Resource planning is a critical business function that helps organizations ensure that all their resources, human and non-human, are optimally used across all operational areas.
Without implementing a proper resource planning process, making any decision is like throwing darts in the air. Thus, it is crucial for businesses to develop a well-defined resource plan to maximize the potential of their workforce, deliver project commitments, and boost profit margins.
It also helps key stakeholders answer questions such as:
“How many and what resources do I need for the coming weeks, months, quarters, or years”?
“Should I hire more people to meet future demands or leverage sales efforts to keep everyone occupied with work”?
“How can I avoid billing loss and control project costs before it’s too late?”
This guide will help you gain an in-depth understanding of resource planning in project management.
Let’s dive deep into it.

2. What is Resource Planning?
Resource planning is the process of forecasting, identifying, allocating, utilizing, and managing business resources, such as personnel, equipment, assets, finance, etc., to deliver projects and achieve organizational goals effectively. It involves estimating current and pipeline resource requirements and assigning best-fit personnel to appropriate project and non-project work based on critical parameters such as capacity, availability, skill sets, costs, etc.
2.1 A Resource Plan Example
Let’s understand this process through an example:
An IT company is managing a growing opportunity pipeline, with several software development projects progressing through various approval stages. Once a project reaches the final approval phase, the project manager begins by assessing the client’s requirements, evaluating the project scope, and determining the resource demand.
Based on this, they submit formal resource requests to the resource manager, detailing the necessary skills, types, and number of resources, along with the timelines for when each resource will be needed throughout the project’s lifecycle. The resource manager reviews these requests in the context of the broader organizational resource pool.
This involves assessing the gap between the projected demand and the available workforce across various departments. If gaps are identified, the resource manager explores options to address them, including reallocating staff from lower-priority projects, bringing in external contractors, or temporarily hiring additional talent.
Thus, the ability to develop a comprehensive strategy to allocate, schedule, and optimize resources across the organization is at the core of resource planning.
Now that we have explored the resource plan example, let’s dive into the various types of resource planning.
2.2 Types of Resource Planning
There are two types of resource planning in businesses. Let’s understand in detail:
2.2.1 Operational Resource Planning
Operational planning addresses the day-to-day activities of a business. It also supports strategic planning to accomplish the overall organizational goals. First, we decide on the short-term objectives and then determine how to achieve them.
Operational resource planning includes regular business activities and operations as per organizational guidelines. For example, it covers pipeline project management, management of FTE and contingency resources, forecasting billable and total utilization, and more.
Read More: What is Operational Workforce Planning and Its Importance?
2.2.2 Strategic Resource Planning
Strategic planning is usually undertaken by top-level management to decide the future direction. It is not limited to projects within a particular department or unit but covers the entire organization. Strategic resource planning looks into the overall long-term resourcing strategy.
It can change drastically based on individual priorities. For example, If an IT firm plans to outsource a temporary requirement, i.e., the resourcing strategy will shift from FTE to contingent staff for IT infrastructure improvements. Similarly, a niche skilled resource’s out-rotation from an existing project to start a new initiative will come under strategic resource planning.
3. Essential Components of Resource Planning Template
A robust resource planning software will enable managers to effectively manage resources, mitigate risks, and drive projects to success.
Here are some salient features that are foundational to an efficient resource planner.
3.1. Multi-dimensional Resource Planner
With a multidimensional resource planner, managers have visibility into resource profiles across multiple dimensions such as seams, departments, locations, etc. It empowers them to allocate appropriate resources in real time to the projects. In other words, it allows managers to assign the best-available-best-fit instead of the first-visible-first-fit resource, enabling competent allocation for all projects.
3.2. Project Pipeline Planning
Project pipeline planning functionality helps firms analyze future projects and estimate the resource requirements ahead of the curve. It allows the resource manager to compare the existing resource capacity against the project demand from multiple perspectives such as role, department, team, skills, etc. This approach minimizes wasteful hiring/firing cycles to ensure that the skilled resources are available for timely project commencement.
