Introduction
A high-priority project comes in, and tasks are assigned based on assumed availability, only to realize later that a key resource is already engaged somewhere else. The result? Burnout, delays, and unhappy clients.
This is exactly where effective resource scheduling becomes essential. It provides real-time visibility into resource availability, capacity, and dependencies, so work is assigned accurately, not based on guesswork. Consequently, it prevents resource conflicts, ensures balanced workloads, and accelerates project delivery.
This guide will take you through the nitty-gritties of resource scheduling, including what it is and how it works.
Let’s begin with the basics:
What is Resource Scheduling?
Resource scheduling is the structured process of planning, assigning, and managing organizational resources, such as people, equipment, and tools, to ensure project work is completed efficiently, without conflicts or delays.
This process involves creating project timelines, allocating resources to specific tasks based on skills or availability, and balancing workloads to prevent burnout or disengagement. It requires managers to account for individual resource availability, holidays, and competing project deadlines to avoid scheduling conflicts. With effective resource scheduling, firms can maintain a steady workflow and ensure timely project delivery.
Read this eBook to learn how resource scheduling doesn’t work in isolation.
With the resource scheduling definition clearly established, the next step is to understand how this structured approach translates into tangible project outcomes.
What are the Benefits of Resource Scheduling in Project Management?
Resource scheduling delivers measurable advantages only when it is executed consistently across projects and aligned with business priorities. Given below are the primary benefits of resource scheduling in firms.

Improves Strategic Alignment
Effective resource scheduling ensures that critical talent is assigned to high-impact, strategic initiatives rather than being diluted across low-value work. By aligning resources with business priorities, organizations can accelerate key programs and initiatives. This ensures that strategic projects consistently receive first access to the right skills and experience.
Ensures Skill-Based Work Allocation
Skill‑based resource allocation maximizes efficiency by matching work requirements with the most suitable capabilities, rather than assigning tasks based solely on availability. This improves quality, reduces rework, and accelerates execution across projects. Over time, this helps identify capability gaps, enabling firms to invest in upskilling, reskilling, or targeted hiring initiatives.
Learn more about resource allocation strategies and best practices in our detailed guide.
Supports On-Time Project Delivery
When resources are scheduled based on real-time availability and capacity, timelines become more realistic and achievable. This eliminates delays caused by overallocations, conflicts, or last-minute reshuffling. As a result, teams can work smoothly without constant firefighting or dependency-driven bottlenecks.
Boosts Resource Utilization Levels
Resource scheduling enables organizations to redeploy resources from low‑priority or non‑billable work to high‑value initiatives. This increases productive resource utilization without increasing headcount or relying on overtime. Moreover, it prevents chronic over‑utilization of critical roles by ensuring equal workload distribution and reducing the risk of employee burnout.
Prevents Project Costs Overruns
Proactive resource scheduling minimizes the need for last-minute firefighting, expensive hiring, premium contractor costs, or unplanned overtime. This enables firms to protect margins and maintain cost predictability, especially in multi‑project environments with shared resources.
Read our blog on cost overruns in project management and discover strategies to prevent them.
Enables Proactive Risk Management
Effective project resource scheduling provides real-time visibility into conflicts, overloads, and dependency risks across projects. This foresight enables managers to identify capacity gaps and schedule slippages well in advance. As a result, risks can be mitigated through timely rescheduling, reprioritization, or staffing adjustments rather than reactive crisis management.
Having understood the importance of resource scheduling, let’s move on to explore how it works in practice.
How Does the Resource Scheduling Process Work (Step-by-Step)?
For PMOs and delivery leaders, project resource scheduling becomes actionable only when it follows a precise operational flow. The steps below outlines a practical, standardized approach across project portfolios.
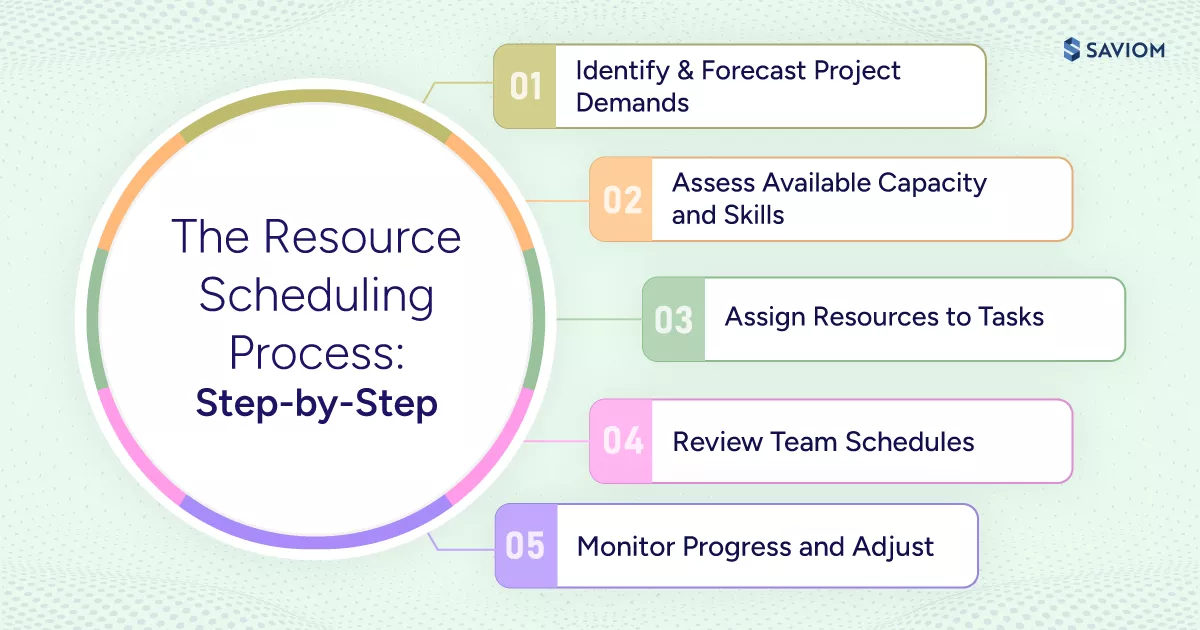
Step 1: Identify & Forecast Project Demands
Effective resource scheduling begins by defining upcoming project requirements in terms of roles, skills, timelines, and effort. By forecasting demand early, firms gain visibility into workload spikes, overlapping initiatives, and delivery pressure points before execution begins. This enables proactive planning instead of reactive firefighting.
