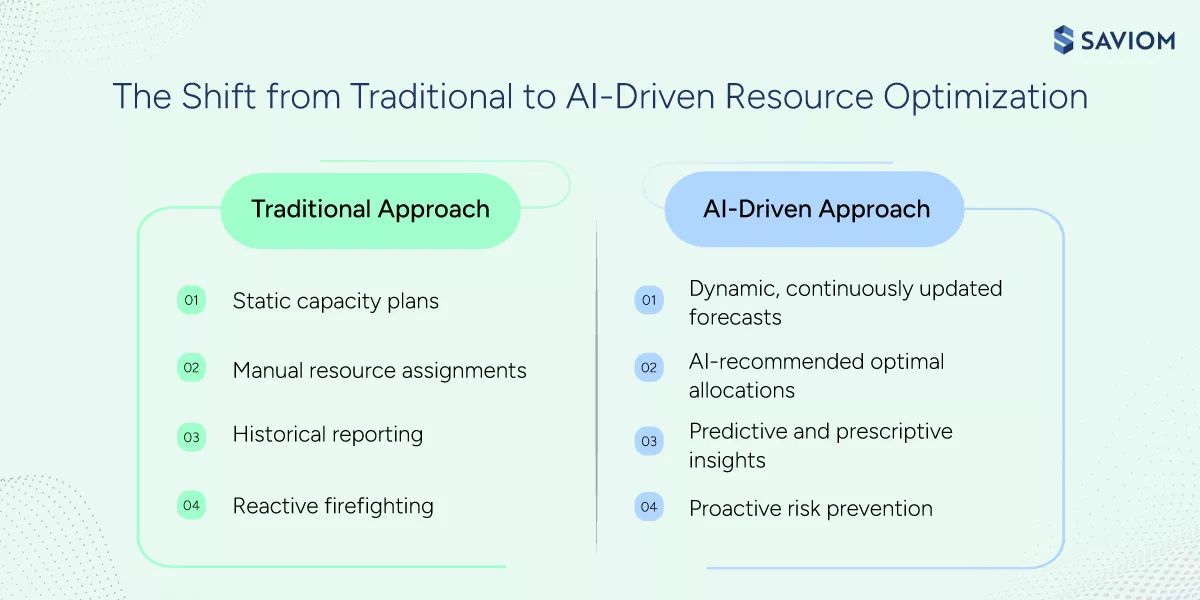
Introduction
How do modern enterprises protect resource health, deliver quality projects, and control costs, all at the same time?
This answer lies in resource optimization. It helps managers balance capacity, skills, and demand, so teams stay productive without burning out; projects are delivered on time with higher quality and resource costs stay under control.
Beyond execution, resource optimization supports long-term workforce readiness. By identifying unused capacity, emerging skill gaps, and workload imbalances early, managers can take timely action on reallocation, upskilling, or hiring. The result is a more adaptable workforce that can keep pace with changing business demands.
The guide explores the fundamentals of resource optimization, its benefits, core components, key techniques, and challenges.
What Is Resource Optimization?
Resource optimization is the strategic process of ensuring business resources, such as people, equipment, time, and budget, are used in the most efficient way to maximize productivity, reduce waste, and achieve project and business objectives.
This process focuses on continuously analyzing and balancing capacity and demand to ensure resources are working productively. It involves leveraging techniques such as resource leveling, smoothing, and scenario planning to identify and mitigate resource risks before they impact delivery. Therefore, it helps eliminate bench time, reduce firefighting, and achieve business objectives.
Read this ebook to learn in detail about real-time planning and optimization.
In the next section, let us take a closer look at the key benefits of resource optimization.
What are the Benefits of Resource Optimization?
Resource optimization directly impacts how predictably projects are delivered, how efficiently costs are controlled, and how well teams are sustained. Here are the core resource optimization benefits:

Enables Competent Resource Allocation
Dynamic resource optimization ensures that the right individual is assigned to the right work based on availability, skills, and priority. This prevents skill mismatches and ensures people work on tasks that match their strengths. As a result, teams experience less frustration, better focus, and sustainable day-to-day workloads.
Facilitates Timely Project Delivery
When teams have the right skills and realistic capacity, the risk of execution errors drops significantly. This reduces avoidable rework, approval cycles, and last-minute corrections that often derail timelines. The result is faster delivery and higher quality project deliverables, without overloading resources or compromising standards.
Use SAVIOM’s advanced resource management software to optimize resource utilization in real time and ensure on-time project delivery. Book a Demo Today.
Reduces Resourcing Costs
Resource optimization enables firms to deploy the right mix of local and global, permanent and contingent, or senior and junior resources based on work complexity and cost efficiency. This prevents unnecessary use of high-cost talent and ensures a balanced staffing model that lowers project costs while maintaining delivery quality and margin control.
Read in detail about project cost management and its types.
Improves Employee Productivity
When workloads are balanced and aligned to the right skills, employees can stay focused on meaningful, high-impact tasks. Dynamic resource optimization reduces unplanned interruptions and constant priority shifts, allowing teams to work with greater focus and efficiency. This translates into higher employee productivity without longer hours.
Prevents Employee Burnout and Disengagement
As per a study by Gallup, “Burned-out employees are 2.6 times more likely to be actively seeking a different job.”
Resource optimization prevents chronic overutilization that leads to fatigue, stress, and burnout. At the same time, it avoids under-allocation that leaves employees disengaged. By distributing workloads fairly and purposefully, organizations protect employee well-being, improve morale, and retain high-performing talent.