3.3. Resource Capacity Planning
With robust resource capacity planning, organizations can analyze the resource capacity vs. project demand gap. This foresight helps identify resource excess or shortage and implement corrective steps to bridge the gap with corrective treatments. In the case of a resource shortage, managers can facilitate proactive strategies such as re-training employees or hiring a contingent workforce. Conversely, when there is a resource excess, they can bring forward the project dates or sell excess capacity at discounted rates.
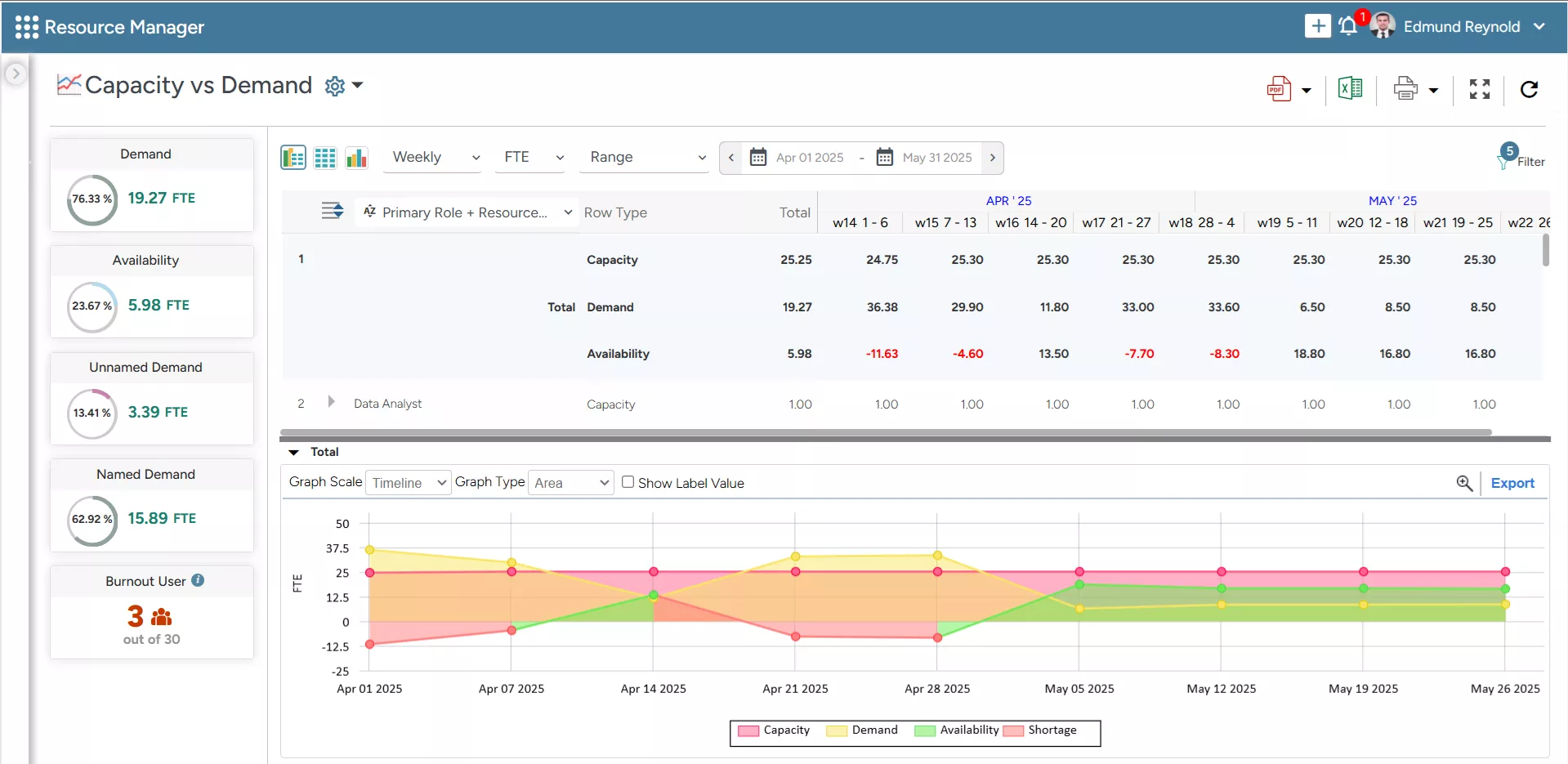
SAVIOM’s Capacity vs. Demand Report helps managers quickly identify resource excesses/shortages and take proactive measures to bridge the demand gaps.