Step 2: Assess Available Capacity and Skills
Here, current and future resource capacity is evaluated across teams, roles, and skill sets. This includes accounting for planned leave, non‑project work, and ongoing commitments. As a result, managers can identify skill gaps, capacity constraints, and underutilized resources before they impact delivery.
Explore how resource capacity planning helps managers initiate projects on time.
Step 3: Assign Resources to Tasks
Next, resources are assigned to tasks based on a combination of skills, availability, priority, and dependency considerations. The goal is to ensure that the right people are working on the right work at the right time. By creating such team schedules, managers can prevent both resource overutilization and increased bench time.
Step 4: Review Team Schedules
Now, managers must review the resource schedules to identify conflicts, dependency risks, and timing inconsistencies before execution begins. This validation is performed against calendars, cross‑project commitments, and priority rules. By doing so, managers can ensure schedules reflect operational reality.
Step 5: Monitor Progress and Adjust
Finally, during project execution, planned versus actual effort and utilization are monitored continuously. Any deviations caused by project scope changes, availability shifts, or priority updates are analyzed to decide if rescheduling or redeployment is required.
Discover practical ways to optimize resource utilization in our blog.
Use SAVIOM’s multi-dimensional resource scheduling feature to assign the right resources to the right task and facilitate timely project initiation. Book a Demo Today to see how it works.
The following section highlights the critical elements that underpin a resource scheduling process.
Core Components of Effective Resource Scheduling
Given below are the four fundamental components that translate scheduling from a planning activity to an execution-ready process.
Centralized Resource and Skills Inventory
A centralized resource and skill inventory acts as a single source of truth for people, roles, experience levels, and capabilities across the organization. This visibility enables managers to assign resources based on skills, not assumptions, thereby minimizing skill mismatches and rework.
Learn the importance of a skill matrix for modern organizations.
Resource Availability and Calendars
A unified resource calendar captures working hours, non‑working time, holidays, and planned absences. These real‑time availability updates immediately spot conflicts, over‑allocations, or sudden changes, allowing teams to address issues before they disrupt timelines.
Dependency and Constraint Management
Effective scheduling accounts for both task dependencies and external constraints that limit flexibility. These include cross‑project interdependencies, fixed project milestones, contractual obligations, and regulatory deadlines. By sequencing work correctly and acknowledging constraints upfront, firms can prevent cascading schedule delays.
Read our blog to understand what project interdependencies are and how to manage them effectively.
Scheduling Rules and Constraints
Clear scheduling rules define how decisions are made for effective resource management. These rules may include priority hierarchies, approval workflows, and assignment conditions tied to billing type, geography, or compliance requirements. This helps reduce ambiguity, speed up decision‑making, and ensure scheduling aligns with both operational realities and business objectives.
Now that we have defined the critical components, let’s shift our focus to common resource scheduling methods.
Key Resource Scheduling Methods & Techniques
Different scheduling techniques help organizations balance time, cost, and capacity constraints under varying conditions. This section explains the most widely used methods and when each is most effective.

Time-Constrained Scheduling
Time‑constrained scheduling prioritizes meeting fixed deadlines, even if it requires assigning additional resources. This approach is common in client‑committed, regulatory‑driven, or market-critical projects where timelines are non‑negotiable. However, it often increases cost pressure and utilization risks.
Read our blog to understand what project scheduling is and how to do it the right way.
Resource-Constrained Scheduling
Resource‑constrained scheduling prioritizes working within fixed capacity limits, even if timelines must be extended. This method focuses on creating sustainable schedules that respect realistic workloads and prevent burnout. It is particularly effective in environments with scarce or highly specialized skills where over‑allocation would jeopardize quality and retention.
Critical Path Method (CPM)
The Critical Path Method identifies the sequence of tasks that directly determine the project’s completion date. Any delay in these tasks immediately impacts the overall timeline. By highlighting zero‑slack activities, CPM helps managers focus effort where it matters most for staying on schedule.