Learn how effective workforce planning can prevent employee burnout.
Strengthens Organizational Agility
Resource optimization provides real-time visibility into how people, skills, and capacity are being used across the organization. This allows managers to spot inefficiencies quickly, rebalance workloads, and reassign resources based on business priorities. As a result, organizations can keep projects on track as demand changes and respond faster to evolving market needs.
Next, let’s understand the differences between resource optimization, resource allocation, and resource planning.
Resource Optimization vs. Allocation vs. Planning: Key Differences
| Parameter | Resource Planning | Resource Allocation | Resource Optimization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Forecast future resource needs and define required capacity and skills | Assign specific resources to tasks or projects | Maximize the value and performance of available resources |
| Key Question Answered | What resources will we need and when? | Who will work on what and when? | How can we use our resources most effectively? |
| Focus Area | Demand forecasting and capacity readiness | Task-level assignment and scheduling | Performance, efficiency, and value realization |
| Inputs Used | Project pipeline, strategic initiatives, historical demand data | Availability, skills, priorities, timelines | Utilization, capacity, skills, and performance metrics |
| Typical Outputs | Capacity plans, hiring plans, skill gap analysis | Resource schedules, assignments, workload plans | Rebalanced workloads, improved utilization, optimized delivery plans |
| Business Impact | Improves preparedness and reduces future delivery risk | Enables execution of planned work | Improves ROI, productivity, margin control, and delivery performance |
| Risks If Ignored | Unplanned hiring, skill shortages, and reactive resourcing | Resource conflicts, overload, and underutilization | Wasted capacity, burnout, margin erosion, inefficiency |
| Relationship to Others | Feeds demand data into allocation and optimization decisions | Executes plans and provides utilization data | Refines planning assumptions and allocation decisions |
Explore our in-depth guide on resource allocation strategies, models, and best practices.
In the following section, let us go through the components of an effective resource optimization framework.
Core Components of an Effective Resource Optimization Framework
An effective resource optimization strategy is built on a few critical components. Let’s examine them.
Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting helps organizations anticipate upcoming project demand with greater accuracy. It enables managers to understand what work is coming and when, rather than reacting to last-minute demands. This foresight is essential for resource optimization, enabling proactive hiring, upskilling, and capacity planning.
Resource Capacity Management
According to a McKinsey report, “90% of leaders consider capacity management a pressing to-do that needs addressing now or soon.”
Resource capacity management provides real-time insights into capacity vs. demand gaps across teams and projects. It reflects true availability after accounting for leave, overhead, and partial allocations, helping managers quickly spot overloads and bench time. This level of accuracy is critical for resource optimization because it prevents overcommitment and resource underutilization.
Explore capacity management in detail and understand its different types.
Resource Scheduling and Allocation
Resource scheduling and allocation ensure the right skills are assigned to the right work at the right time. This reduces rework, quality issues, and delivery delays caused by skill mismatches. As a result, it helps optimize resource productivity and ensure high-quality deliverables by making better use of existing talent.
Resource Utilization Management
Resource utilization management provides clear visibility into how capacity is being used productively across roles and teams. It highlights overload, bench time, and efficiency gaps that directly impact delivery performance. These insights enable managers to oversee and optimize resource usage in real-time for maximum productivity.
Prioritization and Governance
Prioritization and governance ensure resources are focused on high-value, strategic initiatives. This prevents limited capacity from being used for low-impact or non-critical work. As a result, organizations maximize returns from their resources and protect their profit margins.
Performance Monitoring and Analytics
Performance monitoring and analytics provide clear insights into utilization, forecast accuracy, delivery trends, and cost efficiency. They reveal patterns that guide better resourcing decisions over time. This enables continuous optimization and informed, data-driven decisions at both operational and strategic levels.
Scenario Simulation and Modeling
Scenario planning is a simulation-driven technique that helps managers build and test multiple resourcing scenarios within a sandbox environment to support smarter resource optimization. It enables them to evaluate each scenario’s impact on utilization, cost, and project timelines, and select the most profitable and resilient resource plan.
Next, let us understand how to optimize resource utilization effectively.