3.4. Resource Utilization Forecasting
The resource forecasting feature in the planner enables firms to optimize billable and strategic utilization. Managers can refer to comprehensive color-coded heatmaps, forecast vs. actual, and utilization reports to identify and address under/overloading. Moreover, they can forecast future utilization of resources and mobilize them from non-billable to billable work to optimize profitable utilization.
3.5. Bench Management
With a resource planner, managers can gain early foresight into the workforce that will land on the bench due to sudden ramp-down activities. They can look into project vacancy reports and plan work for resources before they hit the bench. This will reduce bench time between projects for most resources and improve the organization’s bottom line. Additionally, with efficient bench management, managers can provide training or shadowing opportunities to selected employees to enhance their billability.
3.6. Using Real-time Business Intelligence Reports
Modern resource planners provide real-time business intelligence reporting and analytics to fast-track decision-making. These configurable dashboards and custom reports empower end-users to slice and dice relevant information effortlessly and present insights through visually intuitive graphs and reports. Moreover, intelligent BI uses a combination of security rights, portal designs, and filters, allowing the end-user to view relevant data and prevent information overload.
Leverage SAVIOM’s Real-time BI Reports and Analytics to make fast resourcing decisions
3.7. What-if Analysis for Resource Simulation
The what-if analysis function within a resource planner allows firms to build and simulate different resource scenarios in a multi-project environment. This helps managers to compare different scenarios and their potential outcomes. Moreover, what-if analysis also helps prioritize profitable projects based on criteria like budget and timeline. As a result, it enables organizations to manage multiple projects’ demands with limited resources.
As we now understand the various components of the resource planning template, let’s go through the various benefits of creating an effective resource plan.
4. Benefits of Resource Planning in Project Management
According to a PMI survey, “26% of companies with a dedicated resource planning solution can estimate and allocate resources to deliver projects on time.”
Thus, resource planning is a crucial part of the project management process as it plays a key role in a project’s success.
Here is a list of the benefits and how planning resources makes a difference in the project management landscape:
4.1 Bridges the Capacity Gap Proactively
An intelligent resource plan helps managers perform a demand vs. supply gap analysis to identify the excess or shortage of resources. If there is an excess of resources, they can bring forward project timelines or sell the additional capacity. Conversely, a shortfall of resources can be mitigated by providing training/upskilling programs or hiring a permanent or contingent workforce based on project duration. This eliminates the chances of last-minute hiring and helps in the timely fulfillment of the project.
4.2. Minimize Project Resource Costs Significantly
An effective resource plan enables managers to make data-driven decisions to eliminate the deployment of over/under-skilled resources on project tasks. This allows managers to implement suitable resourcing measures at the right time. For instance, they can allocate a cost-effective global/local resource or a benched resource to a task. Moreover, they can conduct planned hiring to address any shortages and create the right resource mix to control the project budget.
4.3. Maximize Profitable Resource Utilization
A structured resource plan establishes clear utilization targets for each resource category—permanent, contingent, full-time, and part-time. This clarity allows managers to compare the actual time spent by team members against initial estimates and take corrective actions as needed. For example, if resources are spending excessive time on non-billable tasks, managers can quickly reallocate them to revenue-generating activities, enhancing billable resource utilization.
Read More: What is Resource Utilization and its Significance?
