforce but also significantly reduce project costs. Additionally, succession planning for critical multi-skilled resources can be challenging and expensive. However, distributing their responsibilities among multiple resources helps manage costs effectively.
Track Forecasted vs. Actual Spending to Control Project Cost
Resource management software plays a vital role in tracking key financial metrics of a project, such as costs, revenue, profit margins, and overheads. Regular monitoring of these indicators helps project managers prevent budget overruns. By comparing actual spending with the planned budget, managers can quickly identify any discrepancies and take corrective actions in advance to minimize risks.
Moreover, when budget challenges arise, resource leveling or smoothing can be applied. Resource leveling adjusts the project schedule to align with resource availability, while resource smoothing involves adding additional resources to ensure timely project delivery without exceeding the budget. It also enables better tracking of shared resources across multiple tasks, allowing resource managers to control costs.
Read More: What is Resource Management? A Comprehensive Guide
Negotiate Better Rates for Supplies, Services & Contracts
Project managers should build strong relationships with vendors, suppliers, and service providers to create opportunities for better deals and discounts. For this, managers can explore multiple vendor options, compare prices, and go for bulk purchases, often resulting in significant cost savings. Additionally, negotiating long-term contracts with trusted suppliers can provide more stable pricing and avoid sudden price hikes.
Moreover, establishing flexible payment terms, discounts for early payments, or bundled service packages can also help reduce costs. Regularly reviewing supplier performance and renegotiating contracts, when necessary, ensures that the project benefits from the best market rates. Ultimately, negotiation strategies can help project managers control costs without compromising the quality of supplies or services.
Reduce Last-Minute Hiring Costs for Pipeline Projects
Clear visibility into upcoming projects allows managers to plan resource requirements well in advance. With the help of resource capacity planning tools, they can perform a skill gap analysis to identify any resource surplus or shortage early. Managers can allocate surplus resources to other billable tasks, while managers can plan for upskilling or hiring contingent workers for shortages.
Moreover, proper project pipeline management helps avoid last-minute resource firefighting, often leading to higher costs or hiring resources with mismatched skill sets. Additionally, effective planning ensures that the right talent is available at the right time, maintaining quality and reducing unnecessary bench time, ultimately improving the project’s profitability.
Read More: 4 Steps to Perfect Your Project Pipeline Management Strategy
Reuse & Repurpose Existing Assets or Templates
Reusing and repurposing existing assets or templates is an effective way of managing project costs. Instead of creating everything from scratch, project managers can utilize available resources like previous templates, design frameworks, documentation, or tools. These ready-to-use assets save both time and money while maintaining consistency and quality across projects.
Additionally, reusing technical assets like software components, code libraries, marketing materials, or training modules helps avoid duplication of effort and lowers production costs. Repurposing resources also encourages knowledge sharing and promotes best practices within the organization. Finally, it ensures faster project delivery, reduces labor hours, and minimizes material wastage.
Implement a Job Rotation Strategy to Boost Productivity
Low employee productivity dampens the project quality, spikes costs, and eventually results in unplanned attrition. Allocating employees to project tasks without considering their skills and interests can lead to low productivity. Monotonous and limited work opportunities can cause a feeling of boredom and career stagnation among employees. Therefore, engaging employees in tasks that match their skills can improve productivity.
Resource managers can boost employee productivity by implementing a job rotation strategy. Exposing employees to different project tasks provides them with ample skill-building opportunities. It also encourages employees to build multiple secondary skills in addition to their primary skill set. These secondary skills also improve billability in case there is no available task matching their primary competencies.
Now that we have explored the ways to reduce project costs, let us understand how a project resource management tool can assist in project cost management.
Read More: Employee Productivity: What is it & Why Does it Matter?
How Can an Advanced Project Resource Management Tool Help Manage Cost?
A 5th gen resource management software plays a vital role in project cost management by providing better visibility, accurate planning, and efficient utilization of resources throughout the project lifecycle.
- The software’s all-in-one resource planner enables managers to slice and dice the resource plan across various dimensions, like role, experience, expertise, location, etc., to deploy cost-effective resources.