Resource Leveling
Resource leveling resolves over-utilization by adjusting task start and finish dates to align with actual resource availability. While it may extend project timelines, it ensures schedules are feasible, reduces execution risk, and protects teams from sustained overload and burnout.
Read our blog to get resource leveling right for projects.
Resource Smoothing
Resource smoothing redistributes workloads within available float or slack while keeping project deadlines fixed. The goal is to even out utilization peaks and troughs by shifting non-critical tasks, thereby creating more balanced workloads without impacting delivery commitments.
Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
PERT models task sequences and dependencies in projects where activity durations are uncertain. It maps out which tasks must be completed before others can begin, ensuring work is sequenced correctly and resource conflicts are avoided. This approach enables planners to incorporate probabilistic time estimates like optimistic, most likely, and pessimistic, thereby supporting more realistic scheduling decisions.
Read our guide to understand project duration and how to estimate it accurately.
Now that we have explored the critical resource scheduling techniques, let’s clarify how they differ from resource allocation.
Resource Scheduling vs. Resource Allocation: Key Differences
Although often used interchangeably, resource scheduling and resource allocation serve different purposes and operate at varying levels of detail. Let’s look at the distinction between them:
| Dimension | Resource Scheduling | Resource Allocation |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Determines when resources work on specific tasks. | Determines who is assigned to projects or roles. |
| Time Dimension | Dynamic and continuously adjusted as timelines shift. | Relatively static and reviewed periodically. |
| Level of Detail | Task‑ and activity‑level with defined start and end dates. | Project‑ or role‑level without granular timelines. |
| Planning Horizon | Short‑ to mid‑term, execution‑focused. | Mid‑ to long‑term, structural planning. |
| Decision Inputs | Calendars, dependencies, capacity, and skill data. | Resource availability, roles, and high-level workload assumptions. |
| Impacts on Project Timelines | Determines whether delivery dates are feasible. | Does not guarantee timeline achievability. |
| Common Risks When Misapplied | Over‑allocation, missed deadlines, execution bottlenecks. | Uneven workload, unclear ownership. |
In the following section, we shall see how AI is reshaping resource scheduling for businesses.
How AI and Automation Are Transforming Modern Scheduling?
As project environments grow more dynamic, manual scheduling methods struggle to keep pace with constant change. This section explains how AI and automation elevate scheduling from reactive resource planning to decision‑driven execution.
Predictive Resource Availability and Demand
AI‑driven scheduling systems analyze historical utilization, delivery trends, and pipeline project data to forecast future resource capacity and demand. These forecasts account for seasonality, skill scarcity, recurring workload patterns, etc., thereby identifying capacity & capability gaps early and mitigating them through timely action.
Understand how resource forecasting enables firms to future-proof the workforce.
Scenario Modeling & What-If Simulations
Scenario planning allows leaders to simulate alternative staffing, sequencing, and timeline options before finalizing schedules. Executives can compare outcomes across delivery speed, utilization, and cost under different constraints. This capability enables data‑backed decision‑making, helping organizations confidently choose the plan that best aligns with business priorities and project budget.
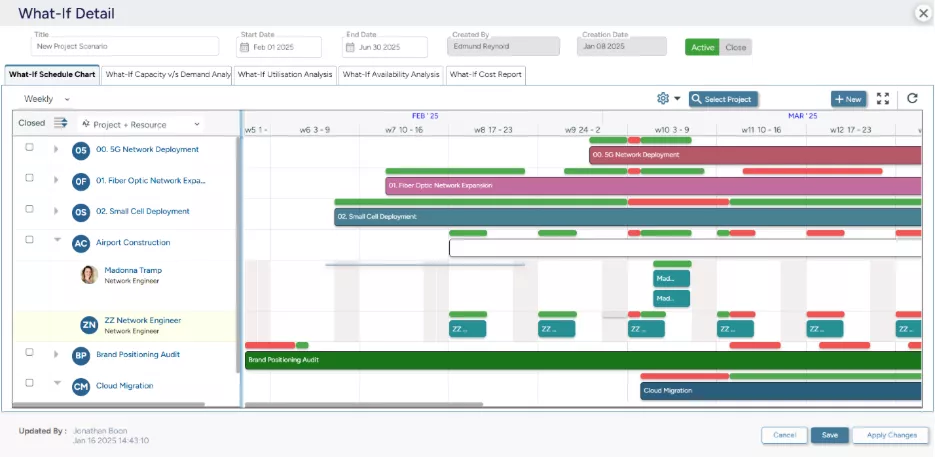 SAVIOM’s What-If Analysis empowers firms to compare and analyze multiple resource scenarios to come up with the most profitable outcome.
SAVIOM’s What-If Analysis empowers firms to compare and analyze multiple resource scenarios to come up with the most profitable outcome.
AI-Assisted Skill Matching and Work Routing
As per the Gallup Q12 engagement survey, “When employees do work matching their strengths/skills, it has increased profitability by 11%, decreased turnover rates by 30%, and reduced safety incidents by 36%. “
AI‑assisted scheduling evaluates far more than availability alone. It considers skill proficiency, prior experience, certifications, preferences, and even career progression when recommending assignments. Also, automated work routing uses rules and learned patterns to direct tasks to the most suitable individuals or teams, improving quality, reducing ramp‑up time, and enhancing employee engagement.