4.4. Ensures Competent Resource Allocation
Resource planning in project management helps managers gain a centralized view of all resource-related information, such as skill sets, cost rate, location, and resource capacity. This visibility helps them in assigning the right resources to the right project at the right time and cost, ensuring competent resource allocation. It reduces the chances of rework, errors, and delays, thereby enhancing project execution and performance.
4.5. Mitigates Resource-Related Risks in Advance
A robust resource plan enables managers to assess resource needs across project phases and identify potential resource risks such as resource shortages, skill obsolescence, employee burnout, etc. By detecting these issues early, managers can take preemptive action to mitigate them, ensuring that the right resources are available at the right time. This proactive approach helps maintain project timelines and ensures the delivery of high-quality outcomes.
4.6. Delivers Project on Time and Within Budget
PwC Project Management Insights states that “60% of project failures are linked to internal project issues (e.g., missed deadlines, insufficient resources).”
Efficient resource planning ensures that all project resourcing requirements are identified and fulfilled. It eliminates last-minute firefighting by guaranteeing that the necessary skill sets are available when needed. Additionally, it ensures competent allocation by matching resource competencies with appropriate project tasks. This helps improve resource productivity and deliverable quality. These factors collectively contribute to the timely completion of the project within budget.
Now, let’s go through the roles of project and resource managers.
5. The Role of Project Managers and Resource Managers in Resource Planning Process
Project managers operate on a project level with projects of different sizes and complexities. A project manager can manage single or multiple projects and ensure they are completed within a stipulated time and budget. However, resource managers operate at the organizational level and oversee allocating resources to several projects.
The project manager initiates the resource request for an open position within his project, and the resource manager’s job is to fulfill the same. Once a resource is allocated to a project for a particular period, the resource manager’s responsibility ends. After that, the project manager’s job begins to ensure that the resource carries out the delivery responsibilities properly.
5.1. Role of Resource Manager
In summary, a resource manager is responsible for the following:
- Planning and allocation based on resource skills, previous experience, and availability.
- Conducts capacity planning to address issues of shortfall and excesses of resources.
- Support project managers with the project resource management plan and related activities.
- Address resource concerns by reallocating resources, negotiating, or assigning additional staff.
- Collate new project requirements from the business and provide them to the hiring team.
- Certain limited HR-related functions.
- Collaboration with other departments, e.g., HR, PMO, Sales, Learning & Development.
- Generating reports and analytics for senior management.
5.2. Role of a Project Manager
The corresponding roles of a project manager are:
- Create a project management plan and define the scope and delivery objectives of the project.
- Capture resource requirements and request for fulfillment.
- Streamline communications with stakeholders/ team members and customers.
- Carry out operational reviews as per project KPIs.
- Estimate time and cost and monitor the budget.
- Report the project’s progress, analyze potential risks, and provide a mitigation strategy.
- Document the project and set the expectations for various team members.
- Work with the empaneled vendors for contingent resources.
Read More: Project Management vs. Resource Management
These are some of the significant responsibilities of resource and project managers. Now, let’s learn about some benefits of resource planning across industries.
6. How Does a Resource Plan Benefit Different Industries?
Let us discuss some of the specific industries where efficient resource planning could benefit significantly:
6.1. IT industry
Due to the rapid advancement in technology, computing, and automation, IT companies face widened tech skills gaps within their workforce. As a result, IT professionals are under constant pressure to acquire new skills throughout their professional careers. Timely forecasting and efficient resource planning will help managers predict the demand for niche skill sets well in advance. Then, managers can develop appropriate training programs to gauge these gaps and create an augmented workforce.
6.2. Audit and Accounting Firm
Most audit and accounting firms consider billable utilization a critical KPI to ensure profitability and sustainability. So, depending on the accounting project’s needs, an effective resource planning solution helps to forecast resource requirements (Accountants, auditors, financial analysts, tax consultants, audit interns, etc.) and create an optimized talent pool and utilize them for productive activities. It also enables firms to hire interns regularly, give them on-the-job training, and make them billable.