Step-by-Step Resource Optimization Process: From Planning to Execution
Here’s a rundown of the various steps organizations can follow to optimize their resources:
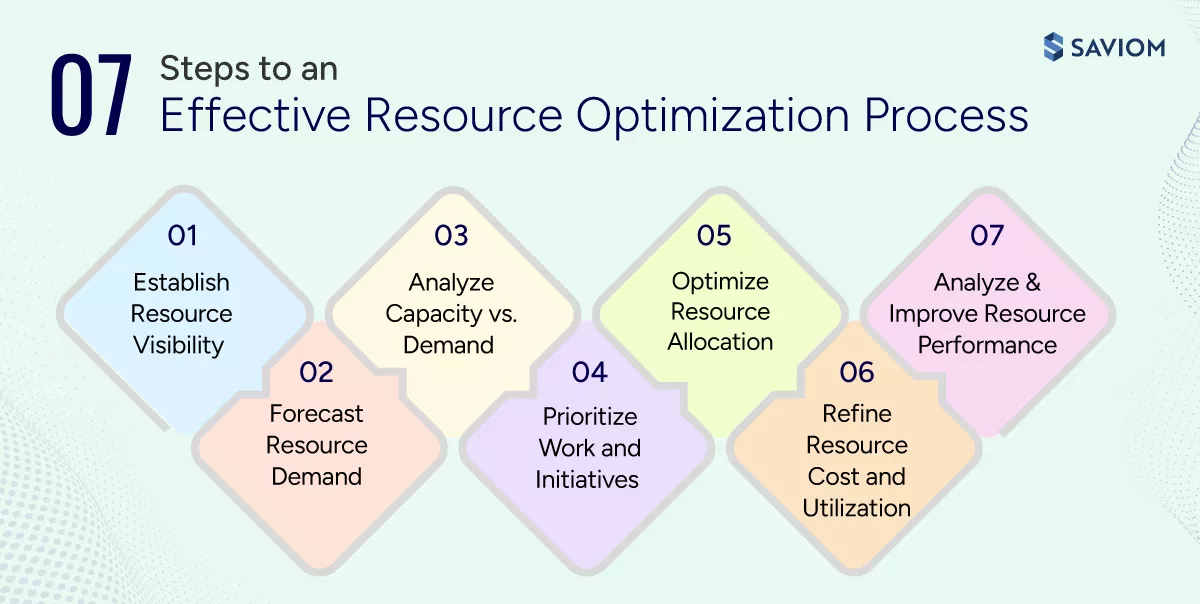
Step 1: Establish Resource Visibility
Start by creating a single source of truth for all resources. Capture skills, roles, availability, costs, and locations in a single system to eliminate data silos. With this level of visibility, managers can make confident, data-backed resourcing decisions that keep projects on time, within budget, and aligned with delivery goals.
Step 2: Forecast Resource Demand
Next, forecast future resource demand to understand what types of resources are needed, when they are required, and how much capacity is needed to support upcoming work. Analyze future opportunities, factor in seasonality, and growth plans to build realistic demand projections.
Read in detail about resource forecasting and its benefits.
Step 3: Analyze Capacity vs. Demand
In this step, compare forecasted demand against available capacity across roles and skills to identify whether there are resource shortages or excesses. This analysis highlights where intervention is needed to take corrective actions such as upskilling, retraining, or hiring.
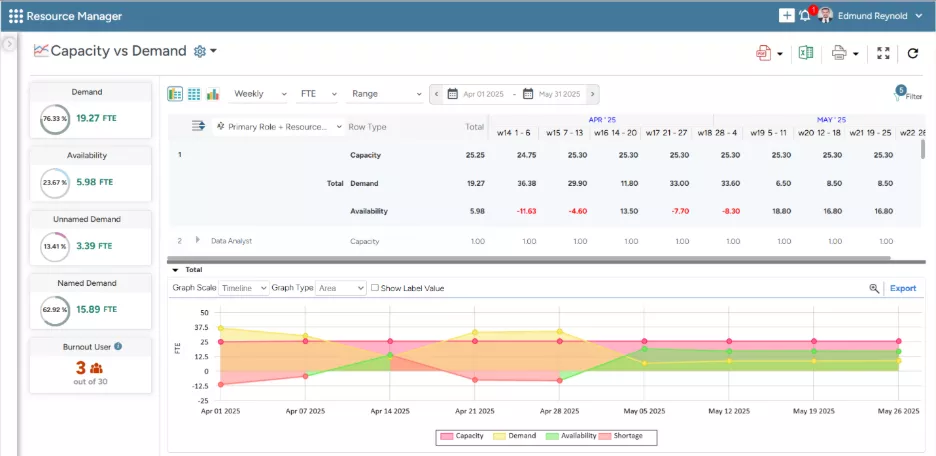 SAVIOM’s Capacity vs. Demand dashboard empowers managers to assess demand gaps and make quick, data-driven decisions.
SAVIOM’s Capacity vs. Demand dashboard empowers managers to assess demand gaps and make quick, data-driven decisions.
Step 4: Prioritize Work and Initiatives
After that, prioritize initiatives based on strategic alignment, business impact, and ROI to determine where capacity should be invested. Allocate scarce and niche-skilled resources to critical, time-sensitive initiatives. On the other hand, defer or re-sequence low-impact or non-critical work to avoid unnecessary resource dilution.
Step 5: Optimize Resource Allocation
At this stage, assign the right people with the right skills to the right work at the right time. Allocating the best-fit resources from the outset ensures there is no disruption in the project midway. Moreover, managers should prioritize internal resources and use external support only when necessary.
Step 6: Refine Resource Cost and Utilization
Next, track resource utilization across billable and non-billable activities to identify and rectify inefficiencies, preventing burnout and disengagement. Furthermore, create a balanced mix of permanent/contingent, senior/junior, and local/global resources for every project to improve productivity, maintain delivery timelines, and minimize cost escalations. This ensures resources are used optimally without compromising delivery quality.
Read our blog to learn in detail about resource utilization and how to optimize it.
Step 7: Continuously Analyze and Improve Resource Performance
In this final step, managers review actual performance against plans to identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and skill gaps. KPIs such as utilization, forecast accuracy, and delivery variance guide improvement actions. These insights are used to refine forecasts, adjust capacity models, and strengthen future allocation decisions, driving continuous optimization.
Key Resource Optimization Techniques: Methods, Examples, and Use Cases
Dynamic resource optimization is driven by a set of proven techniques that improve workforce efficiency and delivery predictability. Let’s explore the resource optimization methods enterprises use at scale.
Resource Leveling
Resource leveling is a project scheduling technique that adjusts task start and end dates to match available resource capacity. It helps balance workloads when resources are limited, preventing overutilization and ensuring projects progress at a sustainable pace.