Learn ways to increase employee productivity in the workplace.
Automated Conflict Detection and Resolution
Modern scheduling systems continuously analyze assignments, calendars, and dependencies to detect conflicts such as resource over‑allocations or double bookings. These issues are flagged before they disrupt execution. AI engines recommend resolution options such as alternative resources or minor timeline adjustments, minimizing disruption while preserving delivery commitments.
Dynamic Schedule Adjustments in Real-Time
As priorities, project scope, or availability change, AI‑enabled systems automatically recalculate schedules to reflect the new reality. This keeps plans aligned with actual resource capacity rather than outdated assumptions. Thus, real‑time adjustments ensure schedules remain executable, even in fast‑moving environments with frequent change.
Read our blog to explore the key benefits of resource scheduling and how they drive project success.
Even mature organizations struggle with execution barriers that undermine scheduling effectiveness. Let’s look at common resource-scheduling challenges and their solutions.
Common Resource Scheduling Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Despite its strategic importance, project resource scheduling is often constrained by complexities that teams must actively navigate and resolve.
Limited Real-Time Visibility
Siloed tools and disconnected spreadsheets prevent managers from seeing accurate resource availability and workloads. As a result, project schedules are built on outdated data or assumptions.
Solution: Centralizing resource data and adopting portfolio‑wide views provides a single source of truth and enables proactive, informed scheduling.
Explore why it is not ideal to use spreadsheets for resource planning.
Inaccurate Resource Estimates
Poor resource estimation leads to unrealistic schedules, constant replanning, and overloaded teams. These inaccuracies compound across projects, eroding trust in delivery plans.
Solution: Using historical data, standardized estimation templates, and rolling‑wave planning steadily improves resource forecast accuracy and schedule stability.
Over-Allocation of Key Resources
Critical skills are often overused across multiple projects, leading to burnout, productivity loss, and schedule slippage. Without early detection, these overloads become systemic risks.
Solution: Implement resource utilization benchmark and early alerts to help managers facilitate equitable workload distribution before overuse becomes a systemic risk.
Read our blog to learn how to track resource utilization effectively.
Frequent Skill Shortages
When required skills are unavailable, task assignments are delayed, and dependencies start cascading. This disrupts timelines and increases delivery risk across the portfolio.
Solution: Early demand forecasting, combined with proactive upskilling or hiring, prevents last-minute disruptions and dependency failures.
Uncontrolled Scope Changes
Urgent or ad-hoc project requests and scope creep frequently derail carefully built schedules. Without guardrails, teams absorb unplanned work at the expense of committed delivery.
Solution: Capacity buffers, formal change control boards, and rapid scenario modeling help absorb change without destabilizing project execution.
Discover the importance of change management in project management.
While tools and techniques enable effective scheduling, long‑term success depends on how consistently scheduling is practiced across the organization. Let us examine some standardized ways of resource scheduling.
Best Practices for Seamless Resource Scheduling
The following resource scheduling best practices outline how organizations ensure schedules remain realistic, governed, and adaptable as demand, priorities, and capacity change.
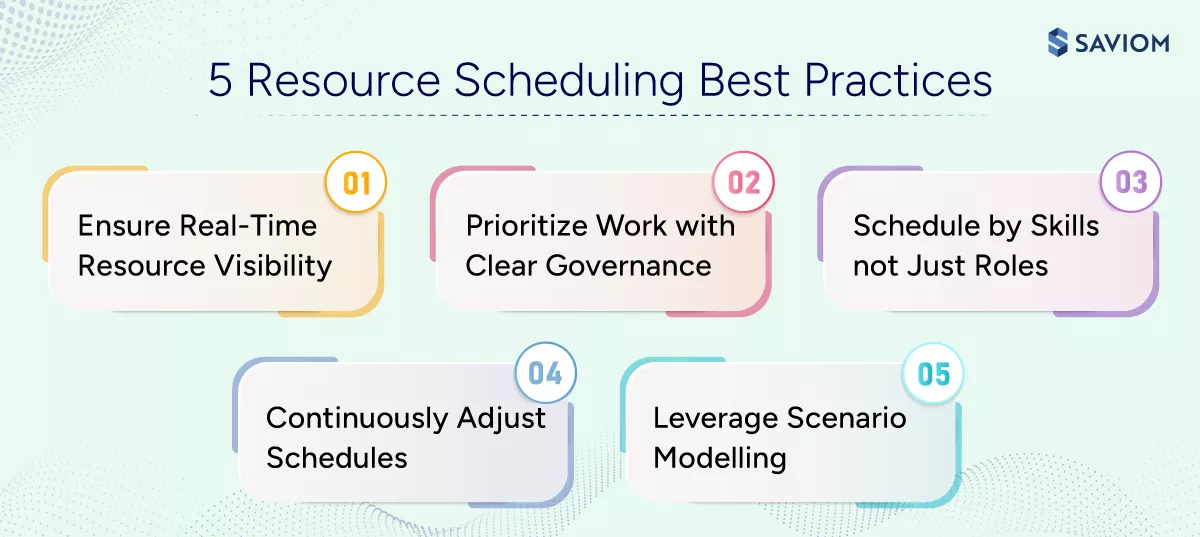
Ensure Real-Time Resource Visibility
Maintain real-time visibility into resource availability, capacity, utilization, and bookings across all projects. Real-time visibility eliminates blind scheduling, exposes hidden overloads early, and enables confident decision-making. It ensures managers always work with accurate, up-to-date data instead of outdated spreadsheets or assumptions.