6.3. Law Firms
Similar to audit and accounting firms, law firms are also run by their partners. Bringing in a client when the firm has inadequate staffing can be detrimental to its reputation and profitability. An effective forecasting and resource planning strategy helps assess future demands and find the right resource (lawyers, legal secretaries, etc.) at the right cost, age demographics, etc. It also enables partners to build an on-demand workforce, create a skill database, and define the total billable hours.
6.4. Engineering Industry
The increased demand in manufacturing has caused skill shortages in the core engineering industry, where competition is fierce for experienced workers (automobile engineers, machinists, designers, etc.). An engineering resource planning solution helps managers provide reskilling and on-the-job learning opportunities for the employees. Thus, it helps to replenish an aging workforce, fill critical positions, and match them to the best potential projects based on talents and interests.
Read More: What is Engineering Resource Planning?
6.5. Construction Industry
Construction and infrastructure projects possess highly volatile resource demands due to changing climatic conditions and sudden increases in maintenance activities. With resource planning solutions, managers gain visibility of all construction resources and recruit skilled labor, architects, civil engineers, etc., throughout the projects. Thus, it maximizes the workforce’s productive utilization and ensures minimal resource conflicts. Therefore, efficient resource planning is key to managing construction resources effectively and preventing hiring/firing costs.
6.6. Consulting & Professional Service Industry
The professional service industry has a unique challenge to balance resource demands across various clients. With efficient resource planning, managers can keep track of resources and their specialized skills. Since the consultants are deployed at a premium rate, keeping them engaged in client billable activities and reducing idle time for maximum profitability is crucial. At the same time, they need to be provided enough opportunities to acquire new skills and ensure no employee burnout.
6.7. Video Game Industry
The game development industry requires a highly competent team of niche-skilled resources. Efficient resource planning enables managers to diversify their expertise to the maximum potential and fulfill the gaming project resource demand. It also helps to identify in-demand skills and cross-train them to build an optimized workforce of game designers, level artists, programmers, QA teams, etc. Thus, effective resource planning can become a game-changer in fast-tracking the development cycle.
Read More: How can Robust Resource Management Future-proof the Gaming Industry?
Now that we’ve explored the benefits of resource planning across different industries, let’s take a look at the common mistakes associated with it in project management.
7. Common Mistakes of Resource Planning in Project Management
Without effective resource planning, a project can suffer significant setbacks, leading to compromised quality and a reduced return on investment (ROI).
This section describes some of the common mistakes made in this area.
7.1. Usage of Spreadsheets/Legacy tools for Resource Planning
Marketwatch states that “88% of spreadsheets are prone to errors.”
Despite its limitations, many organizations still use spreadsheets to plan their resources because they are easily accessible. Excel resource planner causes improper allocation, double booking, and creates additional work. This system is very limiting and a nightmare to maintain. Additionally, the lack of forecasting capabilities prevents managers from forward planning resource demand, leading to costly last-minute hiring and project delays.
Read More: 7 Reasons Why You Shouldn’t Use Excel for Resource Planning
7.2. Planning Resources Without Overall Visibility
When managers allocate resources without full visibility into various attributes—like skills, competencies, availability, etc. —it becomes challenging to assign the right resources to suitable projects at the right time. This restricted visibility also hampers the identification and leveraging of quality resources from low-cost locations.
7.3. Lack of Resource Forecasting for Pipeline Projects
Resource planning for future projects is often taken up at the eleventh hour. The resource managers make the mistake of only taking up the planning activities when the deal is signed. Ideally, it should start after the opportunity reaches a certain probability of closure so there is sufficient lead time to address resource requirements. This results in last-minute activities that create an unbalanced pool as the quality of the resources is compromised.