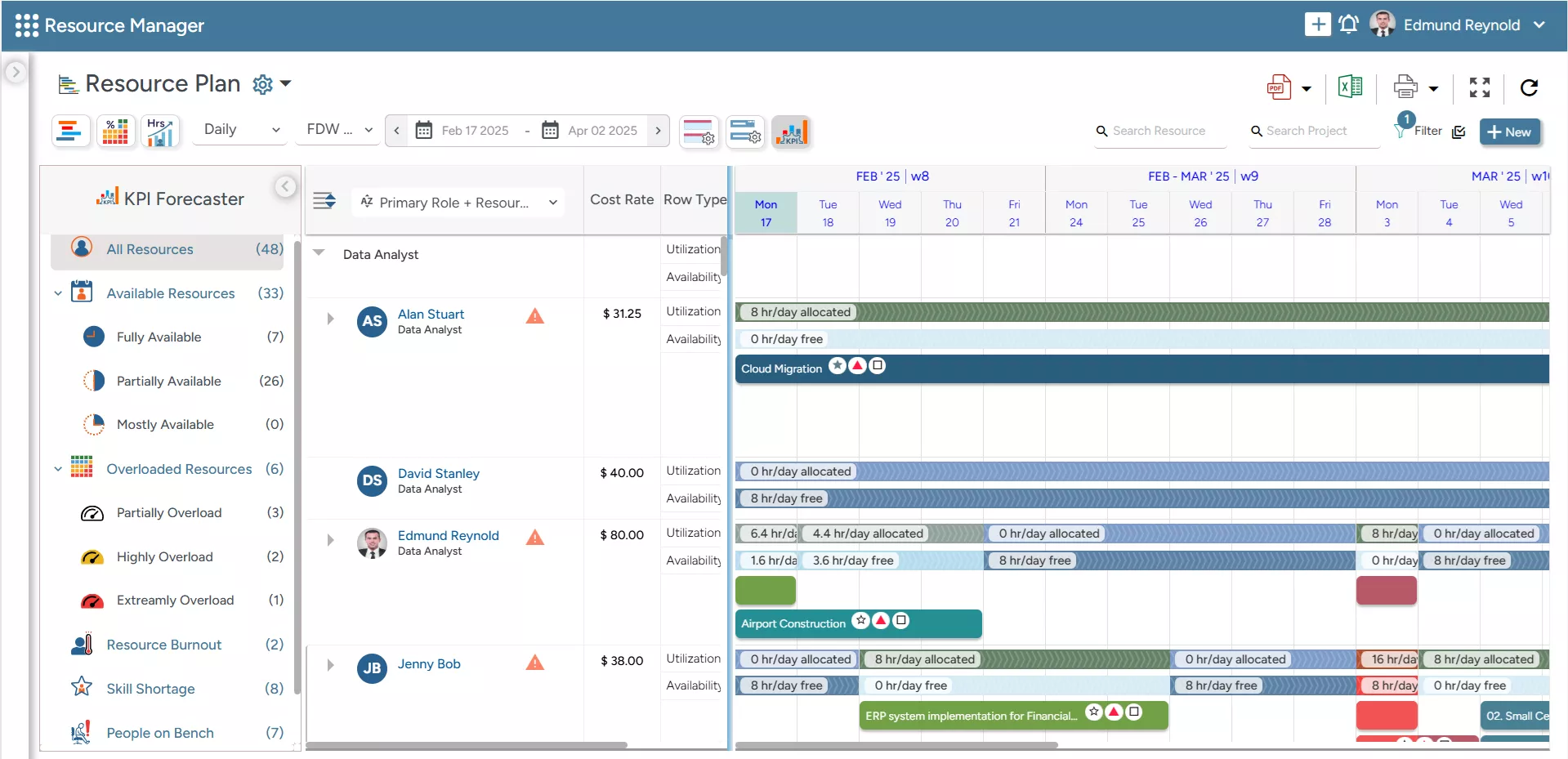
SAVIOM’S All-in-one Resource Planner helps managers customize resource plans across multiple dimensions, such as role, location, cost, etc.
- The embedded capacity planner enables managers to anticipate and assess short and long-term resource requirements. This helps prevent costly last-minute expensive hiring of resources.
- Intelligent KPI forecaster provides early warning of critical resource KPIs such as underutilization, overutilization, people on the bench, skill shortages, and project vacancies. Accordingly, businesses can act proactively to optimize resources.
- The tool’s forecast financial reports help managers track critical project financials such as revenue, costs, and actual spending and identify cost-inefficiencies. It allows them to take corrective measures and control project financials.
- The embedded competency matrix records, tracks, and updates skills in real-time. It enables managers to address skill gaps proactively and avoid expensive ad-hoc staffing.