Understand how structured resource booking improves utilization and delivery control.
Prioritize Work with Clear Governance
Establish clear governance frameworks to prioritize projects, initiatives, and tasks based on business impact, revenue contribution, and strategic alignment. This prevents ad-hoc scheduling decisions and subjective prioritization. Strong governance ensures resources are always deployed where they create the highest business value.
Use Skill-Based Scheduling, Not Just Role-Based
Schedule work based on skills, proficiency levels, certifications, and hands-on experience, not just job titles. Skill-based scheduling improves delivery quality, reduces rework, and lowers execution risk by ensuring tasks are handled by the most capable project resources. It enables more precise staffing and ensures the right expertise is applied to the right work at the right time.
Continuously Monitor and Adjust Schedules
Treat schedules as dynamic, not static. Regularly review and recalibrate project schedules to reflect changes in scope, priorities, availability, and dependencies. Continuous adjustment prevents small disruptions from turning into major delivery delays and keeps execution aligned with reality.
Model Multiple Scenarios Before Finalizing Schedules
As per the Goodfirms survey 2025, “57.5% firms state that accurate budgeting and resource allocation are their primary objectives to use scenario planning.”
Use scenario planning to simulate multiple “what-if” situations such as new project intake, resource unavailability, priority shifts, or delivery delays. Scenario modeling allows teams to assess impact before committing schedules, reduce risk, and choose the most resilient execution plan. This shifts resource scheduling from reactive to predictive.
Discover resource management best practices that improve utilization and enhance project delivery.
As resource scheduling matures from planning to execution, success must be measured, not assumed. The following section covers the top resource scheduling KPIs that firms must monitor.
Top Metrics to Measure Resource Scheduling Effectiveness
Without the right metrics, even well‑designed scheduling practices fail to deliver consistent results. This section defines the core indicators leaders should track to assess scheduling quality.
Resource Utilization Rate
Resource utilization rate measures how effectively resources, such as employees, equipment, and tools, are utilized against their total available capacity. It helps firms identify instances of resource underutilization and overutilization and take corrective actions to prevent burnout and disengagement.
The formula to calculate the resource utilization rate is:
100
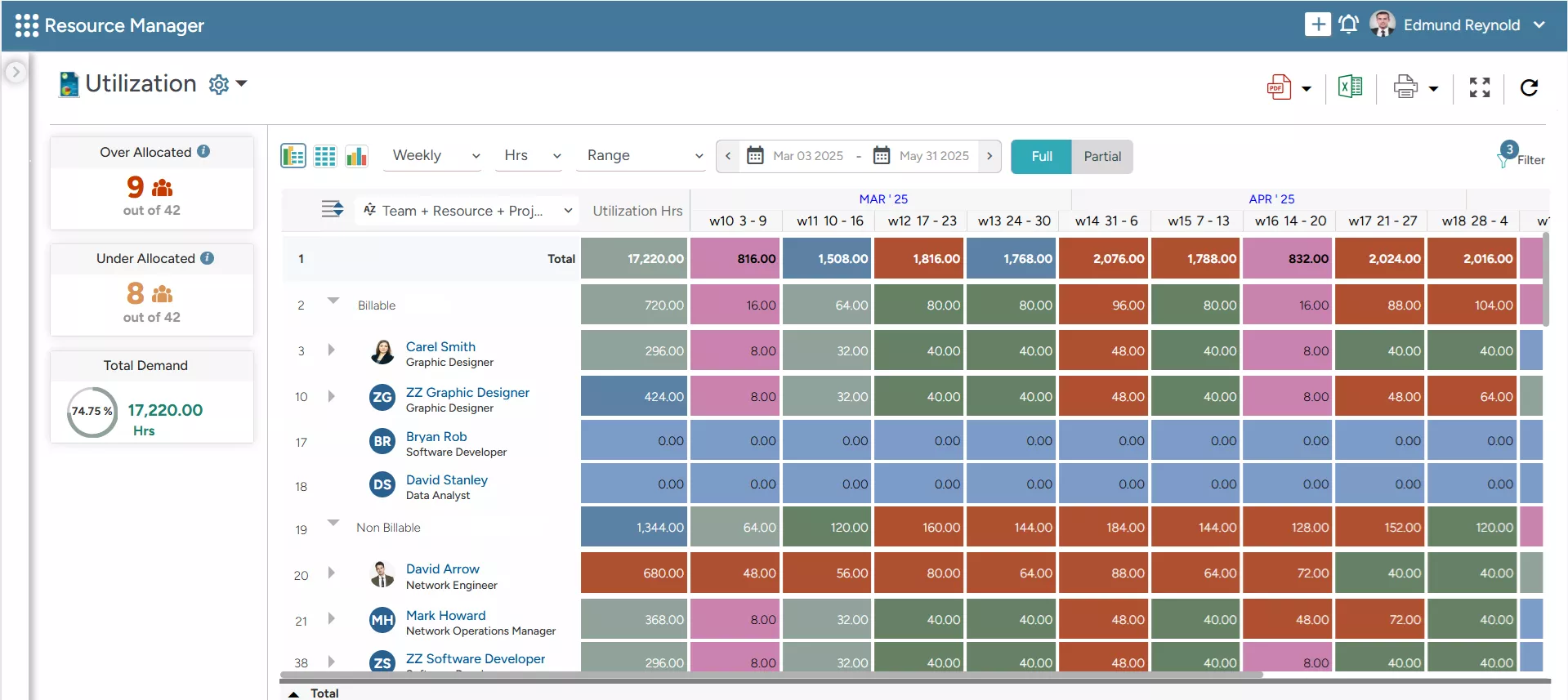 SAVIOM’s Color-Coded Heatmap helps forecast employees’ utilization levels, enabling leaders to identify imbalances and take proactive actions.