7.4. Not Maintaining the Right Mix of Permanent and Contingent Workforce
Businesses try to fulfill project requirements using full-time employees as it is perceived to be a more cost-effective solution. However, if a niche resource is hired for a shorter duration, it becomes challenging to redeploy him after the assignment is complete. Therefore, a resource plan should maintain a judicious blend of permanent and contingent resources. For short-term assignments, a contingent workforce will be less expensive than hiring full-time resources.
7.5. Allocating Under or Over-skilled Resources to the Projects
One of the common mistakes of resource planning in project management is assigning under or overqualified resources to tasks. When resources are under-skilled for the job, it causes project delays. On the other hand, over-skilled resources spike project costs. Not assigning tasks based on skills and interests leads to decreased employee engagement and loss of productivity.
Read More: Resource Allocation: A Guide on How to Apply it to Project Management
7.6. Unplanned Hiring Without Analyzing Project Demands
Resource managers often resort to last-minute hiring activities to fulfill project resource requirements. This unplanned hiring compromises quality and leads to a large bench of mismatched skill sets. So, analyzing project demands with matching skill sets is a prerequisite for informed hiring decisions.
Knowing the common mistakes of project resource planning, let’s understand the effective strategies to mitigate them.
8. How to Create a Resource Plan?
Here are seven effective strategies by which managers can create an efficient project resource plan:
8.1 Understand Project Resource Requirements
At the outset, managers should start the resource planning process by fully understanding the project requirements. This includes assessing the project scope, objectives, timelines, and budget. Based on that, project managers can gauge the resource requirements in terms of skills, types, and numbers.
This initial evaluation helps managers determine whether the existing skills and competency of the workforce align with the overall project goals and take appropriate corrective measures. Therefore, it helps avoid any last-minute firefighting, ensuring successful project delivery.
8.2. Identify Gaps & Implement Measures to Bridge it
The next step involves requesting the necessary resources from resource managers to fulfill the project demand. Resource managers then conduct a capacity vs. demand gap analysis and meticulously analyze shortages or excesses of resources from multiple perspectives, i.e., role, skills, competency, etc.
For instance, in case of shortages, organizations may facilitate retraining/upskilling resources, juggling project priorities, or hiring a permanent/contingent workforce. Conversely, when the resources are in excess, managers can either bring forward project dates or sell excess capacity to optimize the utilization of every resource.
Read More: How to Measure Resource Capacity and Demand?
8.3. Allocate the Right Resources to the Right Project
Effective resource allocation is a critical step in the planning process. Managers can strategically allocate resources based on availability, skills, competencies, location, costs, and interests. This ensures that managers align the right skilled workforce with appropriate expertise at the right time for suitable projects.
Managers can also create the right resource mix of senior/junior employees or contingent/permanent workforce, depending on the project requirements, and allocate them to projects. Further, they can also assign competent, cost-effective global resources to the project. It will help them control the project budget without compromising the quality of deliverables.
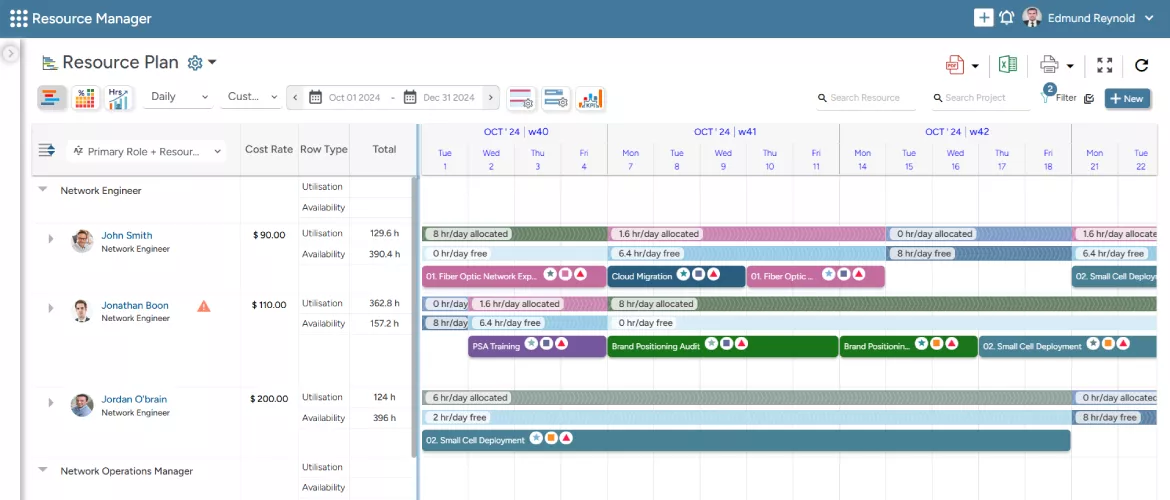
SAVIOM’s All-in-One Resource Planner assists managers to identify and allocate the best-fit resources to projects.