Use Case: In a software project, two critical modules need the same senior backend developer in the same week. Resource leveling shifts one module to the following week to avoid overallocation and keep work moving at a sustainable pace.
Resource Smoothing
Resource smoothing is a scheduling technique that balances workloads without changing the project’s critical path or start and end dates. It redistributes tasks within available slack (float) to prevent resource overload while keeping timelines fixed.
Use Case: AEC firms use resource smoothing to balance workloads across design, procurement, and execution phases by shifting non-critical tasks within available float. This prevents resource overallocation and maintains project timelines.
Read in detail about resource smoothing and how it prevents employee burnout.
Capability Optimization
Capability optimization is the practice of aligning people’s skills and expertise with the right work to improve performance and reduce skill mismatches. It ensures tasks are assigned based on true capability, helping teams deliver higher-quality work while maintaining balanced workloads.
Use case: A legal firm assigns complex cases to senior lawyers and routine legal work to junior associates or paralegals, improving quality, speeding up delivery, and balancing workloads.
Cost Optimization
Cost optimization is the process of assigning the right mix of resources to work based on cost, skill level, and availability. It helps organizations control project costs while maintaining delivery quality by balancing senior, junior, permanent, contingent, global, and local workforce options.
Use case: A professional services firm blends senior consultants with mid-level analysts to deliver large programs while maintaining profitability.
Utilization Optimization
Utilization optimization is the process of distributing work evenly across teams to avoid overloading some resources while others sit idle. It improves productivity, protects team well-being, and ensures consistent use of available capacity.
Use case: A construction company balances site engineer workloads across projects by redistributing inspection tasks and rotating staff, preventing burnout and maintaining steady productivity.
Understand construction resource management in detail with this guide.
Location Optimization
Location optimization is the process of hiring or allocating resources from the right geographic locations based on project requirements, skill availability, and cost considerations. It helps organizations balance quality, cost, and delivery efficiency.
Use case: A manufacturing company assigns quality engineers to plant locations rather than relying on remote teams. This improves response times, minimizes production stoppages, and reduces downtime-related losses.
Seasonal Optimization
Seasonal optimization is the practice of adjusting resource capacity to match predictable demand changes throughout the year. It helps organizations scale up during peak periods and shift focus to training or strategic work during slower phases.
Use case: An audit and accounting firm scales up audit teams during peak tax and financial reporting seasons, then shifts resources to training and advisory work during slower months. This helps the firm handle peak workloads efficiently.
Learn how to optimize resources in audit and accounting firms.
After understanding resource optimization strategies, let’s explore how capacity planning and scenario modeling support dynamic resource optimization.
Capacity Planning and Scenario Modeling for Resource Optimization
Capacity planning and scenario modeling play a foundational role in resource optimization by helping organizations move from reactive staffing decisions to proactive, data-driven resource strategies.
Capacity Planning: Creating a Realistic Resource Baseline
Capacity planning establishes how much work your organization can realistically deliver with available resources.
Its role in resource optimization includes:
- Providing visibility into available capacity across roles, skills, locations, and timelines.
- Comparing current and future demand against real availability.
- Identifying capacity gaps, skill shortages, and surplus resources early.
- Enabling informed decisions around hiring, upskilling, or redeployment.
Without capacity planning, optimization efforts rely on assumptions, leading to over-allocation, burnout, and delivery delays.
Read in detail about agile capacity planning and its benefits.
Scenario Modeling: Testing Optimization Decisions Before Execution
Scenario modeling strengthens capacity planning by allowing organizations to simulate multiple “what-if” situations before committing resources.
Its role in resource optimization includes:
- Evaluating the impact of new initiatives, priority shifts, or project scope changes.
- Testing different options, such as reallocating skills, onboarding new resources, or delaying projects.
- Assessing trade-offs between cost, utilization, timelines, and risk.
- Selecting the optimal resource mix with minimal disruption.
This ensures optimization decisions are risk-aware, cost-efficient, and aligned with business priorities.
Explore the nitty-gritty of scenario planning, including its types and best practices.
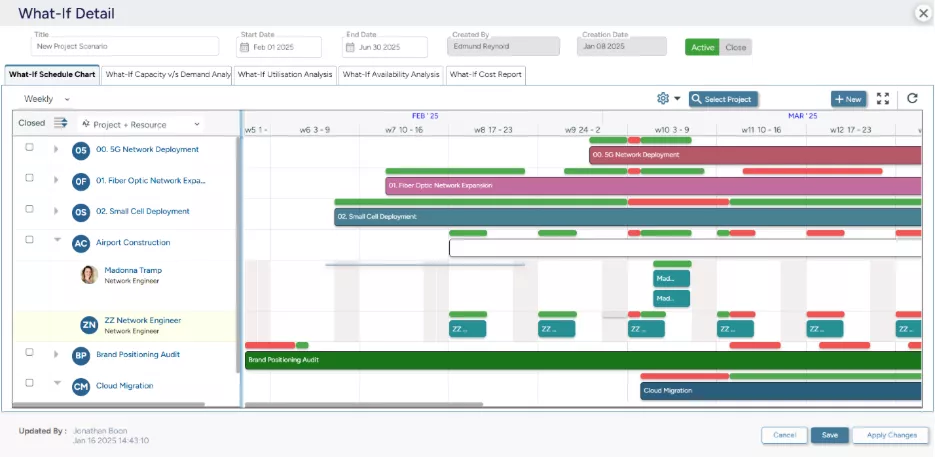 SAVIOM’s What-If Analysis empowers firms to compare and analyze multiple resource scenarios to identify the most profitable outcome.