SAVIOM’s Color-Coded Heatmap helps forecast employees’ utilization levels, enabling leaders to identify imbalances and take proactive actions.
Schedule Variance
Schedule variance compares planned timelines with actual progress to determine whether work is ahead or behind schedule. It highlights delays or accelerations caused by resource constraints or dependency misalignment. This metric serves as a direct indicator of how realistic and achievable scheduling decisions were.
The formula to calculate schedule variance is:
Resource Conflict Resolution Rate
Resource conflict resolution rate reflects how efficiently scheduling clashes, such as overallocations and double bookings, are identified and resolved. It provides insight into operational discipline and planning maturity. Faster resolution indicates proactive control, while slower resolution signals reactive firefighting.
The formula to calculate the resource conflict resolution rate is:
Conflicts) X 100
On-Time Task Completion Rate
On-time task completion rate measures the percentage of tasks delivered within their scheduled timelines. Low on-time completion often indicates unrealistic schedules, capacity constraints, or poor workload balancing. This metric helps validate whether schedules are truly achievable.
Total Number of Tasks Assigned) X 100
Resource Cost Variance
Resource cost variance tracks the difference between forecasted resource costs and actual costs incurred. It helps identify cost overruns driven by inefficient scheduling, poor resource mix, or excessive overtime. Consistent variance indicates weak cost control and planning accuracy.
Read our guide to understand project cost management and how to calculate it.
Resource Idle Time
Resource idle time highlights periods when resources are unassigned or underutilized. It reveals inefficiencies in workload distribution and demand sequencing. High idle time indicates missed opportunities for productive staff deployment and revenue generation.
In the following section, let’s clarify the enterprise-level criteria decision-makers should evaluate when selecting a resource scheduling solution.
Essential Features to Look for in Resource Scheduling Software
Here are the enterprise‑grade capabilities that firms should look for in a modern resource scheduling tool.
Real-Time Resource Availability, Capacity & Utilization
The platform should provide real-time visibility into availability, capacity, and utilization across all projects. This enables accurate, time‑phased scheduling and early identification of capacity risks.
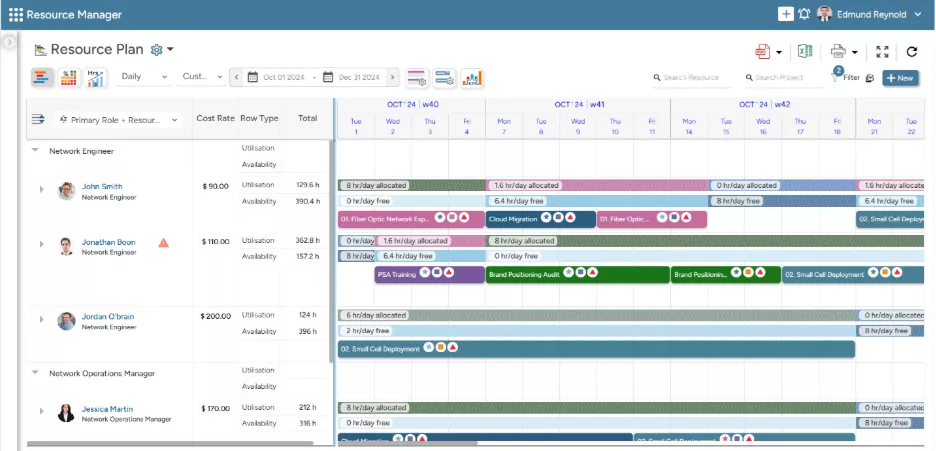 SAVIOM’s Resource Planner helps managers proactively track and optimize resource schedules.
SAVIOM’s Resource Planner helps managers proactively track and optimize resource schedules.
Skill- and Role-Based Scheduling
Effective tools support resource scheduling based on both roles and granular skills. This prevents misaligned assignments and reduces delivery risk caused by underqualified resourcing.