8.4. Consider Factors that Affect Resourcing Strategies
To effectively allocate skilled resources to projects, managers must consider the following factors:
- Long-term/short-term assignment
The foremost step to consider while recruiting resources is the project length. That means whether the role is for a short-term or long-term assignment. For short-term needs, contingent workers or freelancers are ideal, while long-term roles should focus on permanent hires to avoid wasteful hiring and firing cycles.
- Generic vs. niche skill
Then, managers should balance generic vs. Niche skill requirements. Generic skilled resources are relatively easy to plan for, as they are readily available within the organization. On the other hand, hiring resources with niche skills may require additional lead time due to their scarcity, which often results in higher costs.
- Cost of the resource
Resource managers must look into the cost rate of the resource that fits the project budget. They should also factor onsite, offshore, and near-shore options in the recruitment strategy to minimize the overall project resource costs.
- Attrition & succession planning
Managers must implement robust succession plans to identify and train replacements for key positions within the organization. Utilizing an intelligent resource planner can provide a real-time competency matrix, enabling managers to select suitable candidates for leadership positions.
Read More: Ten Effective Strategies to Reduce Employee Turnover
8.5. Monitor and Optimize Project Resources
Continuous monitoring and tracking of resource utilization throughout the project lifecycle are essential to update resource planning. Hence, once resources have been allocated to project tasks, it’s important to regularly track and monitor their utilization levels. This provides valuable insights into resource efficiency and enables timely adjustments to prevent instances of under/over-utilization.
In case of underutilization, managers can bring forth project timelines. On the other hand, managers can implement optimization techniques like resource leveling and smoothing to mitigate overloading. This will ensure timely project delivery within the pre-defined budget and quality standards.
8.6. Conduct a Post-Project Analysis
Upon project completion, it is crucial for managers to conduct a thorough post-project analysis to evaluate the effectiveness of the resource plans and identify areas of achievement and improvement. This will help scrutinize whether resources were allocated efficiently, if project deadlines were met as planned, and if any unexpected circumstances arose.
With these insights, firms can refine and enhance future resource planning efforts by identifying areas of success and potential improvement. They can develop robust and efficient resource plans that align resources with project needs, minimize discrepancies, and ultimately bolster project success rates.
8.7 Use an Advanced Resource Planning Software
Modern resource planning software provides 360-degree visibility into all resources, including their skills, experience, capacity, and availability. This comprehensive view enables managers to identify and assign the most suitable resources with the right skills to projects, ensuring optimal resource utilization. Additionally, the software’s forecasting capabilities and capacity-vs-demand reports allow managers to anticipate skill gaps ahead of time.
Furthermore, the software’s modeling and simulation features enable managers to analyze various scenarios by adjusting key metrics like availability and cost rates. This functionality helps compare different outcomes, allowing managers to determine the most viable strategy before applying it to the actual resource plan.
Now that we have covered the strategies, let’s explore the emerging trends in resource planning.