SAVIOM’s What-If Analysis empowers firms to compare and analyze multiple resource scenarios to identify the most profitable outcome.
How They Work Together for Resource Optimization
Capacity planning provides the current and future capacity baseline, while scenario modeling enables decision validation.
Together, they help organizations:
- Balance workloads and prevent resource overutilization.
- Align resources with strategic priorities and growth plans.
- Reduce last-minute firefighting and costly reactive hiring.
Now, let us learn about the critical metrics that help to measure the success of resource optimization efforts.
Key Metrics to Measure Resource Optimization Success
Metrics convert optimization from theory into measurable performance. Below are the core metrics essential for the effective measurement of resource optimization success.
Resource Utilization Rate
Resource utilization rate measures how effectively resources, such as employees, equipment, and tools, are utilized against their total available capacity. It helps managers identify resource under- and overutilization and take corrective action to prevent burnout and disengagement.
The formula to calculate the resource utilization rate is:
Hours) X 100
Billable Utilization Rate
Billable resource utilization rate measures the percentage of an employee’s available time spent on billable, client-focused work. Low utilization indicates excessive time spent on non-billable activities, while high utilization signals efficient use of resources. Tracking this metric helps organizations optimize productivity and improve profit margins.
The formula to calculate billable utilization is:
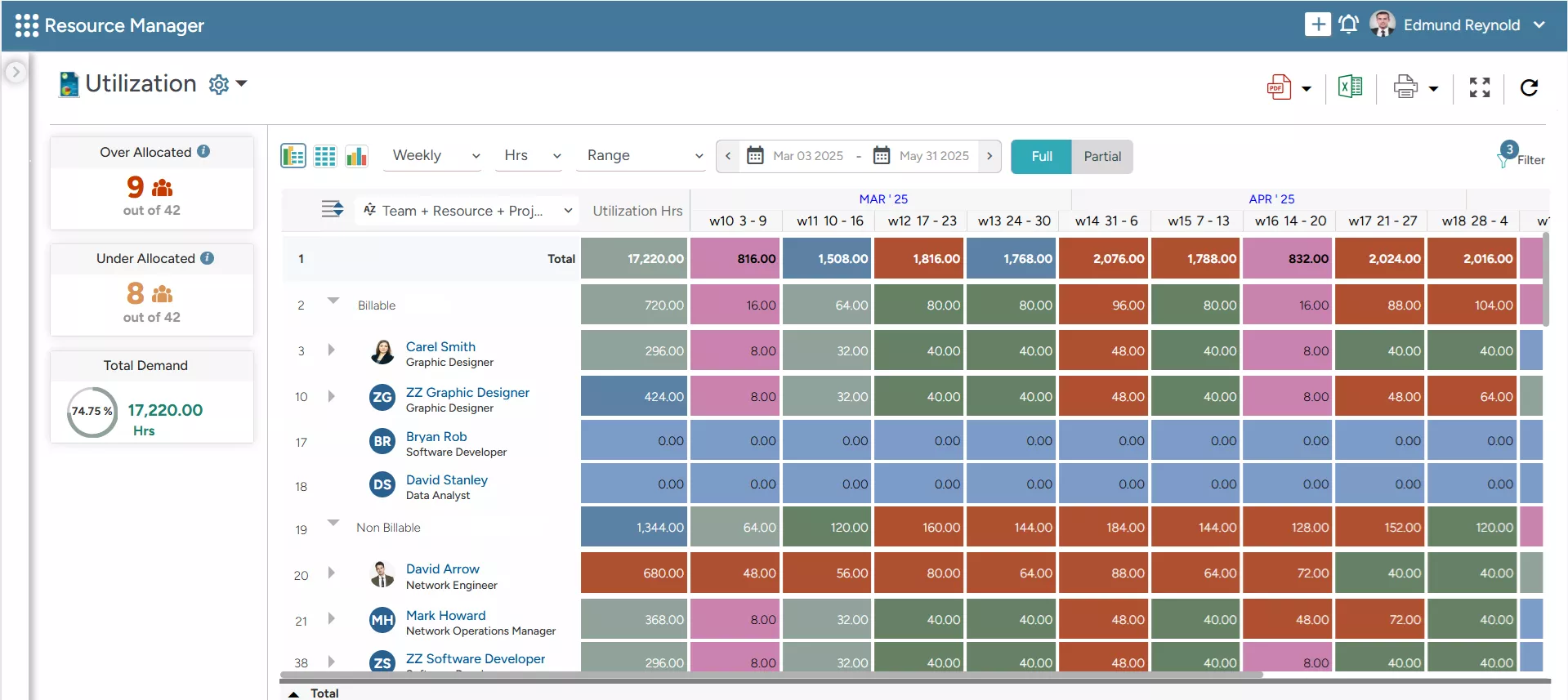 SAVIOM’s Color-Coded Heatmap enables managers to forecast employees’ utilization levels, helping them to identify imbalances and take corrective actions.
SAVIOM’s Color-Coded Heatmap enables managers to forecast employees’ utilization levels, helping them to identify imbalances and take corrective actions.
Learn what billable hours are and how to optimize them effectively.
Capacity Utilization Variance
Capacity utilization variance measures the gap between a resource’s available capacity and the capacity actually consumed by assigned tasks or projects over a given period. Low utilization highlights underused capacity, while high utilization reflects efficient deployment. Monitoring this metric helps managers balance workloads, improve efficiency, and align demand with available capacity.