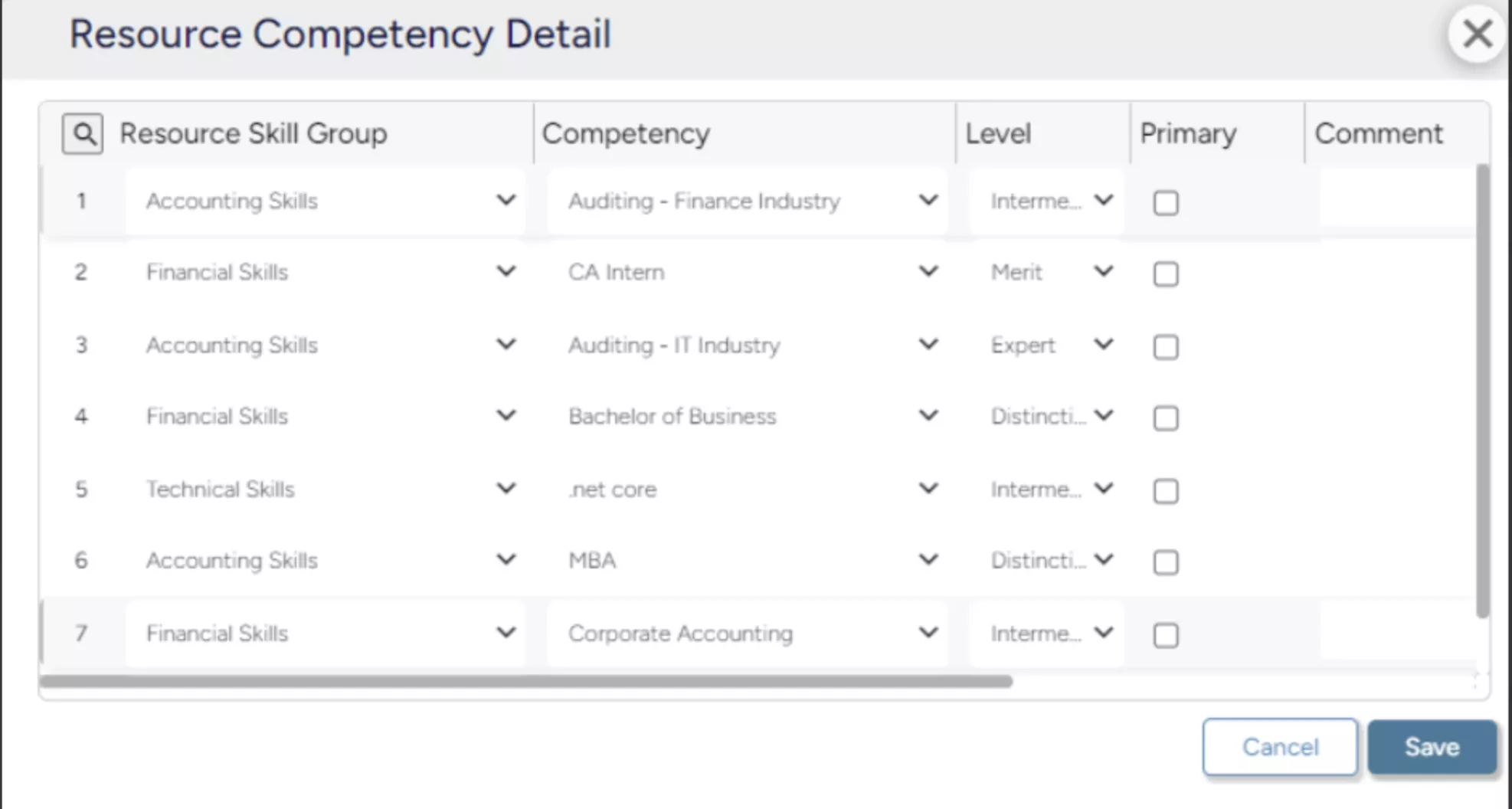 SAVIOM’s Competency Matrix provides visibility into existing skills across the organization, allowing managers to identify skill gaps and initiate targeted training and upskilling programs.
SAVIOM’s Competency Matrix provides visibility into existing skills across the organization, allowing managers to identify skill gaps and initiate targeted training and upskilling programs.
Conflict Detection and Overbooking Alerts
Built‑in alerts detect overbooking, double assignments, and dependency clashes in real time. Early warnings allow teams to resolve issues before execution is disrupted.
Drag-and-Drop Scheduling Interface
An intuitive drag‑and‑drop interface enables rapid schedule adjustments. Conflicts triggered by manual changes are immediately highlighted, thereby improving responsiveness.
Data-Driven Demand Forecasting
Advanced platforms forecast future demand using historical utilization, project patterns, and pipeline data. This helps leaders anticipate skill gaps and capacity shortfalls early.
Learn how demand planning helps optimize inventory levels and streamline operations.
Workflow-Based Resource Requisition
Automated, approval‑driven workflows replace manual emails and informal resource requests. This improves governance, transparency, and prioritization across competing demands.
Real-Time Reporting, Metrics & Dashboards
Real-time dashboards and reports provide actionable insights into key KPIs like utilization, forecast accuracy, and schedule health. These views support faster, data‑driven decision‑making at scale.