9. Emerging Trends of Resource Planning in Project Management
Listed below are some of the emerging trends of resource planning in project management:
- AI and automation are revolutionizing resource planning by streamlining tasks like scheduling, allocation, and reporting. These technologies enable project managers to make data-driven decisions, optimize resource utilization, and predict project outcomes more accurately.
- An automated resource requisition process is becoming a must-have trend in project management, ensuring a transparent and efficient workflow. By maintaining a clear audit trail of requests, this feature simplifies the requisition process, reduces manual errors, and eliminates chances of scheduling conflicts.
- Advanced forecasting techniques are revolutionizing resource planning by providing accurate predictions of future resource needs. This trend is gaining traction as it enables organizations to conduct capacity vs. demand gap analyses for upcoming projects. By identifying gaps early and taking proactive measures, companies can ensure that the right resources are available before a project begins.
- Agile resource planning is increasingly popular due to its flexibility and responsiveness in dynamic project environments. This approach allows for real-time adjustments to resource allocation, ensuring that teams can quickly adapt to changes, meet evolving project requirements, and maintain productivity in fast-paced settings.
Let us now understand how a modern resource management solution helps managers in resource planning.
10. How Does a 5th Gen Resource Management Software Help?
Organizations must forecast, allocate, and utilize the workforce effectively and efficiently throughout the project lifecycle to achieve successful outcomes. This is where a 5th gen resource management software can make a difference. Let’s understand:
1. All-in-One Resource Planner: The tool’s all-in-one resource planner offers 360-degree visibility into critical information and enables managers to make intelligent resourcing decisions. It includes numerous key functionalities like:
- Multi-dimensional Analysis: This helps managers slice and dice resource data by role, location, skill, cost, and more, helping align the right talent to the right task.
- Embedded Capacity Planning: Helps assess resource shortages or excesses and take corrective actions to ensure timely project initiation.
- Embedded Heat Map: Provides real-time insights into workload distribution and helps identify & eliminate over/under utilization to maintain a healthy resource index.
- Intelligent Matchmaking: Assesses multiple parameters (skill, availability, competencies, cost) to assign the best-fit resources to tasks, ensuring competent allocation.
- Early Warning System: Automatically flags overloading, scheduling conflicts, and double-bookings, allowing managers to take corrective measures proactively.
- KPI Forecaster: Offers foresight into key resource KPIs like availability, capacity, utilization, and skill gaps for proactive decision-making in real-time and helps keep projects on track.
2. Resource Forecasting: The resource forecasting feature gives managers full visibility into upcoming resource needs for pipeline projects. It also provides forecast vs. actual cost analysis, helping control project budgets and improve financial planning for upcoming projects.
3. Resource Optimization: This feature enables managers to conduct what-if analysis that helps simulate and compare various scenarios, helping firms arrive at the most profitable resource plan. This helps prevent resource-centric bottlenecks, ensuring timely project initiation and delivery.
4. Task and Time Management: The tool’s task management feature helps assign qualified, cost-effective resources to tasks and projects. It includes timesheet tracking and automated approval workflows, enabling managers to track billable and non-billable hours effectively.
5. Workflow & Integration: The feature allows managers to automate workflows like resource requisition, skill management, etc. It also allows firms to export and import resource data easily in formats like Excel and graphs, saving time. Plus, the platform integrates smoothly with your systems, creating a single source of truth for accurate resource planning.
11. Conclusion
An efficient resource plan fosters you to accomplish more in the same amount of time from the most valuable resources- the people.
Therefore, it is imperative to implement effective resource planning to utilize the workforce to its maximum potential. When resources are planned efficiently, it helps a business to manage risks, reduce delays, optimize resource utilization, etc.
By implementing the above-mentioned processes, businesses can manage their resources intelligently and enhance project outcomes, improving profitability and ROI, thereby increasing client satisfaction.
After all, successful projects depend substantially on strong planning and resources.
Glossary
Read More: Glossary of Resource Workforce Planning, Scheduling and Management