The formula to calculate the capacity utilization variance is:
Resource Forecast Accuracy
Resource demand forecast accuracy refers to the degree to which an organization’s predicted resource demand aligns with the actual resources required. It helps firms understand the reliability of their resource planning, empowering them to make data-driven decisions about hiring, allocation, and utilization.
The formula to calculate the resource forecast accuracy is:
Actual Demand) X 100
Productivity per Resource
Productivity per resource is a metric that measures how effectively an individual resource converts their available time into productive or value-generating output. It is typically calculated by comparing actual productive output (such as completed tasks, deliverables, or billable work) against the time or capacity invested.
The formula to calculate the productivity per resource is:
Capacity
Resource Allocation Effectiveness
Resource allocation effectiveness measures how appropriately an organization assigns its available resources to projects to achieve optimal results with minimal waste. It reflects the organization’s ability to align resources with top priorities, ensuring that the right resources are deployed to the most suitable activities at the right time and at the optimal cost.
The formula to calculate the resource allocation effectiveness is:
Hours) X 100
Discover 15 resource management metrics that bring clarity to resource planning.
The following section outlines common roadblocks to resource optimization and practical ways to overcome them.
Common Resource Optimization Challenges and How to Solve Them
Even the strongest optimization strategies face obstacles. Here are the commonly faced challenges and their solutions.
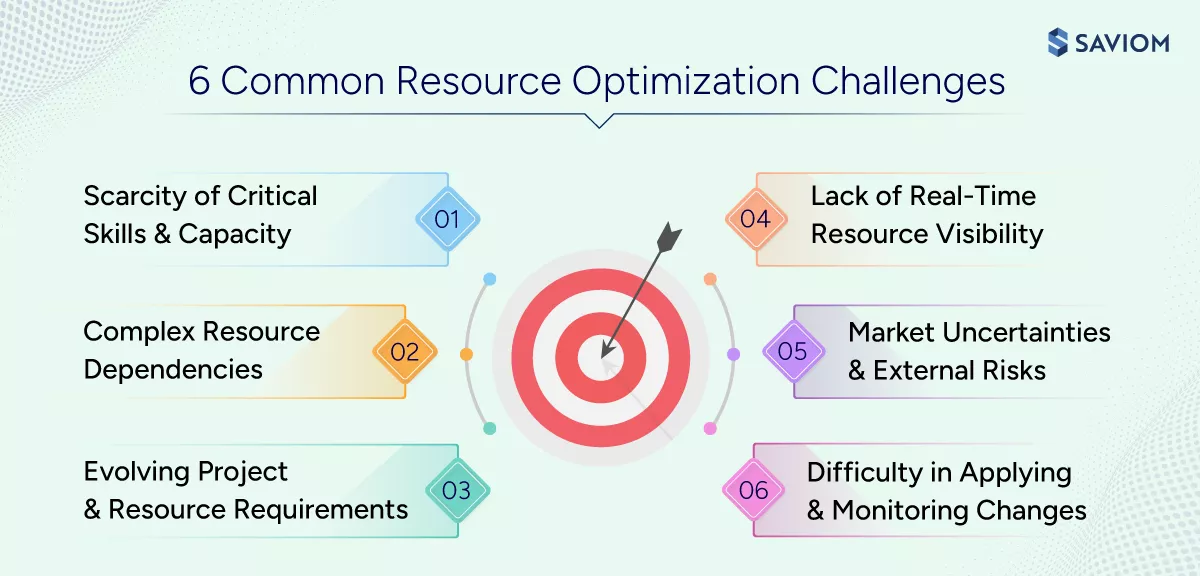
Scarcity of Critical Skills and Capacity
According to a McKinsey & Company study, “87% of companies worldwide already have a skills gap or expect to have one within a few years.”
Limited availability of niche and high-demand skills often forces managers to make tough trade-offs between competing initiatives. Attrition and unplanned absenteeism further restrict access to critical talent, increasing delivery risk.
Solution: Effective resource capacity forecasting enables early identification of gaps so organizations can hire, upskill, or redeploy resources before shortages impact projects.
Complex Resource Dependencies
In multi-project environments, resources are often shared across initiatives with overlapping timelines. This creates complex dependency chains where delays or shortages in one project block progress in others, making it difficult to reschedule work, rebalance workloads, or protect delivery timelines.
Solution: A centralized resource planning approach provides firms with real-time visibility across all projects, roles, and timelines. This enables them to evaluate how each assignment affects parallel initiatives and deploy resources accordingly.
Read in detail about project interdependencies & how to manage them effectively.
Evolving Project and Resource Requirements
Shifting customer expectations, new technologies, and changing business priorities continuously reshape skills and capacity needs. Static resource plans quickly become outdated, leaving teams misaligned and underprepared.
Solution: With dynamic resource forecasting, organizations can stay abreast of changing project demand and skill requirements. This enables them to make timely staffing adjustments to ensure the firm has the right resources to keep delivery on track.
Lack of Real-Time Resource Visibility
When managers lack clear visibility into capacity, availability, utilization, and skills, decisions are based on assumptions rather than facts. This leads to reactive firefighting, last-minute reshuffling, and inefficient resource use.
Solution: Centralized dashboards and real-time insights into resource attributes like skills, capacity, availability, cost, location, etc., help managers make faster and data-driven decisions.