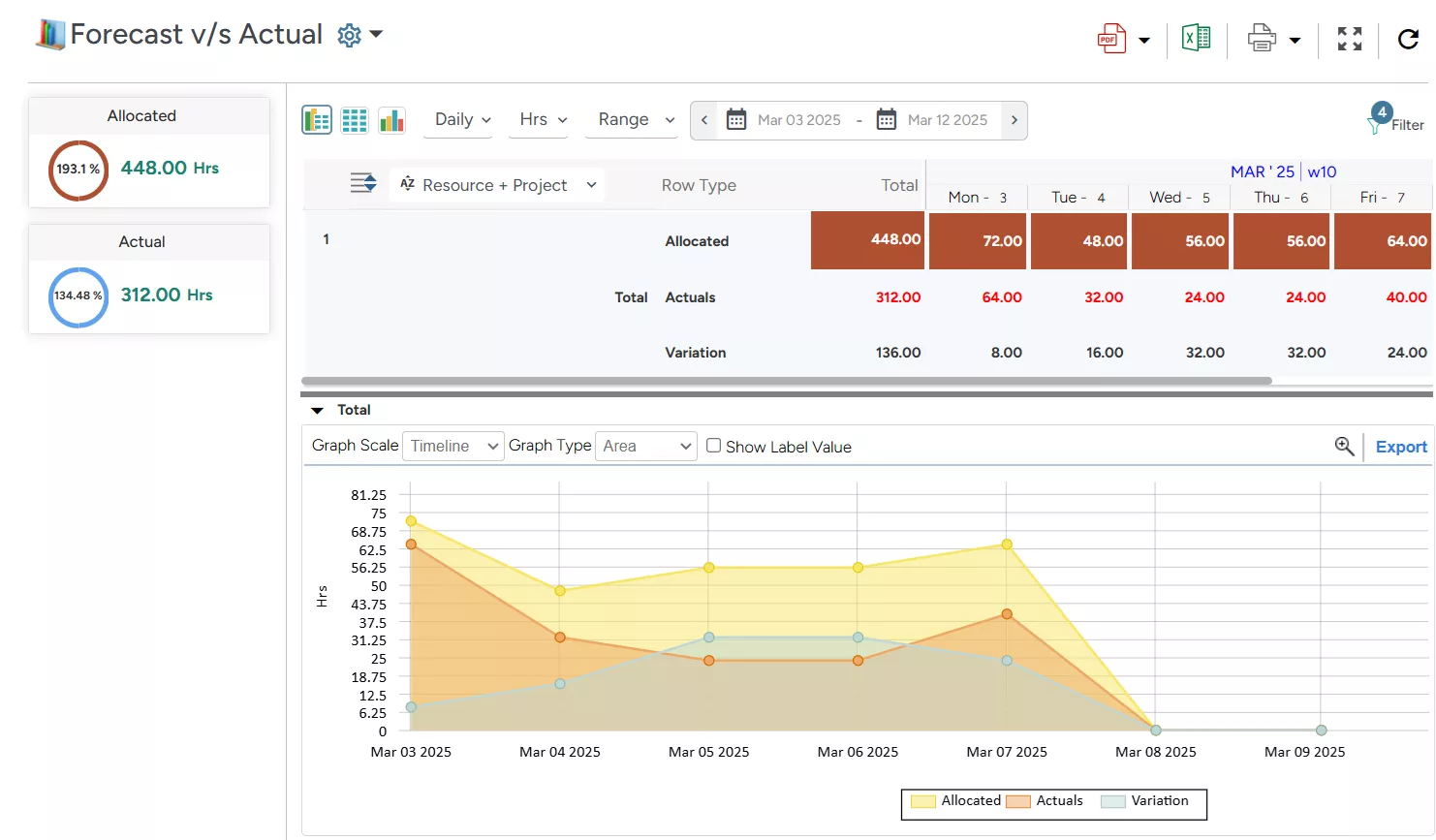 SAVIOM’s Forecast vs. Actual Report highlights estimated vs. actual time spent on tasks, helping managers identify variances and implement course-corrective measures.
SAVIOM’s Forecast vs. Actual Report highlights estimated vs. actual time spent on tasks, helping managers identify variances and implement course-corrective measures.
Conclusion
Resource scheduling is not a one‑time planning exercise; it is a continuous, time‑phased decision process that determines whether projects are truly deliverable. Organizations that master scheduling achieve higher utilization, lower delivery risk, and far greater predictability across portfolios.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Resource scheduling in project management is the process of assigning the right resources to the right tasks at the right time to ensure timely, efficient project delivery.
Resource scheduling is important for project success because it ensures that the right people are assigned to the right tasks at the right time. It prevents delays, reduces conflicts, balances workloads, and improves utilization. Effective scheduling brings predictability, control, and execution discipline to project delivery.
Resource scheduling defines when and for how long resources work on tasks, while resource allocation focuses on assigning ownership and responsibility at a higher level.
Resource scheduling challenges often hinder overall project planning. Given below are a few:
1. Limited Real-time Visibility
2. Inaccurate Resource Estimates
3. Over-Allocation of Key Resources
4. Frequent Skill Shortages
5. Uncontrolled Scope Changes
The common types of resource scheduling methods include:
1. Time-Constrained Scheduling
2. Resource-Constrained Scheduling
3. Critical Path Method (CPM)
4. Resource Leveling
5. Resource Smoothing