- Finally, the what-if analysis feature enables organizations to simulate various resource planning scenarios and evaluate the financial impact of different decisions. This helps managers to arrive at the most effective and budget-friendly plan
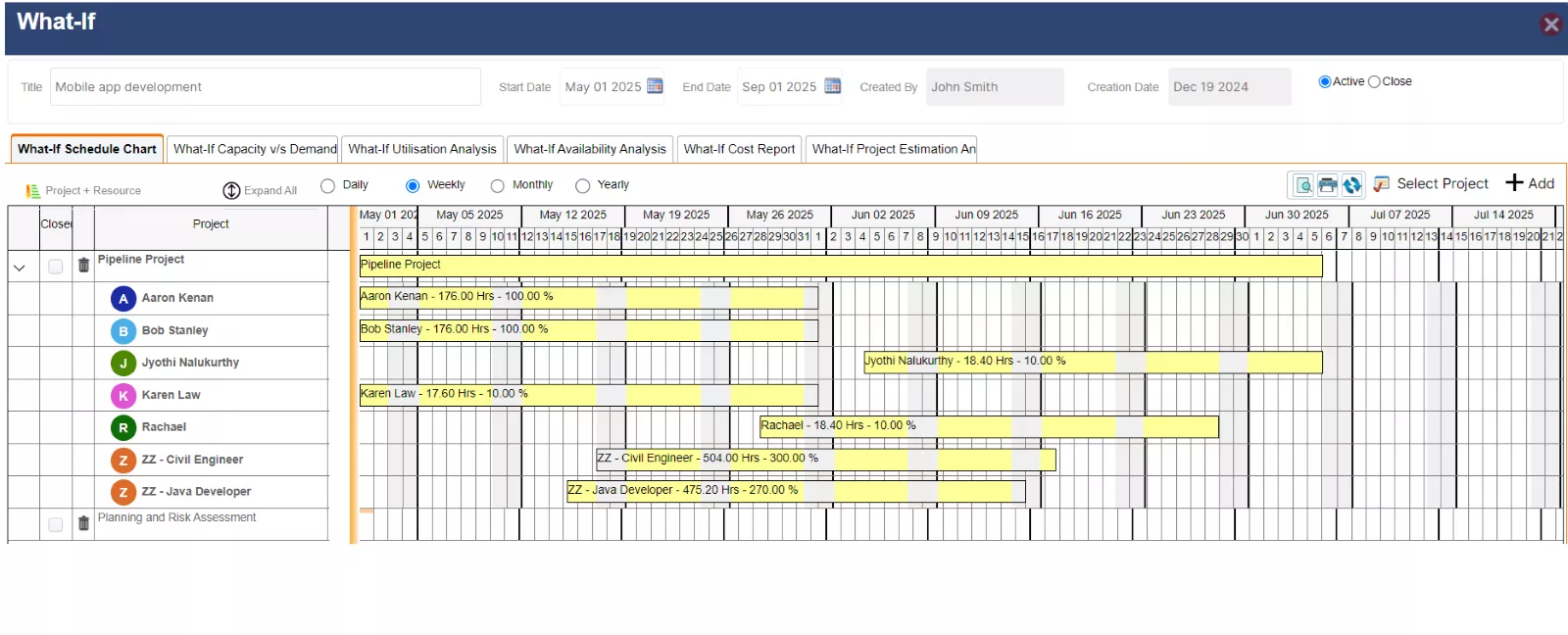 SAVIOM’s What-if Analysis feature allows organizations to compare various scenarios and assess their impact on project metrics.
SAVIOM’s What-if Analysis feature allows organizations to compare various scenarios and assess their impact on project metrics.
Moving forward, here are some best practices and key takeaways to help manage project costs effectively.
Key Takeaways: Project Cost Management Best Practices
Effective project cost management requires a strategic approach and consistent effort. Here are some key takeaways that can help organizations plan, control, and optimize project costs efficiently throughout the project lifecycle.
- Establish a cost baseline to track project performance and measure budget adherence effectively.
- Rely on precise cost estimation methods to ensure accurate financial planning.
- Set aside a contingency reserve for unforeseen expenses to tackle potential budget overruns.
- Provide stakeholders with clear financial insights to support informed decision-making.
- Conduct a financial retrospective of the project to evaluate the cost efficiency.
The Glossary
Read More: Glossary of Resource Workforce Planning, Scheduling and Management