Market Uncertainties and External Risks
Economic volatility, regulatory changes, and technology disruptions can invalidate even the most detailed resource plans. Without flexibility, organizations face delivery delays, eroding profit margins, and missed opportunities.
Solution: With what-if scenario planning, firms can assess how different market, regulatory, or demand shifts would impact capacity and delivery commitments. Based on these modeled outcomes, firms can select the most viable course of action.
Difficulty in Implementing and Monitoring Changes
Even well-designed resource optimization strategies fail without strong execution and monitoring mechanisms. Weak governance, manual processes, and a lack of tracking often lead to sub-optimal allocation, rising costs, and schedule overruns.
Solution: Automated workflows, performance dashboards, and continuous monitoring ensure changes are implemented, measured, and refined in real time.
Read our blog on how to create an efficient resource request workflow.
After understanding the challenges, it’s time to learn how AI and predictive analytics support resource optimization.
AI and Predictive Analytics for Next-Gen Resource Optimization
AI enables proactive, intelligent decision-making at scale by using data-driven insights to anticipate demand, optimize capacity, and detect risks early. It sets the foundation for predictive forecasting, automated recommendations, and real-time pattern detection.

Predictive Demand Forecasting
Predictive demand forecasting analyzes historical project, workload, and utilization data to detect trends and growth patterns, helping organizations anticipate future resource requirements more accurately. This enables organizations to plan capacity proactively, reduce last-minute staffing gaps, and support smarter planning decisions.
AI-Driven Capacity Recommendations
AI-driven capacity recommendations suggest optimal resource allocations aligned with priorities, costs, and capabilities. It reduces manual planning effort and minimizes human bias in decision-making, helping firms deploy resources faster and more consistently at scale.
Learn in detail about capacity requirement planning and its types.
Pattern Detection and Anomaly Alerts
Pattern detection continuously monitors utilization, delivery, and performance data across teams. It identifies unusual trends such as sudden capacity drops, workload spikes, or recurring delays. Moreover, automated alerts serve as an early warning system for potential risks, enabling managers to intervene promptly and prevent issues from escalating.
Let us move on to the parameters to consider when selecting the best resource optimization tool.
How to Select the Right Resource Optimization Tool?
Choosing the right resource optimization tool is critical to scaling your strategy and realizing measurable ROI. It must support enterprise complexity, data-driven decisions, and seamless ecosystem integration.
Define Business Requirements
Start by clarifying your primary goals, such as improving utilization, controlling costs, reducing delivery risk, or accelerating execution. Identify the key stakeholders who will use the tool and the decisions it must support. This ensures the platform aligns with real business needs rather than just technical features.
Evaluate Core Optimization Capabilities
Assess support for capacity planning, skills matching, demand forecasting, workload balancing, and scenario modeling. SAVIOM’s advanced resource optimization software combines capabilities such as a KPI forecaster, an embedded capacity planner, intelligent matchmaking, an early warning system, real-time BI reporting, and what-if analysis. These capabilities enable data-driven optimization at scale.
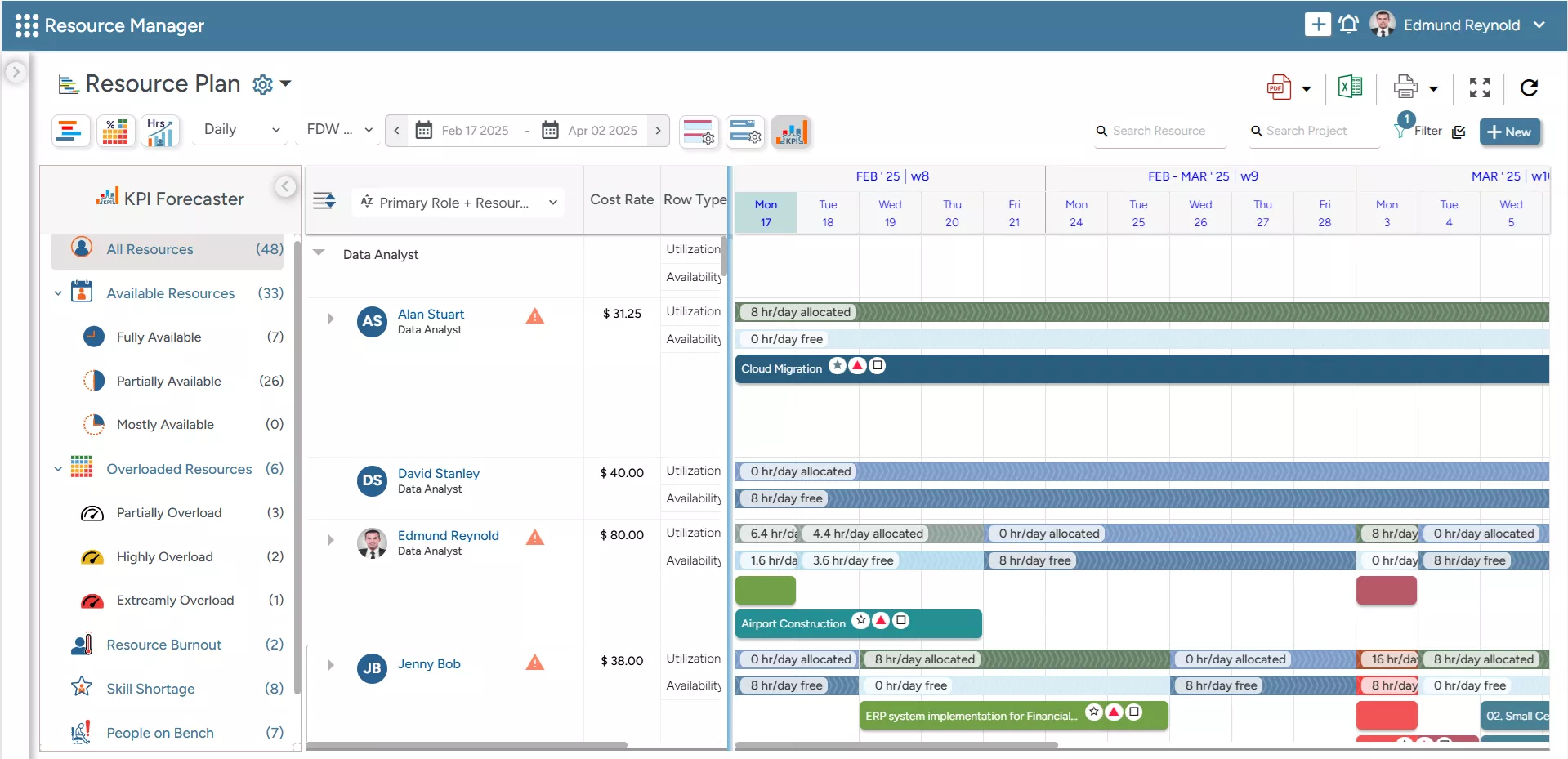 SAVIOM’s KPI Forecaster provides visibility into utilization, availability, and bench time, enabling proactive decisions and better resource planning.
SAVIOM’s KPI Forecaster provides visibility into utilization, availability, and bench time, enabling proactive decisions and better resource planning.
Check Scalability & Configurability
Ensure the tool can handle enterprise-scale complexity across portfolios, programs, and shared resource pools. It should adapt to your structures, workflows, and governance models without heavy customization. SAVIOM’s highly scalable and configurable framework supports complex multi-project and multi-location environments.
Validate Real-Time Visibility & Data Accuracy
Look for real-time views of resource availability, capacity, utilization, and demand across teams and locations. Data should be consistent, accurate, and up to date in real time. SAVIOM’s KPI forecaster and real-time BI dashboards provide a single source of truth for proactive decisions.
Review Integration & Ecosystem Fit
Check how well the tool integrates with HR, ERP, PPM, CRM, and financial systems. Seamless data flow prevents duplication, manual updates, and data inconsistencies. SAVIOM is designed to integrate seamlessly with existing workforce ecosystems, enabling a connected, end-to-end resource intelligence layer.
Assess Security & Compliance Readiness
Ensure the platform meets enterprise security standards, including data protection, role-based access, and audit trails. It should support regulatory and governance requirements across regions. SAVIOM supports enterprise-grade security and compliance with global deployments.
Analyze TCO, ROI & Vendor Fit
Evaluate the total cost of ownership against expected benefits such as utilization gains, cost savings, and delivery improvement. Assess vendor expertise, implementation approach, and long-term roadmap. SAVIOM is trusted by Fortune 500 firms across 50+ countries, reflecting strong domain credibility and long-term partnership value.
Discover the key factors to consider while selecting a resource management software for your firm.
Conclusion
Resource optimization is no longer a nice-to-have; it is a strategic imperative for enterprises facing complex portfolios, tight margins, and evolving skill demands. By aligning capacity, skills, and demand intelligently, organizations unlock higher productivity, stronger margins, and more predictable delivery.
Those who master optimization move faster, adapt quicker, and outperform competitors in both efficiency and resilience.
Resource Optimization FAQs: Answers to Common Questions
Resource optimization in project management is the strategic process of using an organization’s people, time, equipment, and budget most efficiently and effectively. It focuses on aligning resource capacity with demand, balancing workloads, and adjusting assignments to minimize waste, avoid over- or under-utilization, and ensure projects and business objectives are achieved smoothly and on time.
Resource optimization ensures organizations use their people, time, and budget in the most effective way to achieve business goals. It helps maximize productivity by aligning the right skills to the right work while minimizing idle time, overload, and waste. Ultimately, resource optimization enables organizations to ensure optimal usage, deliver projects faster, adapt to change, and sustain long-term operational efficiency and growth.
The key components of the resource optimization framework are:
1. Demand Forecasting
2. Resource Capacity Management
3. Resource Allocation and Scheduling
4. Resource Utilization Management
5. Prioritization and Governance
6. Performance Monitoring and Analytics
The most common resource optimization challenges are:
1. Scarcity of critical skills and capacity
2. Complex resource dependencies
3. Evolving project and resource requirements
4. Lack of real-time resource visibility
5. Market uncertainties and external risks
6. Difficulty in implementing and monitoring changes
The steps of effective resource optimization are:
1. Establish Resource Visibility
2. Forecast Resource Demand
3. Analyze Capacity vs. Demand
4. Prioritize Work and Initiatives
5. Optimize Resource Allocation
6. Refine Cost and Utilization
7. Analyze and Improve Resource Performance
To select the best resource optimization software, consider the following things:
1. Define Business Requirements
2. Evaluate Core Optimization Capabilities
3. Check Scalability & Configurability
4. Validate Real-Time Visibility & Data Accuracy
5. Review Integration & Ecosystem Fit
6. Assess Security & Compliance Readiness
7. Analyze TCO, ROI & Vendor Fit











